
Cranberries vs. Cancer
Drug companies and supplement manufacturers have yet to isolate the components of cranberries that suppress cancer cell growth.

Drug companies and supplement manufacturers have yet to isolate the components of cranberries that suppress cancer cell growth.

Se comparó la capacidad de once frutas comunes para suprimir el crecimiento de células de cáncer in vitro. ¿Cuál es la más eficaz– manzanas, plátanos, arándanos, toronjas, uvas, limas, naranjas, duraznos, peras, piñas o fresas?

About half of doctors admit to intentionally deceiving patients by prescribing placebos, but might the ends justify the means?

Casi 5000 muertes por cáncer de mama al año pueden ser atribuidas al consumo leve de alcohol (hasta una sola bebida al día).
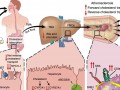
Ampliando la temática de mi próxima participación en “El Show del Dr. Oz”, un nuevo artículo hito en el New England Journal of Medicine muestra que la colina en huevos, carne de ave, lácteos, y carne de pez produce el mismo OTMA tóxico que la carnitina en la carne roja, lo que puede ayudar a explicar la protección que proporciona una dieta basada en plantas ante enfermedades cardíacas y cáncer de próstata.
Plant-based diets appear to offer relief from a variety of menstrual symptoms, including cramping, bloating, and breast pain (cyclical mastalgia).

Longstanding concerns about certain isolated components of the spice tarragon have broadened into questions about the safety of even the leaves themselves.
Two theories about the buildup of subcutaneous fat, involving the chemical spermine and the hormone adiponectin, suggest a plant-based diet may help with cellulite.

The story behind the first U.S. dietary recommendations report explains why, to this day, the decades of science supporting a more plant-based diet have yet to fully translate into public policy.

Un ensayo clínico aleatorizado, doble ciego y controlado con placebo sobre la linaza en pacientes con cáncer de mama descubrió que la linaza parece tener el potencial de reducir el crecimiento del tumor en tan solo cuestión de semanas.

Lignan intake is associated with improved breast cancer survival in three recent population studies following a total of thousands of women after diagnosis.

Las mujeres jóvenes con alto riesgo de cáncer de mama que recibieron sólo una cucharadita de linaza molida al día mostraron un menor número de cambios precancerosos.
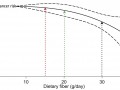
La ingesta inadecuada de fibra parece ser un factor de riesgo para el cáncer de mama, lo cual explica por qué las mujeres con dietas a base de vegetales pueden tener un riesgo menor.

An independent review of the effects of açaí berries was recently published, including studies on immune function, arthritis, and metabolic parameters.

El inicio temprano de la pubertad en las niñas asociado con el consumo de proteína animal podría deberse a un químico contaminante que perturba el sistema endocrino que se encuentra en el suministro de carne.

Those eating more sour fruit may risk greater erosion of their tooth enamel (especially if teeth are brushed in a softened state), but there’s a simple solution.

Plant-based diets may help protect against oral cancer and periodontal (gum) disease, a leading cause of tooth loss.

Los hidrocarburos aromáticos policíclicos en los vapores que se liberan durante la cocción de la carne podrían ser nocivos para el desarrollo del feto y aumentar el riesgo de cáncer.

The boost in detoxifying enzymes triggered by cruciferous vegetable consumption may last for weeks!
Garlic and flavonoid phytonutrients found in fruits, vegetables, nuts, and grains appear to protect against DNA damage induced by mutagenic chemicals found in cooked meat.
Using the cooked meat carcinogen PhIP to turn normal breast cells cancerous, researchers explore the use of green tea to interrupt this malignant transformation.

Even vegetarians could potentially be exposed to the carcinogens typically formed by cooking meat through eggs, cheese, creatine sports supplements, and cigarette smoke.

Those who eat meat risk food poisoning from undercooked meat, but also exposure to cooked meat carcinogens in well-cooked meat. By boiling meat, non-vegetarians can mediate their risk of both.

The cooked meat carcinogen PhIP—found in fried bacon, fish, and chicken—may not only trigger cancer and promote tumor growth, but also increase its metastatic potential, by increasing its invasiveness.

DNA-damaging chemicals, formed when meat is cooked, stimulate breast cancer cells almost as much as pure estrogen, and can infiltrate the ducts where most breast cancers arise.

Apple peels appear to upregulate the tumor suppressor gene maspin, and have strong antiproliferative effects on breast and prostate cancer cell growth in vitro.

Why the spike in antioxidant levels in our bloodstream after drinking apple juice might not be a good thing.

Eating fiber-containing foods—especially nuts—during adolescence may significantly lower the risk of developing potentially precancerous fibrocystic breast disease (fibroadenomas).

Mushrooms, green tea, and soy consumption may decrease breast cancer risk, but how many mushrooms, how much green tea, and what’s the best soy strategy?

Researchers pit plain white mushrooms against breast cancer cells in vitro to measure aromatase activity, and estimate how many mushrooms women may want to strive to include in their daily diet.

The consumption of three portions of whole grains a day appears as powerful as high blood pressure medications in alleviating hypertension.
Plant-based diets appear to protect against metabolic syndrome, also known as syndrome X, which is characterized by the so-called “deadly quartet”—abdominal obesity, high fasting sugars, high triglycerides, and high blood pressure.
The foreign meat molecule Neu5Gc may not only contribute to the progression of cancer and heart disease by supplying inflammation, but may also set children up for life-threatening reactions to E. coli toxins originating in the same animal products.
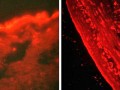
The foreign meat molecule Neu5Gc builds up in human tumors and atherosclerotic plaques, and may play an inflammatory role in the progression of both diseases.
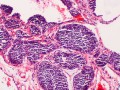
Cancer may use a molecule found in animal products to trick our immune system into feeding it with inflammation.
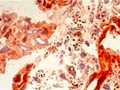
Las dietas basadas en plantas pueden ayudar con la artritis reumatoide al disminuir la exposición a un compuesto inflamatorio que se encuentra en los productos de origen animal.

We may have a billion different types of antibody-releasing cells in our immune system, such that each recognizes a different molecular signature.
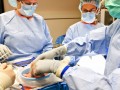
Because certain tumors such as breast cancers thrive in settings of low-grade inflammation, our immune response can sometimes facilitate tumor growth.

La especia fenogreco parece mejorar significativamente la fuerza muscular y la capacidad para el levantamiento de pesas, y ha mostrado propiedades anticancerígenas in vitro.
For decades, studies on Gerson therapy for cancer have questioned its safety and efficacy. But, what does the latest head-to-head trial of a Gerson-style regime, versus chemotherapy, show in terms of survival and quality of life for pancreatic cancer ?