
Turmeric Curcumin & Pancreatic Cancer
Carcinogens in grilled and baked chicken may increase the risk of pancreatic cancer, while curcumin, the yellow pigment in the spice turmeric, may sometimes help even in advanced stages of the disease.

Carcinogens in grilled and baked chicken may increase the risk of pancreatic cancer, while curcumin, the yellow pigment in the spice turmeric, may sometimes help even in advanced stages of the disease.

Feed contaminated with toxic pollutants thought to originate from sewer sludge fed to chickens and fish results in human dioxin exposure through poultry, eggs, and catfish.
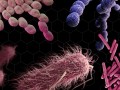
The emergence of pathogens resistant to even our antibiotics of last resort has raised the specter of a “post-antibiotic age” in which drugs to fight infections may be useless. This has focused attention on the mass use of antibiotics in farm animal feed to promote growth and prevent infection in high density production.

The pharmaceutical industry is starting to shift away from designing single target drugs to trying to affect multiple pathways simultaneously, much like compounds made by plants, such as aspirin and curcumin—the pigment in the spice turmeric.
Arsenic-containing drugs intentionally added to poultry feed to reduce the parasite burden and pinken the meat are apparently converted by cooking into carcinogenic inorganic arsenic compounds.

The artificial food coloring Red No. 3 has yet to be banned—despite its purported role in causing thousands of cases of thyroid cancer.

The safety of food additives is determined not by the FDA, but by the manufacturers of the chemicals themselves.
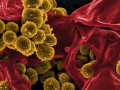
The level of multidrug antibiotic-resistant bacteria contamination is compared between meat from animals raised conventionally, and certified organic meat from animals raised without being fed antibiotics.

How many months does it take to clear 99% of the mercury and other industrial toxins from one’s body, and what role might our fat stores play in holding on to fat-soluble pollutants?

Risk/benefit analysis of 33 fish species contrasts the brain-boosting effects of DHA with the brain-damaging effects of mercury, to determine the net effect on intelligence (IQ).

In response to definitive evidence showing artificial colors may increase inattentiveness, impulsivity, and hyperactivity among young children, a call has been made by consumer groups to ban food dyes.

The artificial butter flavoring diacetyl has been linked not only to deaths of workers handling the chemical, but also to serious lung disease in consumers of microwave popcorn.

Men eating pistachio nuts experienced a significant improvement in blood flow through the penis accompanied by significantly firmer erections in just three weeks—perhaps due to pistachios’ antioxidant, arginine, and phytosterol content.

Carrageenan is a food additive used as a thickener and fat substitute in a variety of dairy and nondairy products. Concerns about potential intestinal tract damage are placed in the context of dietary consequences.

The Director-General of the World Health Organization warns that we may be facing an end to modern medicine as we know it—thanks, in part, to the mass feeding of antibiotics to farm animals to accelerate growth.
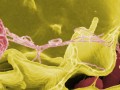
Hundreds of thousands of Americans are Salmonella-poisoned by poultry every year—yet it remains legal to sell meat proven to be contaminated.

The average number of bowel movements a week is compared between those eating prunes, those taking a fiber supplement, and those eating a strictly plant-based diet.

Meat industry public relations campaign to “crush” myths makes false claim about the millions of pounds of antibiotics fed to farm animals.

Do compounded bioidentical hormones for menopause carry the same risks as conventional hormone replacement drugs, such as Premarin?

Death in America is largely a foodborne illness. Focusing on studies published just over the last year in peer-reviewed scientific medical journals, Dr. Greger offers practical advice on how best to feed ourselves and our families to prevent, treat, and even reverse many of the top 15 killers in the United States.
Bacteria-eating viruses (bacteriophages) have been approved as meat additives to reduce the risk of Listeria and Campylobacter found in processed meat and poultry products, but there’s a concern they could spread toxin genes between bacteria.

Employees in natural food stores have been caught giving advice that is not only scientifically baseless, but also risky and downright dangerous.

Are soybeans better than other types of beans for heart disease prevention—or does the soy industry just have more money and clout to tout?

Persin, a natural toxin found in avocados, appears so effective at killing breast cancer cells that it is being considered as a chemotherapy agent.