Reducing Muscle Soreness with Berries
Anti-inflammatory phytonutrients in berries may explain why cherries can speed recovery after a marathon—by reducing muscle pain in long-distance runners.

Anti-inflammatory phytonutrients in berries may explain why cherries can speed recovery after a marathon—by reducing muscle pain in long-distance runners.

Daily citrus fruit consumption during athletic training may reduce muscle fatigue, as evidenced by lower blood lactate concentrations.

Lower levels of the cancer-promoting growth hormone IGF-1 in those eating vegan is not expected to affect their accumulation of muscle mass.

A Consumer Reports investigation into the safety of protein supplements found that more than half exceed the California Prop 65 Safe Drinking Water and Toxic Enforcement Act action levels.

In the context of a healthy, plant-based diet, the nitrates in vegetables can safely be converted into nitric oxide, which can boost athletic performance, and may help prevent heart disease.

If nitrates can boost athletic performance and protect against heart disease, which vegetables have the most—beans, bulb vegetables (like garlic and onions), fruiting vegetables (like eggplant and squash), greens (such as arugula), mushrooms, root vegetables (such as carrots and beets), or stem vegetables (such as celery and rhubarb)?

The nitrate in vegetables, which the body can turn into the vasodilator nitric oxide, may help explain the role dark green leafy vegetables play in the prevention and treatment of hypertension (high blood pressure) and heart disease.

Young infants, and perhaps those with recurrent oxalate kidney stones, should avoid beets. But most commonly, the chief side effect is beeturia, the harmless passage of pink urine, though not all are affected—akin to the malodorous urine (“stinky pee”) that sometimes results from asparagus consumption.

Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, crossover studies convinced the scientific establishment that nitrate-rich vegetables (such as beets) could noticeably improve athletic performance.
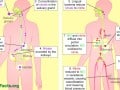
The natural flora on our tongue (lingual bacteria) are essential for the athletic performance-enhancing effect of the nitrates in vegetables such as beetroot.
To understand how beets could reduce the oxygen cost of exercise while improving athletic performance, one must review the biochemistry of energy production (ATP synthase), and the body’s conversion of nitrates to nitrites into nitric oxide.

Beets found to significantly improve athletic performance while reducing oxygen needs—upsetting a fundamental tenet of sports physiology.