
How Bad Are Ultra-Processed Foods?
Are there aspects of ultra-processed foods beyond their nutrient profile that contribute to their deleterious effects?

Are there aspects of ultra-processed foods beyond their nutrient profile that contribute to their deleterious effects?

The metabolism of NAM may deplete our methylation capacity, interfering with the normal metabolism of hormones and neurotransmitters, and produce a neurotoxic compound in the process.

Boost our natural satiety hormone GLP-1 through out diet.

The pros and cons of all the NAD+ supplements and what are the ways to boost NAD+ naturally with diet and lifestyle?

Losing weight without rearranging your gastrointestinal anatomy carries advantages beyond just the lack of surgical risk.

What are the three sources of the liver fat in fatty liver disease and how do you get rid of it?

Were the flax seed studies showing 20 pounds of weight loss just flukes?

Ground ginger powder is put to the test for weight loss and NAFLD, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease.
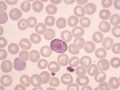
Since white blood cell count is a sign of systemic inflammation, it’s no surprise that those with lower white blood cell counts live longer.

How many cola cancer cases are estimated to be caused by Coke and Pepsi in New York versus California, where a carcinogen labeling law (Prop 65) exists?
The microbiome revolution in medicine is beginning to uncover the underappreciated role our healthy gut bacteria play in nutrition and health.

Protective properties of whole plant foods against diabetes include antioxidants, lipotropes, fiber, and the ability to suppress the estrogen-producing bacteria in our gut.

Saturated fat can be toxic to the insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas, explaining why animal fat consumption can impair insulin secretion, not just insulin sensitivity.

The “twin vicious cycles” explain how the buildup of fat in the cells of our muscles, liver, and pancreas causes type 2 diabetes, which explains why dietary recommendations for diabetics encourage a reduction in fat intake.
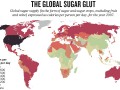
Are table sugar and high fructose corn syrup just empty calories or can they be actively harmful?

Based on studies linking coffee consumption with lower liver cancer risk, coffee is put to the test to see if it can help reduce liver damage in those with hepatitis C.
Plant-based diets appear to protect against metabolic syndrome, also known as syndrome X, which is characterized by the so-called “deadly quartet”—abdominal obesity, high fasting sugars, high triglycerides, and high blood pressure.