Arterial Acne
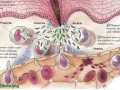
Atherosclerotic plaques in coronary arteries may be more aptly described as pimples, initiated by the infiltration of cholesterol into the lining of our arteries. The ending—should blood flow to our heart muscle be cut off by a clot formed by the rupture of one of these inflamed pockets of pus in our arterial lining—is a heart attack.