
The Effects of Processed Meat on Lung Function
If the nitrites in foods like ham and bacon cause lung damage, what about “uncured” meat with “no nitrites added”?
Topic summary contributed by volunteer(s): Randy
Preservatives can differ in their potential health impact. Citric acid is an example of a preservative that is not considered harmful. However, with many preservatives, we must weigh potential benefits and risks. For example, potassium sorbate, a preservative used to prevent mold growth in certain foods and supplements, may be harmful. Nitrites as a preservative in processed meats help reduce botulism risk but also raise cancer risk (see also here) and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease risk. The preservative BHA may be a carcinogen. Sodium benzoate, a preservative often found in soft drinks, can combine with ascorbic acid in the drink to form the carcinogen, benzene. Sodium benzoate has also been linked with hyperactivity.
Phosphate additives in chicken can both stiffen arteries and appear to dramatically increase the growth of food poisoning Campylobacter bacteria. Phosphorus preservatives and additives in junk foods, meat products, and cola can also be harmful by possibly damaging blood vessels, accelerating the aging process, and contributing to osteoporosis. Yet, the meat industry is not required to list phosphorus content on the nutrition facts label. In this case, reducing our intake of meat, junk food, fast food, and processed cheese, all of which have redily absorbed phosphorus, may help lower intake until labeling is mandated. Some studies found that a 21-day whole plant-food diets without preservatives helped improve several metabolic and cardiovascular disease markers.
For substantiation of any statements of fact from the peer-reviewed medical literature, please see the associated videos below.

If the nitrites in foods like ham and bacon cause lung damage, what about “uncured” meat with “no nitrites added”?

The rise in the U.S. calorie supply responsible for the obesity epidemic wasn’t just about more food but a different kind of food.

What was the meat industry’s response to the recommendation by leading cancer charities to stop eating processed meats, such as bacon, ham, hot dogs, sausage, and lunchmeat?
Sulfur dioxide preservatives in dried fruit, sulfites in wine, and the putrefaction of undigested animal protein in the colon can release hydrogen sulfide, the rotten egg gas associated with inflammatory bowel disease.

Dr. Greger has scoured the world’s scholarly literature on clinical nutrition and developed this new presentation based on the latest in cutting-edge research exploring the role diet may play in preventing, arresting, and even reversing some of our leading causes of death and disability.

The vast majority of chicken and poultry products are injected with phosphorus preservatives, which are often not listed in the ingredients. Reducing one’s intake of meat, junk food, fast food, and processed cheese may help lower intake until labeling is mandated.

The phosphorus preservatives injected into poultry may not just be an arterial toxin. They also appear to dramatically increase the growth of food poisoning Campylobacter bacteria.

The consumption of phosphorus preservatives in junk food, and injected into meat, may damage blood vessels, accelerate the aging process, and contribute to osteoporosis.

In response to definitive evidence showing artificial colors may increase inattentiveness, impulsivity, and hyperactivity among young children, a call has been made by consumer groups to ban food dyes.

Human beings lost the ability to detoxify uric acid millions of years ago. What implications does this have for our health today?

An evolutionary argument for a plant-based diet is presented, in contrast to “Paleo” fad diets.

Within a matter of weeks, participants placed on the vegan diet outlined by the prophet Daniel experienced improvements in blood pressure, cholesterol and insulin levels, insulin resistance, and C-reactive protein levels, a marker of inflammation within the body.

Given their inherent resistance to food-poisoning bacteria, maggots can be used to create an antibacterial food additive to increase the safety of the meat supply.
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease is now the third leading cause of death. The good news is that. in addition to smoking cessation, there are dietary interventions that can help prevent COPD.

The addition of vitamin C to processed (cured) meats such as bacon may actually make them more carcinogenic.

The levels of nitrosamines—considered the most carcinogenic agents in cigarette smoke—were recently measured in an array of processed meats including chicken, turkey, and pork.

Phytonutrients, such as vitamin C, prevent the formation of nitrosamines from nitrites—which explains why adding nitrite preservatives to processed meat can be harmful, but adding more vegetables, with their nitrite-forming nitrates, to our diet can be helpful.

The nitrite preservatives in processed meats such as bologna, bacon, ham, and hot dogs form carcinogenic nitrosamines, but also reduce the growth of botulism bacteria—forcing regulators to strike a balance between consumers risking cancer, or a deadly form of food poisoning.

Nitrites in processed meat form nitrosamines, a class of potent carcinogens found in cigarette smoke, which may explain why hot dog consumption has been associated with the two leading pediatric cancers, brain tumors and childhood leukemia.
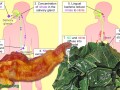
If the nitrates in vegetables such as greens are health-promoting because they can be turned into nitrites, and then nitric oxide, inside our bodies, what about the nitrites added to cured meats—such as bacon, ham, and hot dogs?