
PhIP: The Three-Strikes Breast Carcinogen
The cooked meat carcinogen PhIP—found in fried bacon, fish, and chicken—may not only trigger cancer and promote tumor growth, but also increase its metastatic potential, by increasing its invasiveness.

The cooked meat carcinogen PhIP—found in fried bacon, fish, and chicken—may not only trigger cancer and promote tumor growth, but also increase its metastatic potential, by increasing its invasiveness.

DNA-damaging chemicals, formed when meat is cooked, stimulate breast cancer cells almost as much as pure estrogen, and can infiltrate the ducts where most breast cancers arise.

This week Consumer Reports released a study showing the majority of retail pork tested was contaminated with antibiotic-resistant strains of the foodborne bacteria Yersinia enterocolitica.
In one of the largest nutrition studies ever, total meat consumption was significantly associated with weight gain in men and women—and the link remained even after controlling for calories.

A dramatic difference exists between the anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects of black walnuts versus English walnuts.

Death in America is largely a foodborne illness. Focusing on studies published just over the last year in peer-reviewed scientific medical journals, Dr. Greger offers practical advice on how best to feed ourselves and our families to prevent, treat, and even reverse many of the top 15 killers in the United States.

By preventing the buildup of cholesterol in our bloodstream, we can prevent atherosclerosis in our coronary arteries—the leading cause of death in the United States for both men and women. This involves increasing our intake of fiber-containing plant foods, and decreasing our intake of trans fat, saturated fat, and cholesterol found in junk food and animal products.
Bacteria-eating viruses (bacteriophages) have been approved as meat additives to reduce the risk of Listeria and Campylobacter found in processed meat and poultry products, but there’s a concern they could spread toxin genes between bacteria.
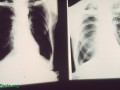
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease is now the third leading cause of death. The good news is that. in addition to smoking cessation, there are dietary interventions that can help prevent COPD.

In a study of a half million people, which was most associated with the risk of developing lymphoma? Red meat, processed meat, poultry, offal, eggs, or milk?
How meat scientists justify their promotion of foods associated with cancer risk.

The addition of vitamin C to processed (cured) meats such as bacon may actually make them more carcinogenic.

The levels of nitrosamines—considered the most carcinogenic agents in cigarette smoke—were recently measured in an array of processed meats including chicken, turkey, and pork.

Phytonutrients, such as vitamin C, prevent the formation of nitrosamines from nitrites—which explains why adding nitrite preservatives to processed meat can be harmful, but adding more vegetables, with their nitrite-forming nitrates, to our diet can be helpful.

The nitrite preservatives in processed meats such as bologna, bacon, ham, and hot dogs form carcinogenic nitrosamines, but also reduce the growth of botulism bacteria—forcing regulators to strike a balance between consumers risking cancer, or a deadly form of food poisoning.

Nitrites in processed meat form nitrosamines, a class of potent carcinogens found in cigarette smoke, which may explain why hot dog consumption has been associated with the two leading pediatric cancers, brain tumors and childhood leukemia.
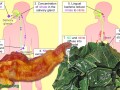
If the nitrates in vegetables such as greens are health-promoting because they can be turned into nitrites, and then nitric oxide, inside our bodies, what about the nitrites added to cured meats—such as bacon, ham, and hot dogs?

500 foods were tested for advanced glycation end products (AGEs).

Excessive intake of kelp (kombu) or thyroid-containing sausages can lead to iodine toxicity.