
Who Says Eggs Aren’t Healthy or Safe?
Freedom of Information Act documents reveal that the U.S. Department of Agriculture warned the egg industry that saying eggs are nutritious or safe may violate rules against false and misleading advertising.

Freedom of Information Act documents reveal that the U.S. Department of Agriculture warned the egg industry that saying eggs are nutritious or safe may violate rules against false and misleading advertising.
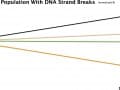
The DNA of those cooking with spices such as ginger, rosemary, and turmeric appears less susceptible to breakage.

Coronary heart disease, our #1 cause of death, was found to be almost non-existent in a population eating a diet centered around whole plant foods.

Canned beans are convenient, but are they as nutritious as home-cooked? And, if we do use canned, should we drain them or not?

One reason why soy consumption is associated with improved survival and lower recurrence rates in breast cancer patients may be because soy phytonutrients appear to improve the expression of tumor-suppressing BRCA genes.

Americans eating meat-free diets average higher intakes of nearly every nutrient, while maintaining a lower body weight—perhaps due, in part, to their higher resting metabolic rates.

Too much choline—a compound concentrated in eggs and other animal products—can make bodily secretions smell like rotting fish, and may increase the risk of heart disease, due to conversion in the gut to trimethylamine.

The beef industry designed a study to show that a diet containing beef was able to lower cholesterol—if one cuts out enough poultry, pork, fish, and cheese to halve one’s total saturated fat intake.

Plant-based diets tend to be alkaline-forming. This may help protect muscle mass, and reduce the risk of gout and kidney stones. The pH of one’s urine can be estimated with natural pigments, using kitchen chemistry.
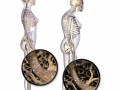
The decades-old dogma that the acid-forming quality of animal protein leads to bone loss has been called into question.

Reducing the ratio of animal to plant protein in men’s diets may slow the progression of prostate cancer.

Plant-based diets may prove to be a useful nutrition strategy in both cancer growth control as well as lifespan extension, because these diets are naturally lower in methionine.

Methionine restriction—best achieved through a plant-based diet—may prove to have a major impact on patients with cancer because, unlike normal tissues, many human tumors require the amino acid methionine to grow.

A higher rate of cancer deaths among those that handle and process meat is attributed to infection with viruses, and chronic exposure to animal proteins.

Changing food perceptions and incorporating puréed vegetables into entrees can improve the dietary quality of kids and grown-ups.

Those eating a more plant-based diet may naturally have an enhanced antioxidant defense system to counter the DNA damage caused by free radicals produced by high-intensity exercise.

Dr. Greger has scoured the world’s scholarly literature on clinical nutrition, and developed this brand-new live presentation on the latest in cutting-edge research on how a healthy diet can affect some of our most common medical conditions.

Most children don’t drink water from when they wake up to when they go off to school. Interventional trials show this mild state of dehydration may negatively affect scholastic performance.
What happens when men with prostate cancer and prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia (PIN) are placed on a relatively low-fat diet, supplemented with ground flax seeds?

Plant-based diets in general, and certain plant foods in particular, may be used to successfully treat Parkinson’s disease—in part, by boosting L-DOPA levels.

The early onset of puberty in girls associated with animal protein consumption may be due to endocrine-disrupting chemical pollutants in the meat supply.

The polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the vapors released from cooking meat may be hazardous for fetal development, and increase the risk of cancer.

The boost in detoxifying enzymes triggered by cruciferous vegetable consumption may last for weeks!
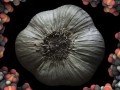
Garlic and flavonoid phytonutrients found in fruits, vegetables, nuts, and grains appear to protect against DNA damage induced by mutagenic chemicals found in cooked meat.
Using the cooked meat carcinogen PhIP to turn normal breast cells cancerous, researchers explore the use of green tea to interrupt this malignant transformation.

Even vegetarians could potentially be exposed to the carcinogens typically formed by cooking meat through eggs, cheese, creatine sports supplements, and cigarette smoke.
The foreign meat molecule Neu5Gc builds up in human tumors and atherosclerotic plaques, and may play an inflammatory role in the progression of both diseases.

A research group is suggesting that human protein requirements may have been underestimated.
Why is the intake of animal protein associated with heart disease—even independent of saturated fat—and the intake of plant protein protective?

Of all animals, the bodies of insects may have the lowest saturated fat content.

An evolutionary argument for a plant-based diet is presented, in contrast to “Paleo” fad diets.

To maintain the low IGF-1 levels associated with a plant-based diet, one should probably eat no more than 3-5 servings of soy foods a day.

Vegans consuming 7 to 18 servings of soy foods a day may end up with circulating IGF-1 levels comparable to those who eat meat.
While animal proteins increase levels of the cancer-promoting growth hormone IGF-1, and most plant proteins bring levels down, “high quality” plant proteins, such as soy, may not significantly affect levels in either direction. This, however, may depend on the quantity consumed.

The reason animal proteins trigger the release of the cancer-promoting growth hormone IGF-1 more than plant proteins may be because the relative ratios of amino acids in animal proteins more closely resembles our own.

Animal protein consumption triggers the release of the cancer-promoting growth hormone IGF-1.

Meat consumption is not only associated with weight gain, but specifically abdominal obesity, which is the most metabolically concerning.

The secret to naturally boosting serotonin levels in the brain may include eating foods such as pumpkin seeds, with a high tryptophan-to-total protein ratio. This may help explain why studies show that those eating plant-based diets have superior mood states.

Contrary to popular belief, the consumption of animal foods may actually decrease tryptophan levels in the brain. Carbohydrates, on the other hand, can boost transport across the blood-brain barrier, which has been used to explain premenstrual cravings.

Death in America is largely a foodborne illness. Focusing on studies published just over the last year in peer-reviewed scientific medical journals, Dr. Greger offers practical advice on how best to feed ourselves and our families to prevent, treat, and even reverse many of the top 15 killers in the United States.