
Alzheimer’s Disease: Grain Brain or Meathead?
Grain consumption appears strongly protective against Alzheimer’s disease, whereas animal fat intake has been linked to dementia risk.

Grain consumption appears strongly protective against Alzheimer’s disease, whereas animal fat intake has been linked to dementia risk.

Nutritional quality indices show plant-based diets are the healthiest, but do vegetarians and vegans reach the recommended daily intake of protein?

Farmed Atlantic salmon, the kind of salmon most commonly found in restaurants and supermarkets, may be the single largest source of toxic dietary pollutants.

Industrial pollutants that build up in our own body fat may help explain the link between obesity and diabetes.

The levels of arsenic, banned pesticides, and dioxins exceeded cancer benchmarks in each of the 364 children tested. Which foods were the primary sources of toxic pollutants for preschoolers and their parents?

Unlike most other anticancer agents, the phytates naturally found in whole plant foods may trigger cancer cell differentiation, causing them to revert back to behaving more like normal cells.

Foods of animal origin (especially fish) appear to be the most important source of human exposure to industrial pollutants such as alkylphenol xenoestrogens.

The dramatic rise of allergic diseases such as eczema and seasonal allergies may be related to dietary exposure to endocrine-disruptor xenoestrogens, such as alkylphenol industrial pollutants.

The oxidation of high-fat and cholesterol-rich foods in our stomachs may help explain why eating antioxidant packed foods appears to reduce heart attack and stroke risk.

Freedom of Information Act documents reveal that the U.S. Department of Agriculture warned the egg industry that saying eggs are nutritious or safe may violate rules against false and misleading advertising.

The famous surgeon Denis Burkitt suggests an explanation for why many of our most common and deadliest diseases were rare or even nonexistent in populations eating plant-based diets.
The yellow pigment curcumin in the spice turmeric may work as well as, or better than, anti-inflammatory drugs and painkillers for the treatment of knee osteoarthritis.

Eating meat or eggs before pregnancy may increase the risk of gestational diabetes.

To stay out of oxidative debt, we need to take in more antioxidants than we use up.

If the bulk of fast food chicken nuggets is not actually chicken meat, what’s in them?

Coronary heart disease, our #1 cause of death, was found to be almost non-existent in a population eating a diet centered around whole plant foods.

Those eating calorie-dense diets may have a reduced capacity to enjoy all of life’s pleasures by deadening dopamine pathways in the brain.

Americans eating meat-free diets average higher intakes of nearly every nutrient, while maintaining a lower body weight—perhaps due, in part, to their higher resting metabolic rates.

Too much choline—a compound concentrated in eggs and other animal products—can make bodily secretions smell like rotting fish, and may increase the risk of heart disease, due to conversion in the gut to trimethylamine.

The beef industry designed a study to show that a diet containing beef was able to lower cholesterol—if one cuts out enough poultry, pork, fish, and cheese to halve one’s total saturated fat intake.

Simple changes in diet and lifestyle may quadruple a woman’s survival rate from breast cancer.

A plant-based diet may not only be the safest treatment for multiple sclerosis; it may also be the most effective.

By age 10, nearly all kids have fatty streaks in their arteries. This is the first sign of atherosclerosis, the leading cause of death in the United States. So the question for most of us is not whether we should eat healthy to prevent heart disease, but whether we want to reverse the heart disease we may already have.

Within a few weeks of eating healthier, our taste sensations change such that foods with lower salt, sugar, and fat content actually taste better.

Since both coronary heart disease and impotence can be reversed with a healthy diet, sexual dysfunction can be used as a motivator to change poor lifestyle habits.

Nori seaweed snacks may favorably alter estrogen metabolism by modulating women’s gut flora, resulting in decreased breast cancer risk.

Those eating a more plant-based diet may naturally have an enhanced antioxidant defense system to counter the DNA damage caused by free radicals produced by high-intensity exercise.

Dr. Greger has scoured the world’s scholarly literature on clinical nutrition, and developed this brand-new live presentation on the latest in cutting-edge research on how a healthy diet can affect some of our most common medical conditions.

Dioxins, endocrine disrupting pollutants, heavy metals, saturated fat, and steroids in the meat supply may be affecting sperm counts, semen quality, and the ability of men to conceive.

About half of America’s trans fat intake now comes from animal products.

Based on studies of atomic bomb survivors, Chernobyl victims, and airline pilots exposed to more cosmic rays at high altitudes, it appears that fruits and vegetables may decrease radiation-induced chromosome damage.
A more plant-based diet may help prevent vaginal infections, one of the most common gynecological problems of young women.
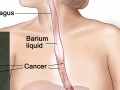
A randomized phase II clinical trial on the ability of strawberries to reverse the progression to esophageal cancer.
Expanding on the subject of my upcoming appearance on The Dr. Oz Show, a landmark new article in the New England Journal of Medicine shows that choline in eggs, poultry, dairy, and fish produces the same toxic TMAO as carnitine in red meat—which may help explain plant-based protection from heart disease and prostate cancer.
Plant-based diets appear to offer relief from a variety of menstrual symptoms, including cramping, bloating, and breast pain (cyclical mastalgia).

The story behind the first U.S. dietary recommendations report explains why, to this day, the decades of science supporting a more plant-based diet have yet to fully translate into public policy.
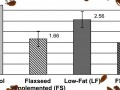
Researchers set out to find out what it was about a flax seed-supplemented, lower-fat diet that so effectively appeared to decrease prostate cancer growth.
What happens when men with prostate cancer and prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia (PIN) are placed on a relatively low-fat diet, supplemented with ground flax seeds?

Plant-based diets in general, and certain plant foods in particular, may be used to successfully treat Parkinson’s disease—in part, by boosting L-DOPA levels.

Sellers of coconut oil use a beef industry tactic to downplay the risks associated with the saturated fat in their products.