
The Optimal Dose of Vitamin D Based on Natural Levels
Why do some recommend thousands of units of supplemental vitamin D when the Institute of Medicine set the recommended daily intake at just 600 to 800 units?

Why do some recommend thousands of units of supplemental vitamin D when the Institute of Medicine set the recommended daily intake at just 600 to 800 units?
Those with higher vitamin D levels tend to have lower rates of obesity, diabetes, and hypertension, but is it cause and effect? Interventional trials finally put vitamin D to the test.

The field of nutrition got human protein requirements spectacularly wrong, leading to a massive recalculation.

How many cola cancer cases are estimated to be caused by Coke and Pepsi in New York versus California, where a carcinogen labeling law (Prop 65) exists?
What happens when you take blood from people before and then again four hours after almond consumption, and drip that blood on bone cells?

What about the studies that show a “u-shaped curve,” where too much sodium is bad, but too little may be bad too?

What is the optimal daily dietary calcium intake and might benefits for your bones outweigh the risks to your heart from taking calcium supplements?

The unnaturally large, rapid, and sustained calcium levels in the blood caused by calcium supplements may explain why calcium from supplements, but not from food, appears to increase the risk of heart attacks.

What effect does coffee and tea consumption have on longevity, cancer risk, GERD reflux, bone fractures, glaucoma, sleep quality, and atrial fibrillation (irregular heartbeat)?

Dr. Greger has scoured the world’s scholarly literature on clinical nutrition and developed this new presentation based on the latest in cutting edge research exploring the role diet may play in preventing, arresting, and even reversing some of our most feared causes of death and disability.

Endocrine-disrupting industrial toxins in the aquatic food chain may affect genital development of boys and sexual function in men.

The galactose in milk may explain why milk consumption is associated with significantly higher risk of hip fractures, cancer, and premature death.

The majority of polyphenol phytonutrients may be bound to fiber, helping to explain the marked difference in health impacts between whole fruit and fruit juice.

Legumes such as lentils, chickpeas, beans and split peas may reduce cholesterol so much that consumers may be able to get off their cholesterol-lowering statin drugs, but to profoundly alter heart disease risk we may have to more profoundly alter our diet.

A bacteria discovered on Easter Island may hold the key to the proverbial fountain of youth by producing rapamycin, which inhibits the engine-of-aging enzyme TOR.

Freedom of Information Act documents reveal that the U.S. Department of Agriculture warned the egg industry that saying eggs are nutritious or safe may violate rules against false and misleading advertising.

Randomized controlled trial comparing the safety and efficacy of drugs versus curcumin, the yellow pigment in the spice turmeric, for the treatment of autoimmune inflammatory rheumatoid arthritis.
The cardiovascular benefits of plant-based diets may be severely undermined by vitamin B12 deficiency.

Women who consume the most high-phytate foods (whole grains, beans, and nuts) appear to have better bone density.

The consumption of phosphorus preservatives in junk food, and injected into meat, may damage blood vessels, accelerate the aging process, and contribute to osteoporosis.

Plant-based diets tend to be alkaline-forming. This may help protect muscle mass, and reduce the risk of gout and kidney stones. The pH of one’s urine can be estimated with natural pigments, using kitchen chemistry.
The decades-old dogma that the acid-forming quality of animal protein leads to bone loss has been called into question.

Dr. Greger has scoured the world’s scholarly literature on clinical nutrition, and developed this brand-new live presentation on the latest in cutting-edge research on how a healthy diet can affect some of our most common medical conditions.

Most children don’t drink water from when they wake up to when they go off to school. Interventional trials show this mild state of dehydration may negatively affect scholastic performance.
Expanding on the subject of my upcoming appearance on The Dr. Oz Show, a landmark new article in the New England Journal of Medicine shows that choline in eggs, poultry, dairy, and fish produces the same toxic TMAO as carnitine in red meat—which may help explain plant-based protection from heart disease and prostate cancer.

The consumption of three portions of whole grains a day appears as powerful as high blood pressure medications in alleviating hypertension.

For the same reason aspirin should be avoided in pregnancy, chamomile has such powerful anti-inflammatory properties that regular consumption may result in a serious fetal heart problem—premature constriction of the fetal ductus arteriosus, which allows the fetus to “breathe” in the womb.

Advanced glycation end products (AGEs) in our diet are thought to accelerate the aging process.
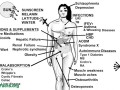
The latest revision of the official vitamin D recommendations was based on the body’s reaction to protect bone health—but what about the other three dozen affected organs?

Vitamin D deficiency may shorten one’s lifespan, but getting too much vitamin D may also adversely affect longevity.

The Institute of Medicine’s conservative position on vitamin D is understandable, given the history of hyped vitamin supplements (vitamin A, beta carotene, folic acid, vitamin C, vitamin E) that turned out worthless—or worse.

Should the vitamin D levels found in lifeguards be considered the norm for our species, given the fact that we evolved running around naked all day in equatorial Africa?

The Institute of Medicine tripled their official vitamin D recommendation, based on target blood levels that indicate a large percentage of the U.S. population is deficient.

Soy milk should be shaken before pouring to get at the calcium that settles to the bottom.