
EPIC Findings on Lymphoma
In a study of a half million people, which was most associated with the risk of developing lymphoma? Red meat, processed meat, poultry, offal, eggs, or milk?

In a study of a half million people, which was most associated with the risk of developing lymphoma? Red meat, processed meat, poultry, offal, eggs, or milk?

Frying bacon outdoors decreases the concentration of airborne nitrosamine carcinogens.
Since foods are effectively a package deal, what’s the best way to get vitamin B12 (cobalamin)?

The antioxidant power of American breakfast fare is compared to a smoothie that contains berries, white tea leaves, and Indian gooseberry (amla) powder.

Some herbs and spices—including cinnamon, cloves, lemon balm, marjoram, oregano, and peppermint—are so rich in antioxidants that just a small pinch can go a long way.
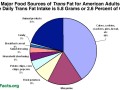
The intake of trans fats, which come mostly from junk food and animal products; saturated fat, mostly from dairy products and chicken; and cholesterol, coming mostly from eggs and chicken, should be as low as possible.

Salmonella, the leading cause of food poisoning-related death, can survive most common egg cooking methods—including scrambled, over-easy, and sunny side up. Cross-contamination onto fingers, utensils, or kitchen surfaces may pose an additional threat.

Following the recommendations of the 2010 Dietary Guidelines Advisory Committee to “shift food intake patterns to a more plant-based diet,” the latest USDA guidelines include a vegan adaptation.

Unlike the United States, where the agriculture department is the lead agency on formulating dietary recommendations, other countries such as Greece rely on their health department. What do their dietary guidelines look like?
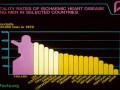
The success story in Finland shows that science-based dietary guidelines can save millions of lives.

How have the Dietary Guidelines for Americans evolved over the years since they were first issued in 1980?

What happens when the twin mandates of the USDA—to both promote agribusiness, and protect our nation’s health—come into conflict?

The egg industry is attempting to improve the fatty acid lipid profile of eggs by feeding blubber from the Canadian harp seal hunt to laying hens.
Chicken and eggs are the top sources of arachidonic acid in the diet—an omega-6 fatty acid involved in our body’s inflammatory response.
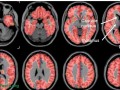
The purported role arachidonic acid plays in brain inflammation could explain why eliminating chicken, fish, and eggs may improve symptoms of mood disturbance, depression, anxiety, and stress within two weeks.

The top three sources of industrial toxins in the diet are fish oil, fish, and eggs.

Eating chicken during pregnancy may affect the size and development of one’s son’s penis due to phthalate contamination of the meat.

To help deflect criticism from the cholesterol content of their product, the egg industry touts the benefits of two phytonutrients, lutein and zeaxanthin, that have indeed been shown to be beneficial in protecting one’s eyesight against vision-threatening conditions, such as cataracts and macular degeneration. But how do eggs stack up against plant-based sources?

Eggs and brains are the two most concentrated sources of cholesterol in the diet.

Cardiology experts warn that eating even a single egg a day may exceed the safe upper limit for cholesterol intake.

Rate your diet on a scale of 0 to 100 using the phytochemical index, and compare your score to the Standard American Diet.

On average, plant foods have 64 times more antioxidant power than red meat, poultry, fish, dairy, and eggs— but is it a fair comparison?

In the most extensive study of its kind ever published, the amount of anti-aging anticancer antioxidants is measured across thousands of different foods.