Melatonin
Based on twin studies, insomnia has a heritability of 40 percent, meaning our genes account for less than half of insomnia risk. What can we do to flex the bulk we may have control over? Sleeping pills are a nonstarter. Hypnotics are the class of sleeping pills that includes Ambien, the one most commonly prescribed, and people who are prescribed even just half a dose or more a year appear to have more than three times the risk of dying prematurely compared to those receiving none. They may not even work. The most authoritative meta-analysis concluded that Ambien and Ambien-type drugs do not significantly increase total sleep time.
Some experts recommend melatonin, a hormone secreted by the “third-eye” pineal gland in the middle of our head, as a first-line agent to treat insomnia in older adults. The World Sleep Society disagrees, due to its low efficacy. Subjectively, people report better sleep on melatonin, though, objectively, a meta-analysis of studies found that melatonin only helped people get to sleep four minutes faster and extended overall sleep duration by thirteen or so minutes. Concerning contaminants have also been found, though there are also natural sources in the diet.
A total of seven randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trials of melatonin for Alzheimer’s disease have been performed on hundreds of patients, lasting between 10 days and 24 weeks. Those randomized to melatonin appeared to sleep better, but, sadly, melatonin had no effect on improving cognitive abilities.
For substantiation of any statements of fact from the peer-reviewed medical literature, please see the associated videos below.
Image Credit: Image by Sammy-Sander from Pixabay. This image has been modified.
Popular Videos for Melatonin


How to Treat Jet Lag with Melatonin-Rich Food
There may be a way to get the benefits of over-the-counter melatonin supplements without the...
Kiwifruit for Insomnia
Two kiwi fruit an hour before bedtime may improve sleep quality and duration, without the...
Natural Dietary Remedy for Insomnia
Lactucin, the hypnotic component of lettuce, is put to the test in a randomized, double-blind,...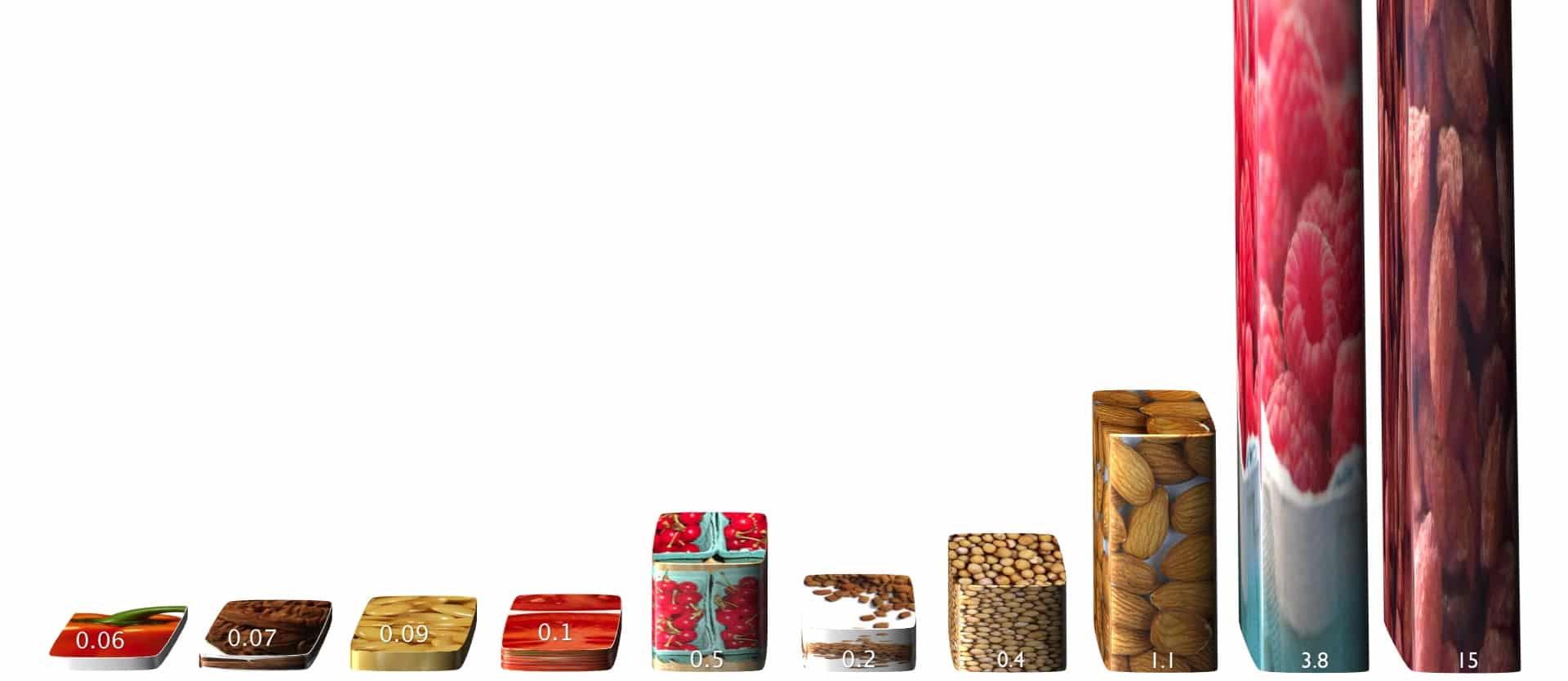
Tart Cherries for Insomnia
The melatonin content in certain plant foods such as almonds, raspberries, and goji berries may...
Yoga Put to the Test for MS, Back Pain, Neck Pain, Insomnia, and Breast Cancer
Is yoga better than other types of exercise, better than nothing but similar to other...
How to Get a Good Night’s Sleep Without Sleeping Pills
Taking less than just 18 Ambien-class sleeping pills in an entire year may triple the...
Is Six Hours of Sleep Enough?
Just because we don’t have evidence that there is a growing epidemic of sleep deprivation...All Videos for Melatonin
-

Melatonin Supplements for Sleep and Anti-Aging?
The secretion of melatonin appears to progressively decline with age, dropping as much as 70 percent between middle and older age.
-

How to Get a Good Night’s Sleep Without Sleeping Pills
Taking less than just 18 Ambien-class sleeping pills in an entire year may triple the risk of dying prematurely.
-

Do Mobile Phones Affect Sleep?
The effects of cell phone radiation on sleep quantity and quality.
-

How to Treat Jet Lag with Melatonin-Rich Food
There may be a way to get the benefits of over-the-counter melatonin supplements without the risk.
-

Are Melatonin Supplements Safe?
Over-the-counter melatonin (“anti-gonad hormone”) supplements tend not to contain what they say they do, and the contaminants could be dangerous.
-

How to Treat Jet Lag with Light
Use cheat sheets to figure out exactly when and how to treat jet lag using light exposure and light avoidance at specific times of the day, based on which direction you’re going and how many time zones you cross.
-

Aloe for the Treatment of Advanced Metastatic Cancer
What are the effects of aloe on radiation burns caused by cancer treatment and on the cancer itself?
-

The Best Way to Get Vitamin D: Sun, Supplements, or Salons?
If one is going to make an evolutionary argument for what a “natural” vitamin D level may be, how about getting vitamin D in the way nature intended—that is, from the sun instead of supplements?
-

Tart Cherries for Insomnia
The melatonin content in certain plant foods such as almonds, raspberries, and goji berries may explain the improvement in sleep quality associated with tart cherry consumption.
-
Human Neurotransmitters in Plants
The consumption of certain fruits is suggested as a potential treatment for depression, given the presence of psychoactive neurotransmitters such as serotonin, dopamine, and melatonin in many plant foods.
