How to Prevent Toxoplasmosis
The risk of contracting the brain parasite toxoplasma from kitty litter vs. meat.
Topic summary contributed by volunteer(s): Randy
Up to nearly 10% of Americans may be infected with brain parasites found in undercooked meat. One example is the brain-invasive pork tapeworm, which is the most common cause of adult-onset epilepsy. Allergenic fish worms found in nearly two-thirds of retail fish tested can trigger allergic reactions in sensitive individuals. There have been migratory skin worms found in undercooked fish (like in sushi). Cheese may contain mites and maggots and organ meats may contain other worms. Nearly 95% of tested retail U.S. beef (including burgers) has been found to be parasite infested. The meat industry has responded to this problem by feeding arsenic to chickens and turkeys to reduce the parasite load; this arsenic may be linked to increased cancer risk in consumers, and adding bacteria-eating viruses to meat would not help one avoid the brain parasite, toxoplasma, the second leading cause of foodborne disease-related death in the United States. Being bitten by the external parasite, a lone star tick, may result in developing an allergy to meat.
For substantiation of any statements of fact from the peer-reviewed medical literature, please see the associated videos below.

The risk of contracting the brain parasite toxoplasma from kitty litter vs. meat.

A brain parasite is considered “probably one of the most important risk factors for schizophrenia.”
The effect of toxoplasma brain parasites can cause personality alterations.
Nearly one quarter of Americans have already been infected with the brain parasite toxoplasma.

What role do antibiotics play in the development and treatment of autism spectrum disorder?

Gnathostomiasis from raw fish is a growing problem, manifested by tiny worms that burrow under our skin and, in rare cases, can get into our eyes and brain.
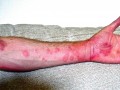
The rising incidence of tick-bite induced meat allergies may account for cases of previously unexplained (“idiopathic”) persistent hives among children.

Our immune response against a foreign molecule present in animal products may play a role in some allergic, autoimmune, and inflammatory disorders. This reaction is thought to underlie tick bite-triggered meat allergies.
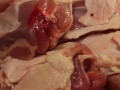
Arsenic-containing drugs intentionally added to poultry feed to reduce the parasite burden and pinken the meat are apparently converted by cooking into carcinogenic inorganic arsenic compounds.

Chronic headaches such as migraines or “tension” headache symptoms may be a sign of pork tapeworms in the brain.

A higher rate of cancer deaths among those that handle and process meat is attributed to infection with viruses, and chronic exposure to animal proteins.

Delusional parasitosis is a form of psychosis characterized by the false belief that one is infested with some sort of parasite. It can be triggered by a variety of brain diseases, including parasites themselves.
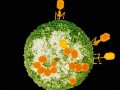
Bacteria-eating viruses (bacteriophages) have been approved as meat additives to reduce the risk of Listeria and Campylobacter found in processed meat and poultry products, but there’s a concern they could spread toxin genes between bacteria.

A case report (and video) of the worm-like, bloodsucking parasite Linguatula serrata, found in organ meats, that can migrate through the intestinal wall, into the bloodstream, and then inside one’s eyeball.

Cheese manufacturers use spider-like insects and fly larvae to impart particular flavors and aromas to certain cheeses.
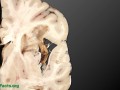
Avoiding pork tapeworm parasites (cysticercosis) is not as easy as just avoiding pork.
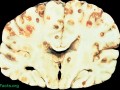
Neurocysticercosis, infection with pork tapeworm larvae brain parasites, is an increasingly serious public health problem in the United States, potentially causing headaches, dizziness, seizures, other neurological disorders, and sudden death.

The role of a parasitic worm in allergic reactions to chicken and fish.

Cleveland Clinic pathologists dissect fast food burgers to see what’s inside.