
Pesticide Exposure and Hypospadias Birth Defects in Vegetarians
What role do vegetarian diets and organic foods play in the prevention or promotion of a birth defect called hypospadias?
Topic summary contributed by volunteer(s): Linda
Diet may affect erectile function. In a case study featured in the Journal of the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics, a man following the low-carb, Atkins diet, lowered his weight, but also suffered chest pains and lost his ability to have an erection. Erectile dysfunction may be an early sign of vascular disease and cardiovascular risk. Pistachio nut intake may improve penial erectile function (as well as lower cholesterol). Watermelon, because it contains the amino acid citrulline, may also help with penile blood flow in mild erectile dysfunction cases, and eating antioxidant-rich plant foods may improve blood flow to all parts of the body, including penile arteries.
Diet during pregnancy can also be important for an infant’s penis health. A mother’s chicken consumption during pregnancy may affect the size and development of her son’s penis due to phthalate contamination of the meat. The risk of a birth defect of the penis called hypospadias was found to be doubled when the mother frequently consumed conventional (non-organic) high-fat dairy products. Endocrine-disrupting compounds sometimes found in fish may reduce eventual penis size in boys and adversely affect sexual functioning in men.
For substantiation of any statements of fact from the peer-reviewed medical literature, please see the associated videos below.

What role do vegetarian diets and organic foods play in the prevention or promotion of a birth defect called hypospadias?

Weight loss can decrease dementia risk and improve mental performance and infertility.

Natural topical remedies for eczema, including licorice root gel, St. John’s Wort cream, and emollients such as coconut oil, mineral oil, and petroleum jelly, are put to the test.

What are the effects of both oral and topical application of the spice saffron for impotence in men?

The spice saffron may not only work as well as SSRI antidepressant drugs like Prozac, Paxil, and Zoloft without the side effects, but it may even be able to treat the adverse sexual side effects that occur in up to 70 percent of people taking the drugs.

When done right, love may protect your lover’s life.

Endocrine-disrupting industrial toxins in the aquatic food chain may affect genital development of boys and sexual function in men.

Test tube studies show advantages of organic produce, such as better cancer cell growth suppression, but what about in people, not Petri dishes?

More people might be open to changing their diet and lifestyle if they knew how little modern medicine has to offer for combating chronic diseases.

The dramatic rise of allergic diseases such as eczema and seasonal allergies may be related to dietary exposure to endocrine-disruptor xenoestrogens, such as alkylphenol industrial pollutants.

Cancer-causing viruses in poultry may explain increased risks of death from liver and pancreatic cancers.

Men eating pistachio nuts experienced a significant improvement in blood flow through the penis accompanied by significantly firmer erections in just three weeks—perhaps due to pistachios’ antioxidant, arginine, and phytosterol content.

Since both coronary heart disease and impotence can be reversed with a healthy diet, sexual dysfunction can be used as a motivator to change poor lifestyle habits.
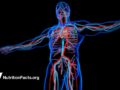
Because penile arteries are only about half the size of the coronary arteries in the heart, erectile dysfunction can be a powerful predictor of cardiac events—such as sudden death.
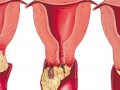
Most young women get infected with human papilloma virus, the cause of cervical cancer, but most are able to clear the infection before the virus causes cancer. What dietary changes can improve viral clearance?

Watermelon is a rich source of citrulline, which has been found to improve erection hardness in men with mild erectile dysfunction (impotence).

The largest study to date on poultry workers found a significantly increased risk of dying from penile cancer, thought to be due to exposure to oncogenic (cancer-causing) chicken viruses, which raise consumer concerns as well.

A case report in the Journal of the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics (formerly Journal of the American Dietetic Association) of a man who went on the Atkins diet, lost his ability to have an erection—and nearly lost his life.
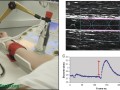
Antioxidants protect NO synthase—the enzyme that produces the artery-relaxing signal, nitric oxide. This may explain why those who eat especially antioxidant-rich plant foods have improved flow-mediated dilation of the brachial arteries.

Eating chicken during pregnancy may affect the size and development of one’s son’s penis due to phthalate contamination of the meat.
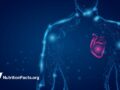
Erectile dysfunction may be an early warning sign for heart disease.