
Golden vs Brown Flaxseed: Which Has More Benefits?
Which kind of flaxseed has more cancer-fighting lignans?
Topic summary contributed by volunteer(s): Claire
The 2005 Ornish study indicated that the plant-based diet may be beneficial for reducing and reversing the occurrence of prostate cancer. Some specific foods that may be effective include flaxseed, cranberries, turmeric, and almond milk. The occurrence of prostate cancer may also decrease if the following items are restricted in the diet: the amino acid methionine, choline and cows’ milk. Benign prostatic hypertrophy and benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) may be less of a natural consequence of aging, and more indicative of eating an unhealthy diet and not exercising enough. The same kinds of healthy lifestyle interventions that have been shown to be effective at reducing the occurrence of prostate cancer are also helpful in keeping BPH in check.
For substantiation of any statements of fact from the peer-reviewed medical literature, please see the associated videos below.

Which kind of flaxseed has more cancer-fighting lignans?

Given the clear harms and the small and uncertain benefits, most men would presumably decide to decline PSA testing if they knew all the facts, but that’s up to each man to decide.

In this live lecture, Dr. Greger offers a sneak peek into his latest book, How Not to Age, a New York Times Best Seller.

Hot peppers, soy foods, and pumpkin seeds may help with hair loss.

Cranberries and pumpkin seeds are put to the test for benign prostatic hypertrophy.

Green tea is put to the test against precancerous lesions, prostate cancer, and metastatic cancer, and compared to the effects of black tea.

One third of men in their 30s may already have tiny, cancerous tumors in their prostates. How much tea would we have to drink to build up cancer-suppressing levels in our prostate tissue?

Might appeals to masculinity and manhood help men with prostate cancer change their diet to improve their survival?

Unlike most other anticancer agents, the phytates naturally found in whole plant foods may trigger cancer cell differentiation, causing them to revert back to behaving more like normal cells.

Dramatically lower cancer rates in India may in part be attributable to their more plant-based, spice-rich diet.

The dramatic rise of allergic diseases such as eczema and seasonal allergies may be related to dietary exposure to endocrine-disruptor xenoestrogens, such as alkylphenol industrial pollutants.

Does the hormonal stimulation of human prostate cancer cells by cow milk in a petri dish translate out clinically in studies of human populations?

If doctors can eliminate some of our leading killers by treating the underlying causes of chronic disease better than nearly any other medical intervention, why don’t more doctors do it?

Choline may be the reason egg consumption is associated with prostate cancer progression and death.

Reducing the ratio of animal to plant protein in men’s diets may slow the progression of prostate cancer.

Methionine restriction—best achieved through a plant-based diet—may prove to have a major impact on patients with cancer because, unlike normal tissues, many human tumors require the amino acid methionine to grow.

Drug companies and supplement manufacturers have yet to isolate the components of cranberries that suppress cancer cell growth.
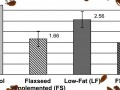
Researchers set out to find out what it was about a flax seed-supplemented, lower-fat diet that so effectively appeared to decrease prostate cancer growth.
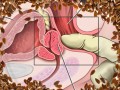
What happens when men with prostate cancer and prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia (PIN) are placed on a relatively low-fat diet, supplemented with ground flax seeds?

Rooibos (red) tea may reduce stress levels by suppressing adrenal gland function. Nettle tea is mineral-rich, but may have estrogenic side effects.
Eating a plant-based diet may protect against BPH (benign prostatic hypertrophy, an enlarged prostate).
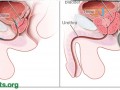
All men should consider eating a prostate-healthy diet, which includes legumes (beans, peas, lentils, soy); certain vegetables (like garlic and onions); certain seeds (flax seeds); and the avoidance of refined grains, eggs, and poultry.
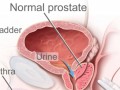
Benign prostatic hyperplasia, or BPH—an enlarged prostate gland—affects 80% of older men, but like many other Western chronic diseases, it appears to be a consequence of our diet.

The risk of glaucoma, the second leading cause of blindness, appears to be dramatically reduced by kale or collard greens consumption, thanks to the phytonutrient pigments lutein and zeaxanthin.

Coffee consumption is associated with a modest reduction of total cancer incidence.

The anti-proliferative effects of cruciferous vegetable phytonutrients may decrease the metastatic potential of lung cancer, the number one cancer killer of women.

The nitrite preservatives in processed meats such as bologna, bacon, ham, and hot dogs form carcinogenic nitrosamines, but also reduce the growth of botulism bacteria—forcing regulators to strike a balance between consumers risking cancer, or a deadly form of food poisoning.
New research suggests that multivitamin use may significantly increase the risk of breast cancer and prostate cancer.

Breast cancer can take decades to develop, so early detection via mammogram may be too late.

Dr. Dean Ornish turns from reversing heart disease to trying to reverse prostate cancer.

A landmark study pitted 34 common vegetables against 8 different lines of human cancer cells.