
Fukushima & Radioactivity in Seafood
The majority of radioactive fallout from the Fukushima nuclear power plant tragedy was absorbed by the Pacific Ocean. What does that mean for seafood safety?

The majority of radioactive fallout from the Fukushima nuclear power plant tragedy was absorbed by the Pacific Ocean. What does that mean for seafood safety?

Modest lifestyle changes that include the avoidance of alcohol may cut the odds of breast cancer in half, but certain grapes appear to contain natural aromatase inhibitors that may undermine the ability of breast tumors to produce their own estrogen.

Black raspberries may cause complete clinical regression of precancerous oral lesions (oral intraepithelial neoplasia).

Nearly 5,000 breast cancer deaths a year may be attributable to just light drinking (up to one drink a day).

The story behind the first U.S. dietary recommendations report explains why, to this day, the decades of science supporting a more plant-based diet have yet to fully translate into public policy.

A similar exponential increase in carotid artery plaque buildup was found for smokers and egg eaters.

An independent review of the effects of açaí berries was recently published, including studies on immune function, arthritis, and metabolic parameters.

Even vegetarians could potentially be exposed to the carcinogens typically formed by cooking meat through eggs, cheese, creatine sports supplements, and cigarette smoke.

The cooked meat carcinogen PhIP—found in fried bacon, fish, and chicken—may not only trigger cancer and promote tumor growth, but also increase its metastatic potential, by increasing its invasiveness.

DNA-damaging chemicals, formed when meat is cooked, stimulate breast cancer cells almost as much as pure estrogen, and can infiltrate the ducts where most breast cancers arise.
Plant-based diets appear to protect against metabolic syndrome, also known as syndrome X, which is characterized by the so-called “deadly quartet”—abdominal obesity, high fasting sugars, high triglycerides, and high blood pressure.

Since chronic inflammation underlines many disease processes, and saturated fat appears to facilitate the endotoxic inflammatory reaction to animal products, researchers have looked to wild animals for less unhealthy meat options.
In one of the largest nutrition studies ever, total meat consumption was significantly associated with weight gain in men and women—and the link remained even after controlling for calories.

Death in America is largely a foodborne illness. Focusing on studies published just over the last year in peer-reviewed scientific medical journals, Dr. Greger offers practical advice on how best to feed ourselves and our families to prevent, treat, and even reverse many of the top 15 killers in the United States.

A competing risks analysis of the Harvard Nurses’ Health Study compares the danger of smoking cigarettes to the danger of animal product consumption (cholesterol), and the benefits of plant foods (fiber) to the benefits of exercise.
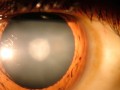
Risk of developing cataracts was compared in meat-eaters, fish-eaters, vegetarians, and vegans.

Dietary interventions, including increasing fruit and vegetable intake and decreasing meat intake, may not only help slow the progression of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, but may actually improve lung function.
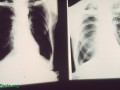
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease is now the third leading cause of death. The good news is that. in addition to smoking cessation, there are dietary interventions that can help prevent COPD.

Even after controlling for a variety of dietary and nondietary factors, those eating plant-based diets appear to have lower overall cancer rates.

Coffee consumption is associated with a modest reduction of total cancer incidence.

Eating broccoli appears to make DNA more resistant to damage.

The effect of kale juice on LDL and HDL cholesterol, and the antioxidant capacity of the blood.

The levels of nitrosamines—considered the most carcinogenic agents in cigarette smoke—were recently measured in an array of processed meats including chicken, turkey, and pork.

Nitrites in processed meat form nitrosamines, a class of potent carcinogens found in cigarette smoke, which may explain why hot dog consumption has been associated with the two leading pediatric cancers, brain tumors and childhood leukemia.
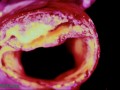
What dietary behaviors may cut the odds of developing of an abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA) in half?
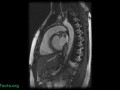
A million Americans have a silent aneurysm in their abdominal aorta (AAA) that may become life-threatening over time.

Eggs and brains are the two most concentrated sources of cholesterol in the diet.