
Exercise Is Medicine
The evidence supporting the overall health benefits of physical activity is overwhelming.
Topic summary contributed by volunteer(s): Linda
Smoking is responsible for 90% of lung cancer cases and is a risk factor for coronary disease, Alzheimer’s, abdominal aortic aneurysm, cataracts, and GERD (gastroesophageal reflux disease). Not smoking is one of the American Heart Association’s “Simple Seven” healthy behaviors. Research has identified nine lifestyle habits—including not smoking—that collectively may be more effective than taking medications: for example, lifestyle can reduce cardiovascular disease risk by 90%, compared to a 20-30% reduced risk from pharmacological therapies.
Smoking used to be the #1 cause of death in the U.S., but diet has bumped smoking to #2. Some unhealthy foods expose the body to the same dangers as smoking. Cigarette smoke contains nitrosamines, a class of powerful carcinogens. One hot dog has as many nitrosamines and nitrosamides as five cigarettes, and these carcinogens are also found in fresh unprocessed meat. Consuming the amount of cholesterol found in a single egg per day appears to cut a woman’s life short as much as smoking five cigarettes a day for 15 years. Inhalation of cigarette smoke exposes humans to cadmium, a highly toxic metal that is linked to a variety of serious illnesses, including cancer; seafood and organ meat have higher levels of cadmium than cigarette smoke. Smoking, as well as high temperature cooking of meat, exposes the body to carcinogenic heterocyclic amines. Eating a diet rich in animal proteins may make you four times more likely to die of cancer than someone with a low-protein diet, which is a mortality risk factor comparable to smoking.
Dietary interventions, including increased fruit and vegetable intake and decreased meat intake, may counteract some of smoking’s harmful effects on the human body. A plant-based diet may help prevent chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) or slow its progression and improve lung function. Curcumin (found in turmeric) may decrease DNA mutations caused by smoking, but not to the level of non-smokers. (Broccoli had a similar effect.) The significant health benefits of green tea may help mitigate the risks of smoking. And smokers get cholesterol-lowering benefits from antioxidant-rich foods, although not as much as non-smokers.
The carcinogenic risk of a chest CT scan is like the risk of smoking 700 cigarettes. Smoke inhalation is bad no matter what the source: in terms of lung cancer risk, smoking a single joint of marijuana may be like smoking an entire pack of cigarettes.
It took more than 7,000 scientific studies and the death of countless smokers before the first Surgeon General’s report against smoking was released in the 1960’s. Some say that moving to a plant-based diet is the nutritional equivalent of quitting smoking. There are similarities between the strategies used by the tobacco industry in the mid-20th century and those used by food industries in the 21st century—carefully worded denials, attempts to bury damaging reports, funding supportive research, and heavy investment in lobbyists and political influence.
For substantiation of any statements of fact from the peer-reviewed medical literature, please see the associated videos below.
Image Credit: Pixabay. This image has been modified.

The evidence supporting the overall health benefits of physical activity is overwhelming.

Those who stay hydrated tend to maintain a healthier body weight, but is it cause and effect?

Approximately half of the variability of age of menopause among women is explained by genetics. What behaviors or circumstances can help explain the rest?
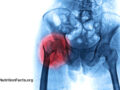
Stomach acid–blocking proton pump inhibitor drugs—PPIs with brand names like Prilosec, Prevacid, Nexium, Protonix, and AcipHex—appear to significantly increase the risk of bone fractures.

Taking less than just 18 Ambien-class sleeping pills in an entire year may triple the risk of dying prematurely.

Not all plant foods are linked to less cellular aging based on telomere attrition, and not all animal foods are linked to more.

The anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties of plant-based diets may explain why they can effectively reverse cellular aging by elongating telomeres.

What diet should oncologists recommend?

How can mandating healthy eating messaging on fast-food ads ironically make things worse?

How might we replicate one of our great public health victories—the reduction of smoking rates—in the field of nutrition?

Burning incense has been found to generate about four times the particulate matter as burning cigarettes.

Why are Black Americans sicker and die younger than their white counterparts, and what can we do about it?

If you care about your health so much that it would be unthinkable to light up a cigarette before and after lunch, maybe you should order a bean burrito instead of a meaty one.

Big Meat downplays the magnitude of meat mortality.

The meat industry comes up with a perversion of evidence-based medicine.

How did Big Corn Syrup and other corporate sugar titans hijack the scientific process?

Might biotin or zinc supplements prevent hair loss in men and women?

Lactucin, the hypnotic component of lettuce, is put to the test in a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of lettuce seeds.

Adding a healthy option can actually drive people to make even worse choices, thanks to a mind-blowing glitch of human psychology.

I quantify the risks of colon and rectal cancers from eating bacon, ham, hot dogs, sausage, and lunch meat.

How did the meat industry, government, and cancer organizations respond to the confirmation that processed meat, like bacon, ham, hot dogs, and lunch meat, causes cancer?

Why are nuts associated with decreased mortality, but not peanut butter?

The so-called optimism bias may get in the way of a healthy lifestyle.

Billion-dollar drugs pulled from the market for carcinogenic contamination less than that found in a single serving of grilled chicken.

What can physicians do to promote healthy, life-extending, lifestyle changes?

Do potato eaters live longer or shorter lives than non-potato eaters?

The leading risk factor for death in the United States is the American diet.

Women with breast cancer should include the “liberal culinary use of cruciferous vegetables.”

What do hospitals have to say for themselves for feeding people meals that appear to be designed to inspire repeat business?

If the nitrites in foods like ham and bacon cause lung damage, what about “uncured” meat with “no nitrites added”?
Laboratory models suggest that extreme doses of heme iron may be detrimental, but what about the effects of nutritional doses in humans? A look at heme’s carcinogenic effects.

What are the different impacts of plant protein versus animal protein, and do the benefits of plant proteins translate to plant protein isolates?

How do we explain studies that suggest overweight individuals live longer?

The temporary quintupling of heart attack risk associated with cannabis smoking may be due to the increased heartrate, blood pressure, and carbon monoxide levels.

What do randomized controlled trials of high-dose daily vitamin B12 supplementation show about the effects on cancer risk, death, and longevity?

An entire issue of a cardiology journal dedicated to plant-based nutrition explores the role an evidence-based diet can play in the reversal of congestive heart failure.

The EAT-Lancet Commission lays out the best diet for human and planetary health.

Why is hospital food so unhealthy?

Did traffic fatalities go up or down after cannabis legalization?

Two cups of cold water on an empty stomach a few times a day for weight loss.