Cannabis vapor has less tar, but may contain more ammonia. What happens to respiratory symptoms when regular users of joints, blunts, pipes, and bongs switch to a vaporizer?
There are many ways people inhale marijuana, but most smoke it in a bowl, pipe, joint, or bong. This is concerning, since, in many ways, smoke is smoke, and using “devices with water filters, like bongs and hookahs,” doesn’t help in terms of the tar exposure. As I discuss in my video Smoking Marijuana vs. Using a Cannabis Vaporizer, where there’s fire, there’s smoke, and where there’s smoke, there are inflammatory irritants. In fact, the “regular smoking of cannabis…is associated with significant airway inflammation that is similar in frequency, type, and magnitude to that observed in the lungs of tobacco [cigarette] smokers,” which can result in prolonged respiratory symptoms, such as chronic coughing, excess sputum production, wheezing, and shortness of breath, as well as an increased incidence of bronchitis and other respiratory infections.
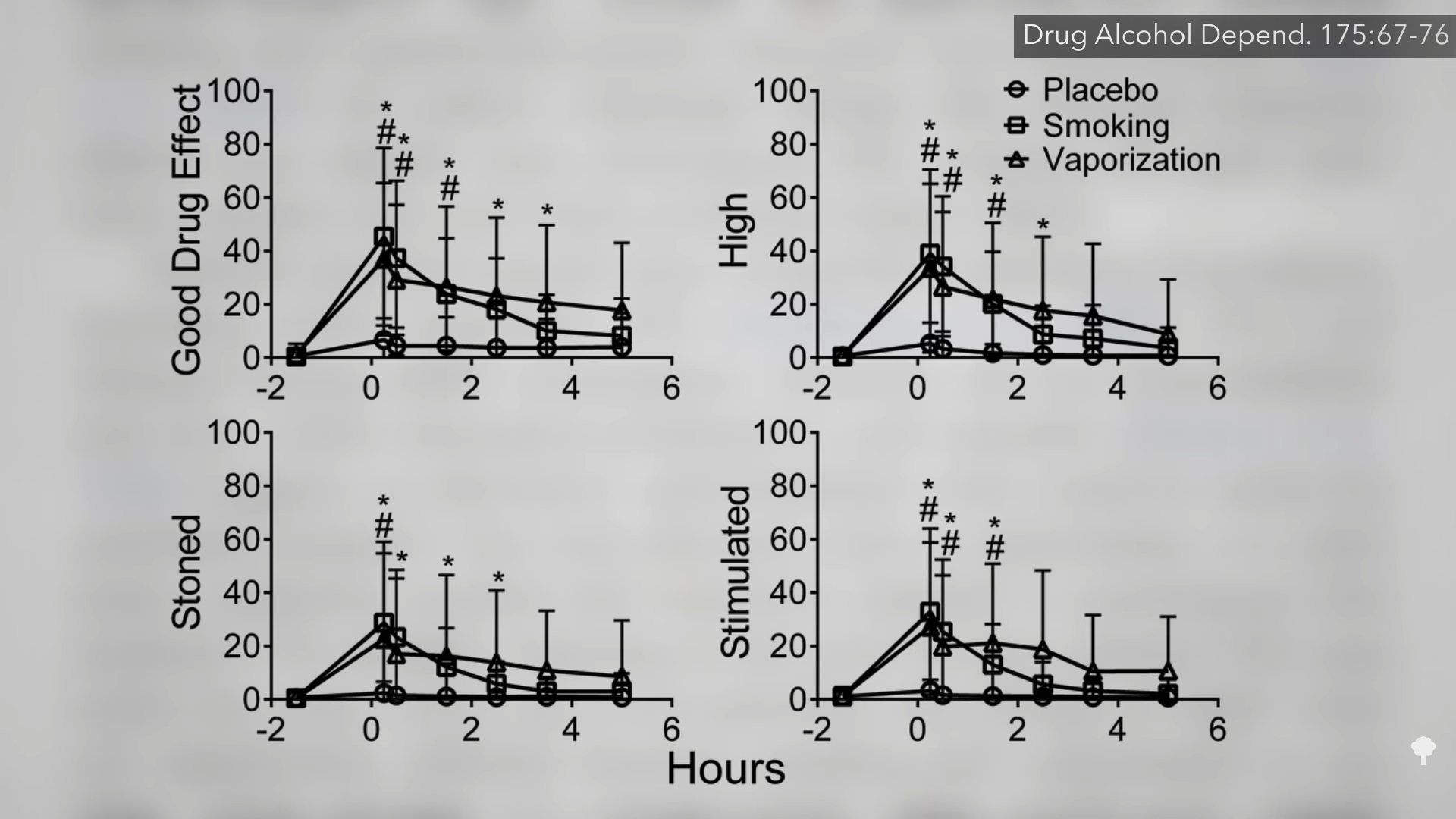
As I said, in many ways, smoke is smoke, whether it’s from burning plants in a forest fire or burning plants in a joint or cigarette. There are harmful by-products of combustion—any combustion—like carbon monoxide. In fact, you get five times more carbon monoxide per puff in cannabis than tobacco, since pot smokers inhale more deeply than cigarette smokers and then hold the smoke in longer. You can avoid that completely by eating cannabis instead, but the “slow, erratic absorption produced by oral cannabis” doesn’t give the same kind of immediate high. Inhaling cannabis vapor, however, could potentially offer the best of both worlds. At 1:28 in my video and below, you can see charts indicating that vapor appears to give the same kind of high in terms of subjective ratings compared to smoking it, but with significantly less carbon monoxide exposure. So, we’re talking about “similar effects to smoked cannabis while reducing exposure to toxic by-products”—though not necessarily all toxic by-products.
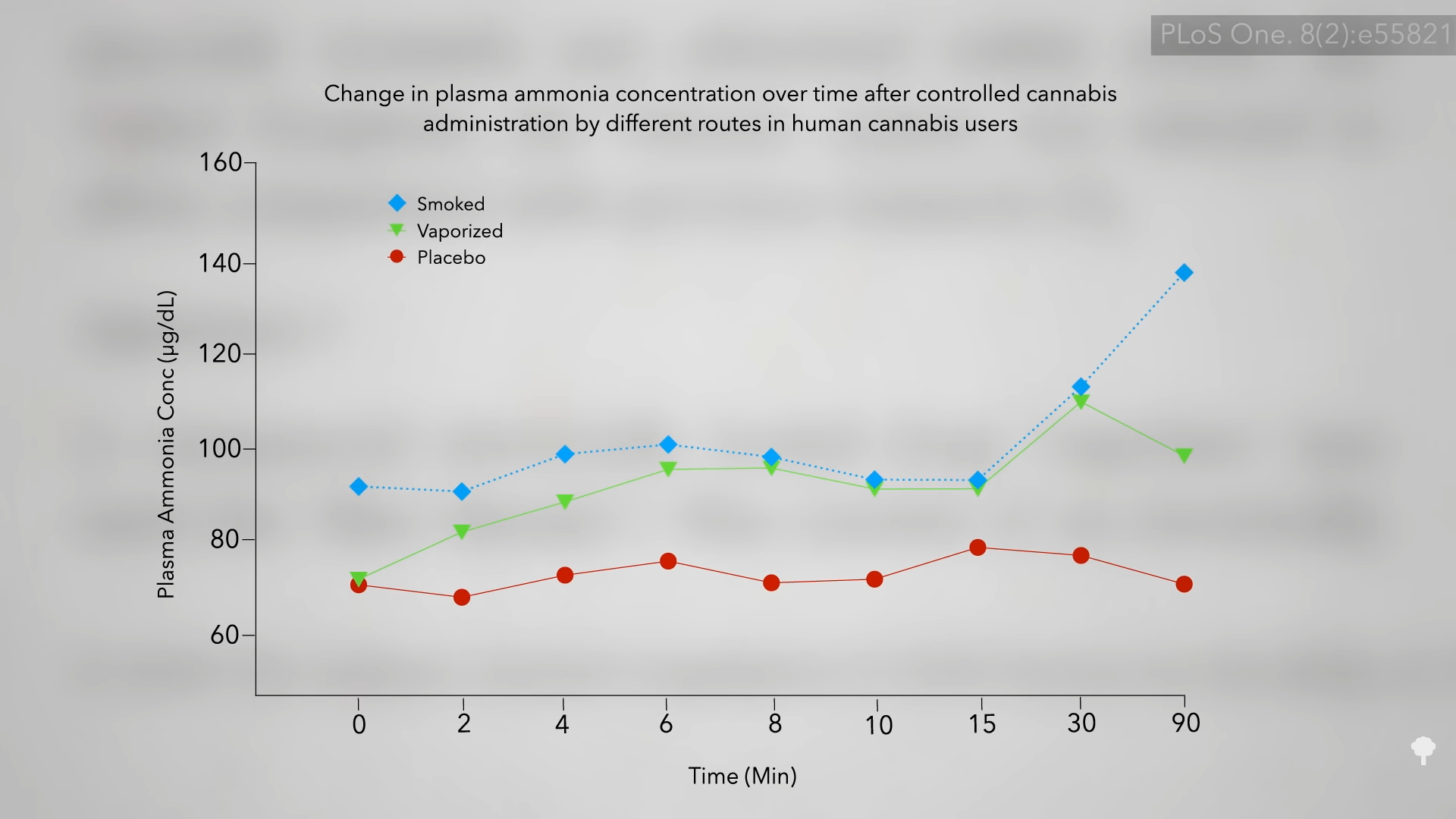
Both cannabis smoke and vapor “contain high concentrations of ammonia,” and, sometimes, vapor can even be worse. So, although vapor has less tar, it may have more ammonia. This was seen in a study using a “commercial electrically heated drug ‘vaporizer’…(the ‘Blue Meanie’).” As you can see below and at 2:04 in my video, using a hot air vaporizer, like ones from the Volcano brand, results in ammonia levels in the bloodstream more comparable to smoking it. The only reason we care about contaminants, though, is because we’re trying to cut down on the inflammation. So, does cannabis vapor produce fewer respiratory symptoms than smoke?
According to one study, which happened to be the first of its kind, yes. Now, vaporizing doesn’t help with dependence issues, impaired driving, or brain damage among heavy adolescent users, but it may improve “cannabis drug safety by minimizing pulmonary [lung] troubles.” The researchers concluded that “regular users of joints, blunts, pipes, and water pipes might decrease respiratory symptoms by switching to a vaporizer,” but this finding was based just on a snapshot-in-time internet survey that asked people about their symptoms. You don’t know for sure until you…put it to the test.
In a study funded by a pro-legalization group, the researchers recognized that “debates about cannabis policy often mention respiratory symptoms as a negative consequence of use,” thereby serving as a stumbling block in pro-legalization efforts. Might inhaling cannabis vapor rather than smoke “minimize respiratory complaints”? The researchers had 20 frequent cannabis smokers with respiratory symptoms switch to using a vaporizer for a month. The results? “The 12 participants who did not develop a respiratory illness during the trial significantly improved respiratory symptoms…”
But, hold on. Eight out of 20 subjects got a respiratory illness within just a single month? That’s 40 percent, which doesn’t sound good. Additionally, the self-reported improvements may have been tinged with bias, as the smokers may have thought such results might be good for the legalization cause. This may have backfired though, as there are calls in the medical literature to legalize just smokeless forms or at least set up policy so that smoked marijuana is more heavily taxed.
