Plant-based diets are put to the test for treating migraine headaches.
Headaches are one of the top five reasons people end up in emergency rooms and one of the leading reasons people see their doctors in general. One way to try to prevent them is to identify their triggers and avoid them. Common triggers for migraines include stress, smoking, hunger, sleep issues, certain foods (like chocolate, cheese, and alcohol), your menstrual cycle, or certain weather patterns (like high humidity).
In terms of dietary treatments, the so-called Father of Modern Medicine, William Osler suggested trying a “strict vegetable diet.” After all, the nerve inflammation associated with migraines “may be reduced by a vegan diet as many plant foods are high in anti-inflammatory compounds and antioxidants, and likewise, meat products have been reported to have inflammatory properties.” It wasn’t put to the test, though, for another 117 years.
As I discuss in my video Friday Favorites: Foods That Help Headache and Migraine Relief, among study participants given a placebo supplement, half said they got better, while the other half said they didn’t. But, when put on a strictly plant-based diet, they did much better, experiencing a significant drop in the severity of their pain, as you can see in the graph below and at 1:08 in my video.
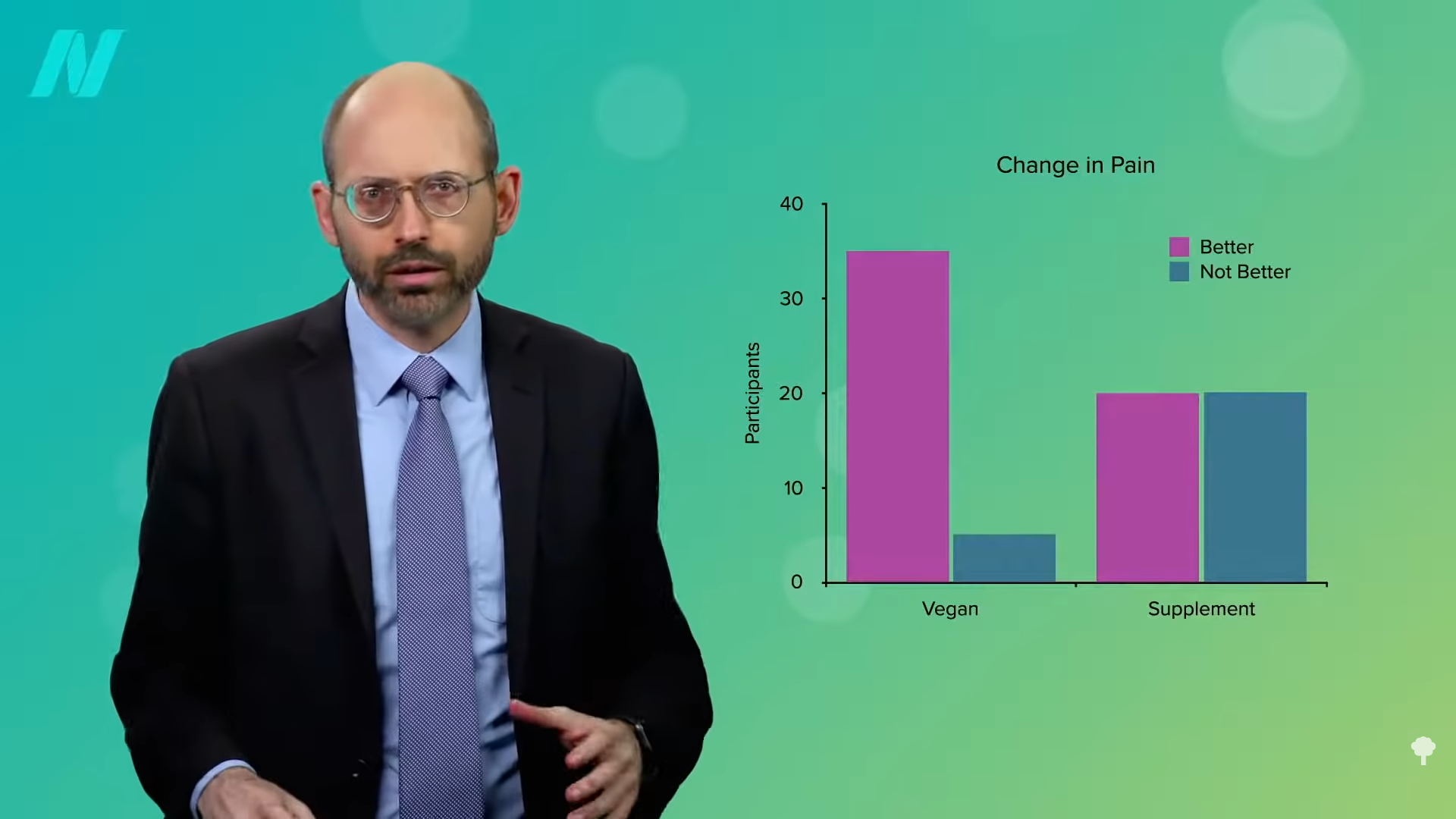
Now, “it is possible that the pain-reducing effects of the vegan diet may be, at least in part, due to weight reduction.” The study participants lost about nine more pounds when they were on the plant-based diet for a month, as shown below, and at 1:22.
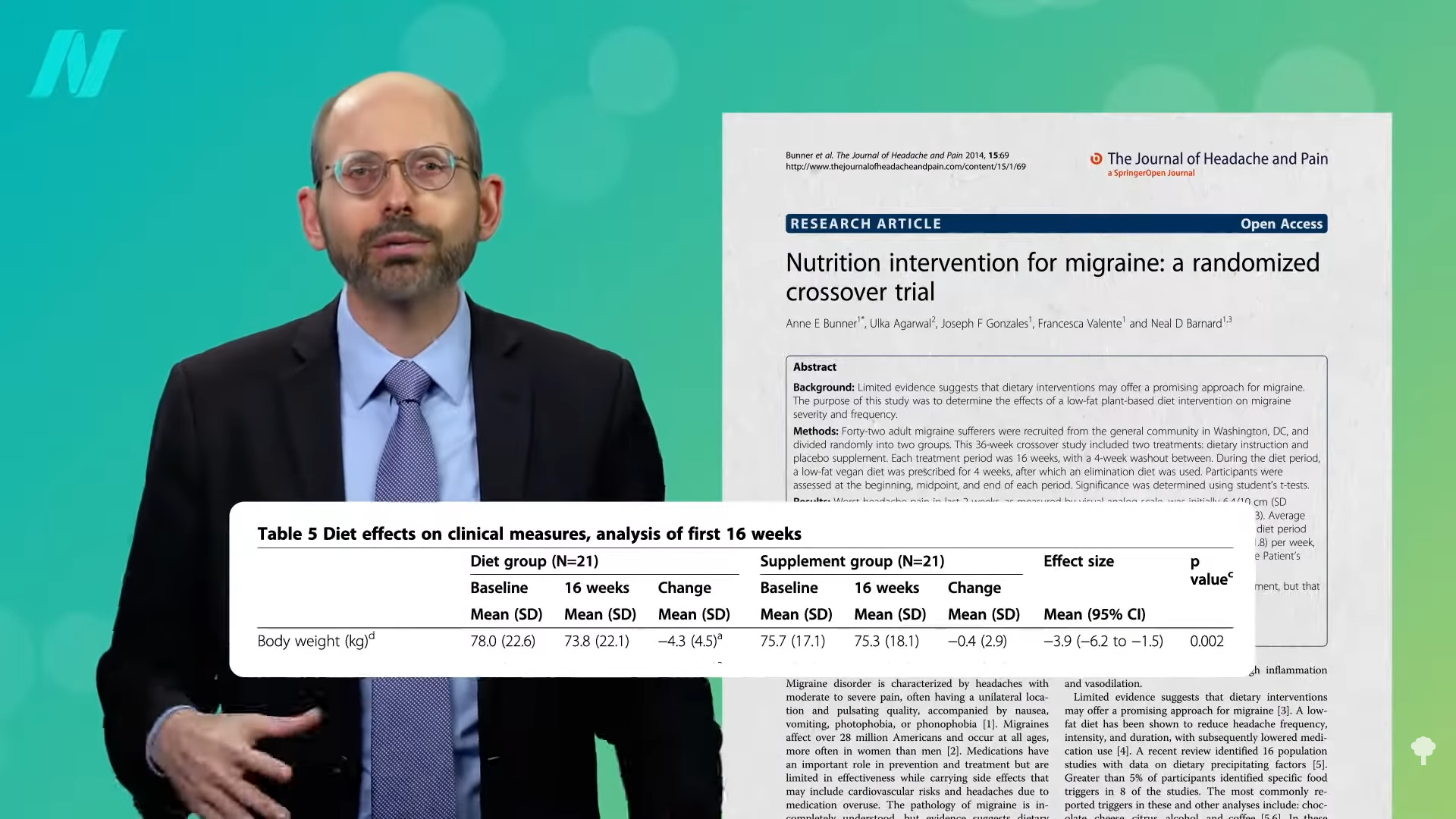
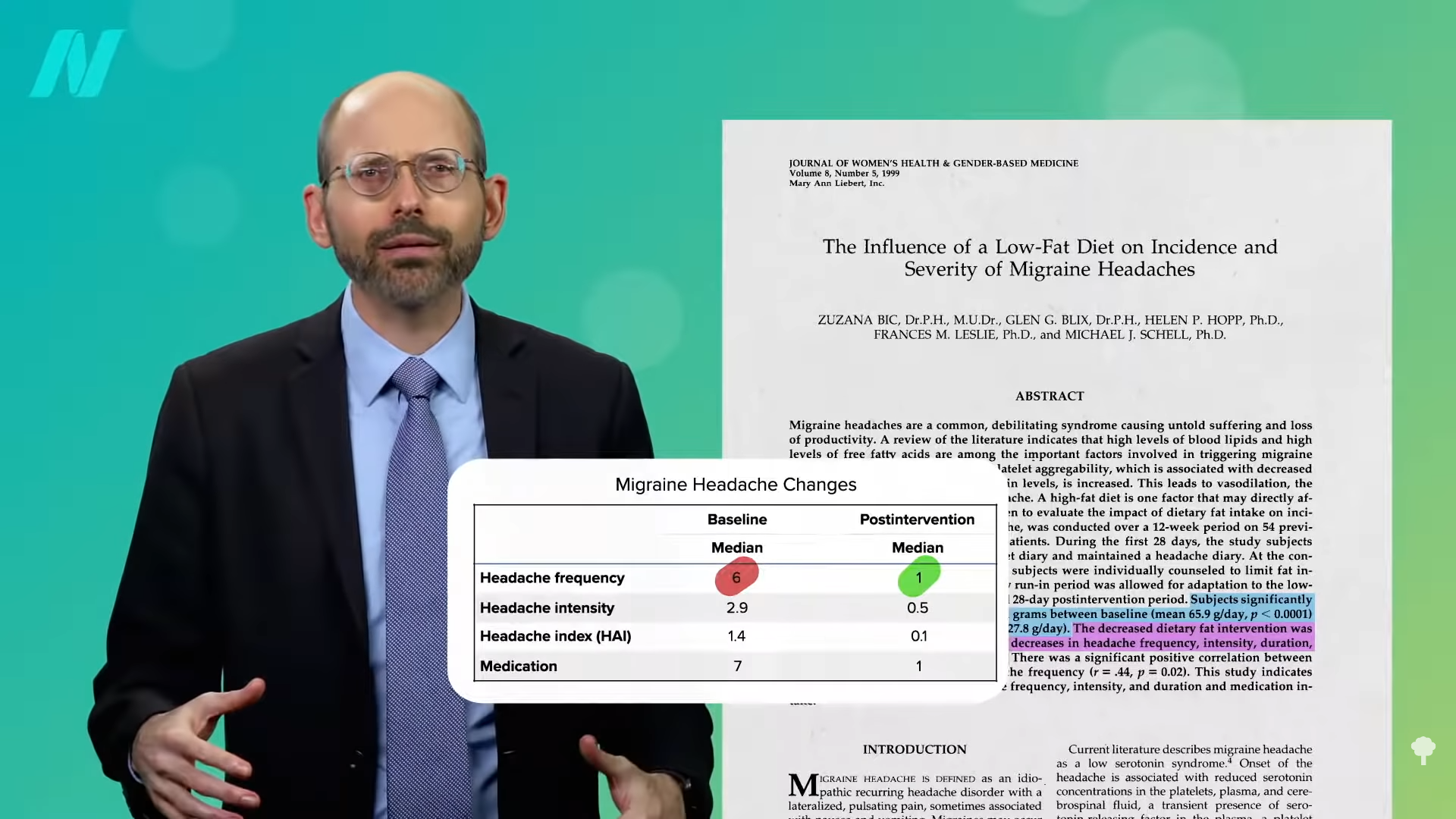
Even just lowering the fat content of the diet may help. Those placed on a month of consuming less than 30 daily grams of fat (for instance, less than two tablespoons of oil all day), experienced “statistically significant decreases in headache frequency, intensity, duration, and medication intake”—a six-fold decrease in the frequency and intensity, as you can see below and at 1:44 in my video. They went from three migraine attacks every two weeks down to just one a month. And, by “low fat,” the researchers didn’t mean SnackWell’s; they meant more fruits, vegetables, and beans. Before the food industry co-opted and corrupted the term, eating “low fat” meant eating an apple, for example, not Kellogg’s Apple Jacks.
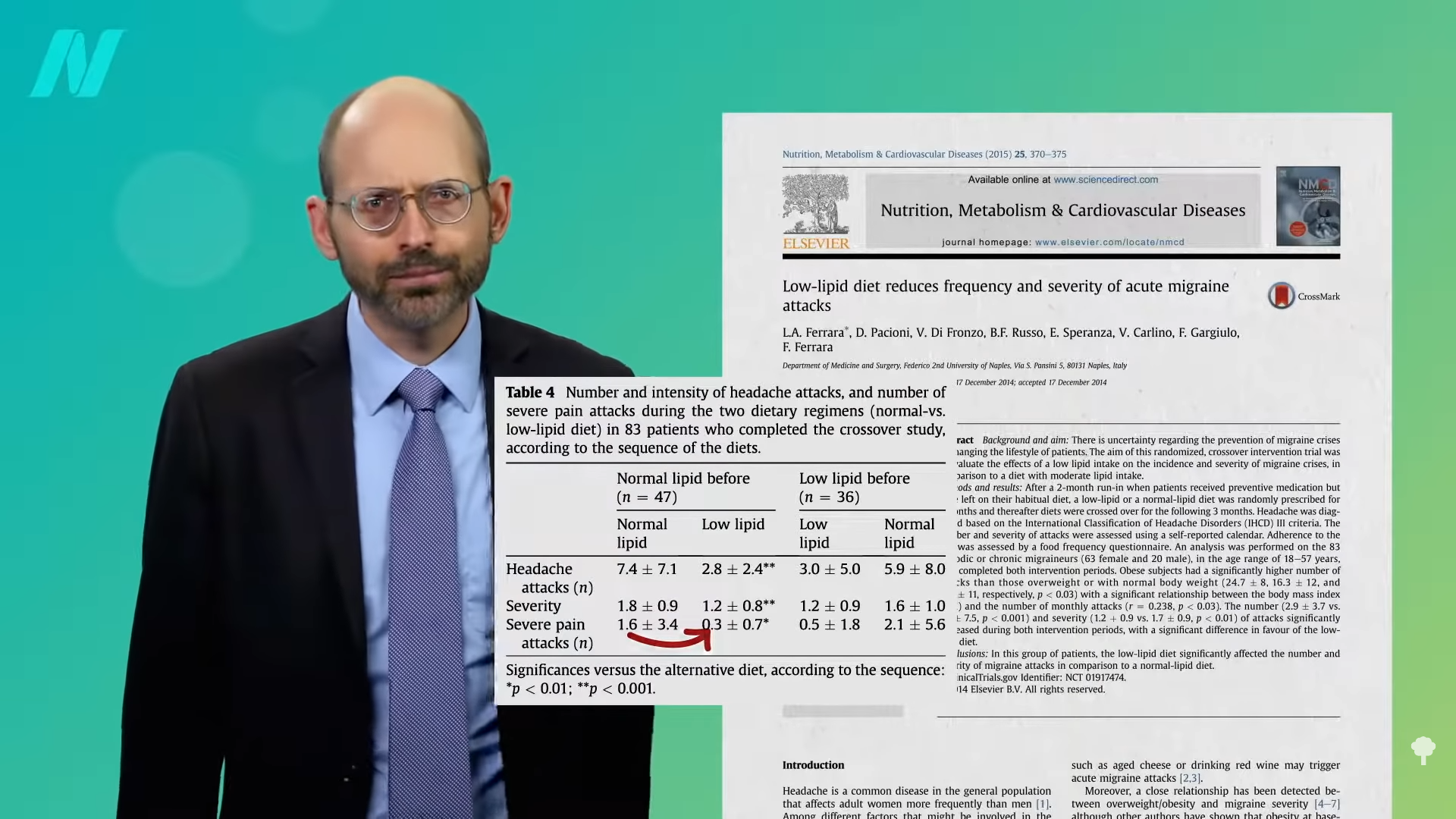
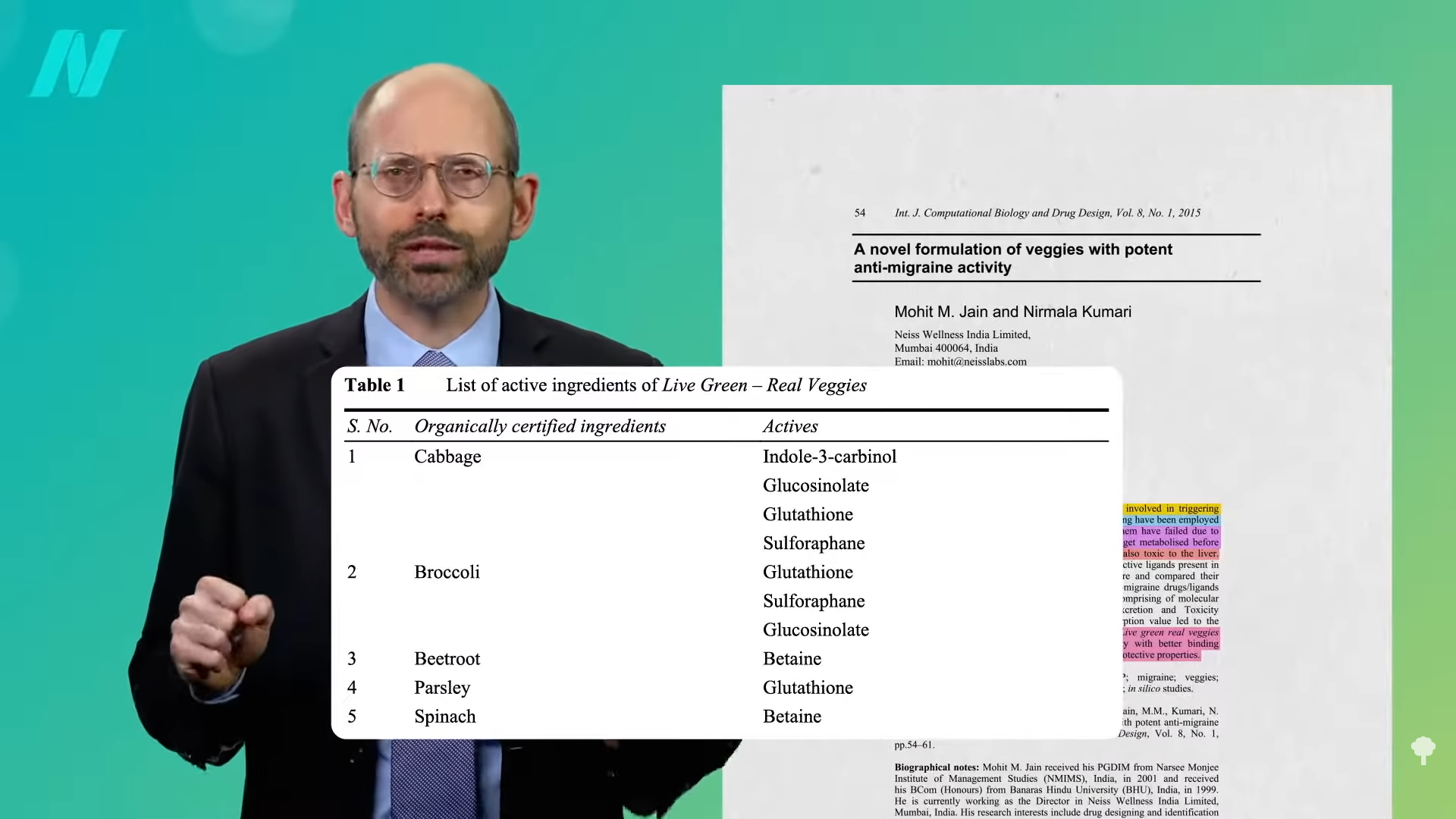
Now, they were on a low-fat diet—about 10 percent fat for someone eating 2,500 calories a day. What about just less than 20 percent fat compared to a more normal diet that’s still relatively lower fat than average? As you can see below and at 2:22 in my video, the researchers saw the same significant drops in headache frequency and severity, including a five-fold drop in attacks of severe pain. Since the intervention involved at least a halving of intake of saturated fat, which is mostly found in meat, dairy, and junk, the researchers concluded that reduced consumption of saturated fat may help control migraine attacks—but it isn’t necessarily something they’re getting less of. There are compounds “present in Live green real veggies” that might bind to a migraine-triggering peptide known as calcitonin gene-related peptide, CGRP.
Drug companies have been trying to come up with something that binds to CGRP, but the drugs have failed to be effective. They’re also toxic, which is a problem we don’t have with cabbage, as you can see below and at 3:01 in my video.
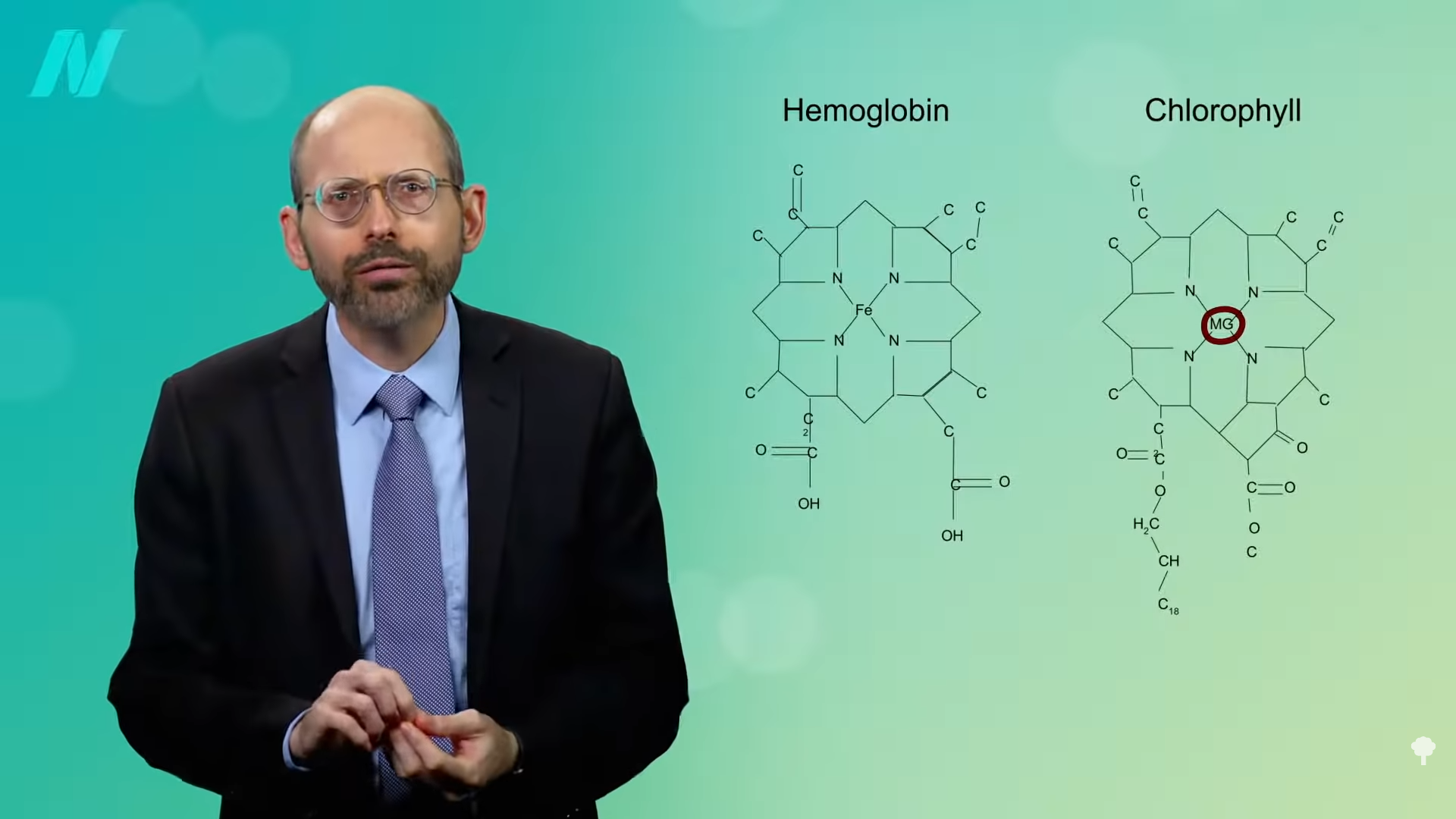
Green vegetables also have magnesium. Found throughout the food supply but most concentrated in green leafy vegetables, beans, nuts, seeds, and whole grains, magnesium is the central atom to chlorophyll, as shown below and at 3:15. So, you can see how much magnesium foods have in the produce aisle by the intensity of their green color. Although magnesium supplements do not appear to decrease migraine severity, they may reduce the number of attacks you get in the first place. You can ask your doctor about starting 600 mg of magnesium dicitrate every day, but note that magnesium supplements can cause adverse effects, such as diarrhea, so I recommend getting it the way nature intended—in the form of real food, not supplements.
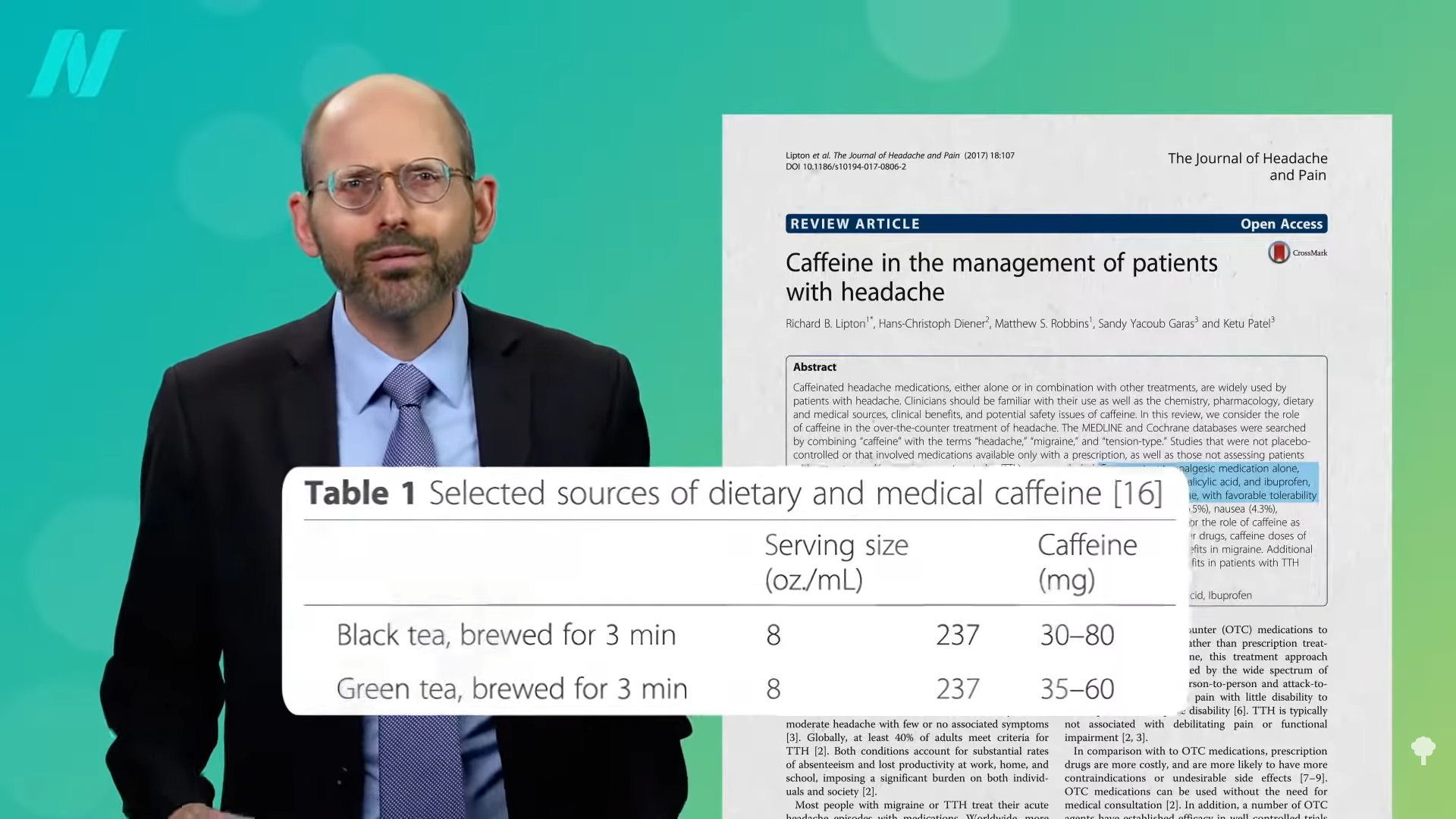
Any foods that may be particularly helpful? You may recall that I’ve talked about ground ginger. What about caffeine? Indeed, combining caffeine with over-the-counter painkillers, like Tylenol, aspirin, or ibuprofen, may boost their efficacy, at doses of about 130 mg for tension-type headaches and 100 mg for migraines. That’s about what you might expect to get in three cups of tea, as you can see below, and at 4:00 in my video. (I believe it is just a coincidence that the principal investigator of this study was named Lipton.)
Please note that you can overdo it. If you take kids and teens with headaches who were drinking 1.5 liters of cola a day and cut the soda, you can cure 90 percent of them. However, this may be a cola effect rather than a caffeine effect.
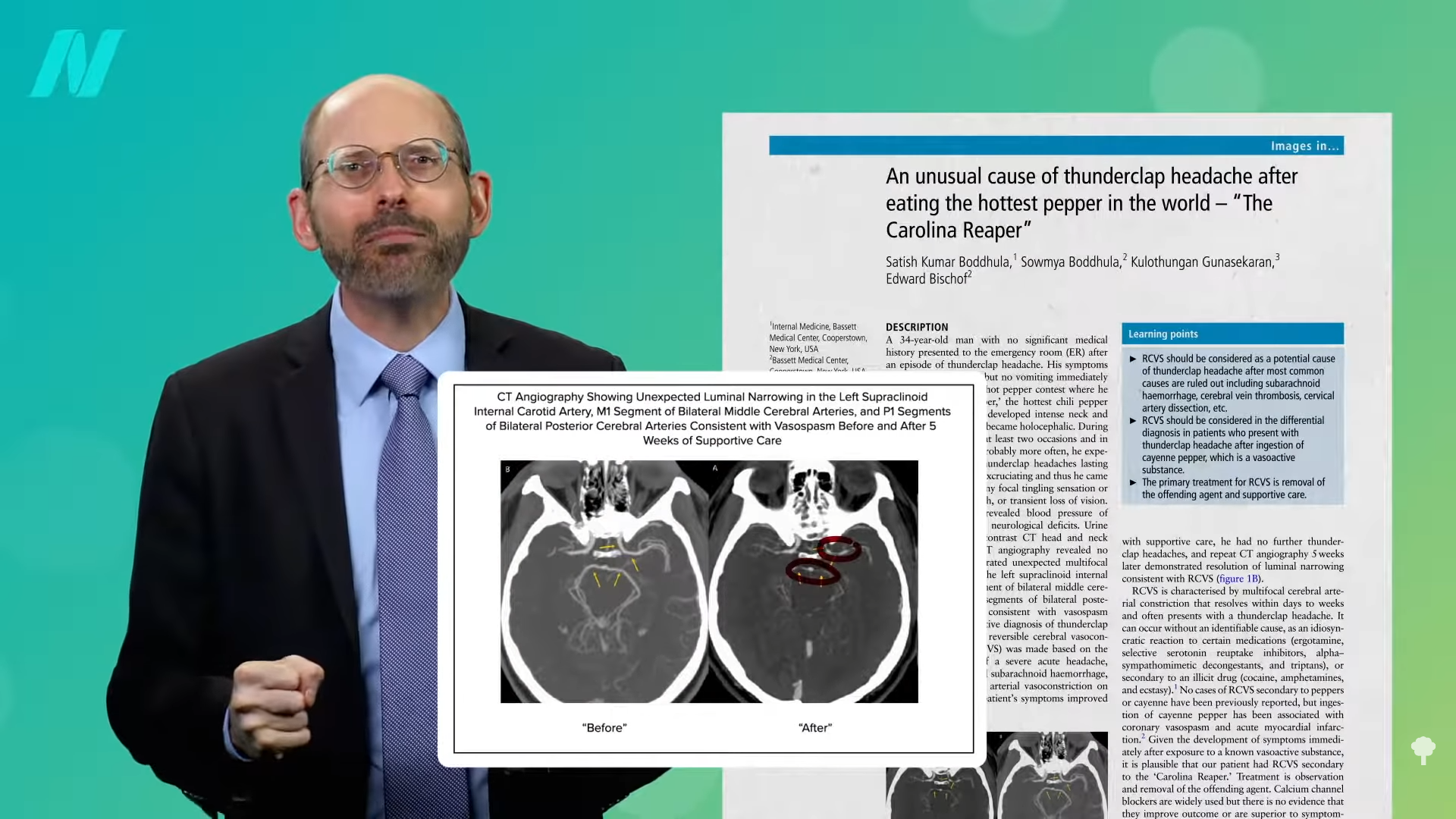
And, finally, one plant food that may not be the best idea is the Carolina Reaper, the hottest chili pepper in the world. It’s so mind-numbingly hot it can clamp off the arteries in your brain, as seen below and at 4:41 in my video, and you can end up with a “thunderclap headache,” like the 34-year-old man who ate the world’s hottest pepper and ended up in the emergency room. Why am I not surprised it was a man?
I’ve previously covered ginger and topical lavender for migraines. Saffron may help relieve PMS symptoms, including headaches. A more exotic way a plant-based diet can prevent headaches is by helping to keep tapeworms out of your brain.
Though hot peppers can indeed trigger headaches, they may also be used to treat them. Check out my video on relieving cluster headaches with hot sauce.
