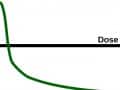
Xenohormesis: What Doesn’t Kill Plants May Make Us Stronger
A new concept in biology tries to explain why the consumption of certain natural compounds in plants may mimic the lifespan-enhancing benefits of caloric restriction.

A new concept in biology tries to explain why the consumption of certain natural compounds in plants may mimic the lifespan-enhancing benefits of caloric restriction.

Plants and animals share similar biochemical pathways and signaling systems, which may explain why so many phytonutrients are beneficial to our physiology.

The relationship between fish consumption and diabetes risk may be due to toxic pollutants that build up in the aquatic food chain.

Whole fruits and vegetables were compared to both antioxidant pills, as well as supplements containing fruits and vegetable extracts, for their ability to treat seasonal allergies, improve lung function, and control asthma.

Increasing fruit and vegetable consumption to seven servings a day appears to cut asthma exacerbation rates in half, whereas restricting consumption to Standard American Diet levels leads to a significant worsening of lung function and asthma control.

A study involving more than a million kids suggests the striking worldwide variation in childhood rates of allergies, asthma, and eczema is related to diet.

Unlike most other anticancer agents, the phytates naturally found in whole plant foods may trigger cancer cell differentiation, causing them to revert back to behaving more like normal cells.

Phytic acid (phytate), concentrated in food such as beans, whole grains, and nuts, may help explain lower cancer rates among plant-based populations.

Less than a teaspoon a day of turmeric appears to significantly lower the DNA-mutating ability of cancer-causing substances.

Dramatically lower cancer rates in India may in part be attributable to their more plant-based, spice-rich diet.

The consumption of blueberries and strawberries is associated with delayed cognitive aging by as much as 2.5 years—thought to be because of brain-localizing anthocyanin phytonutrients, as shown on functional MRI scans.

The oxidation of high-fat and cholesterol-rich foods in our stomachs may help explain why eating antioxidant packed foods appears to reduce heart attack and stroke risk.

Antioxidant intake from foods (not supplements) is associated with lower cancer risk.
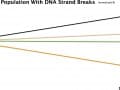
The DNA of those cooking with spices such as ginger, rosemary, and turmeric appears less susceptible to breakage.

An elegant experiment is described in which the blood of those eating different types of spices—such as cloves, ginger, rosemary, and turmeric—is tested for anti-inflammatory capacity.
Kale and collard greens contain vision-protecting plant nutrients, such as zeaxanthin, that may significantly lower the risk of glaucoma—a leading cause of blindness.

To stay out of oxidative debt, we need to take in more antioxidants than we use up.
Even nine servings of fruits and vegetables a day may not reach the minimum recommended intake of antioxidants if one doesn’t make the right choices.
How many antioxidant-rich foods do we need to eat every day just to stay out of oxidative debt?

Might the antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties of plant-based diets undermine some of the benefits of exercise?

Men eating pistachio nuts experienced a significant improvement in blood flow through the penis accompanied by significantly firmer erections in just three weeks—perhaps due to pistachios’ antioxidant, arginine, and phytosterol content.

Since both coronary heart disease and impotence can be reversed with a healthy diet, sexual dysfunction can be used as a motivator to change poor lifestyle habits.

Those eating a more plant-based diet may naturally have an enhanced antioxidant defense system to counter the DNA damage caused by free radicals produced by high-intensity exercise.

Two kiwi fruit an hour before bedtime may improve sleep quality and duration, without the side effects associated with sleeping pills.
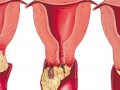
Most young women get infected with human papilloma virus, the cause of cervical cancer, but most are able to clear the infection before the virus causes cancer. What dietary changes can improve viral clearance?

Dioxins, endocrine disrupting pollutants, heavy metals, saturated fat, and steroids in the meat supply may be affecting sperm counts, semen quality, and the ability of men to conceive.

A component of cooked ginger root protects human white blood cells in vitro against radiation-induced genetic damage, and lemon balm tea appears to protect radiology staff against radiation-induced oxidative stress.

Based on studies of atomic bomb survivors, Chernobyl victims, and airline pilots exposed to more cosmic rays at high altitudes, it appears that fruits and vegetables may decrease radiation-induced chromosome damage.

Black raspberries may cause complete clinical regression of precancerous oral lesions (oral intraepithelial neoplasia).
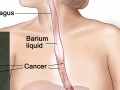
A randomized phase II clinical trial on the ability of strawberries to reverse the progression to esophageal cancer.

Drug companies and supplement manufacturers have yet to isolate the components of cranberries that suppress cancer cell growth.

The ability of eleven common fruits to suppress cancer cell growth in vitro was compared. Which was most effective—apples, bananas, cranberries, grapefruits, grapes, lemons, oranges, peaches, pears, pineapples, or strawberries?

Cinnamon can no longer be considered a safe and effective treatment for diabetes.
A daily tablespoon of ground flax seeds for a month appears to improve fasting blood sugars, triglycerides, cholesterol, and hemoglobin A1c levels in diabetics.

Hibiscus tea elevates the antioxidant level of one’s bloodstream within an hour of consumption.

Plant-based diets in general, and certain plant foods in particular, may be used to successfully treat Parkinson’s disease—in part, by boosting L-DOPA levels.

An independent review of the effects of açaí berries was recently published, including studies on immune function, arthritis, and metabolic parameters.

Plant-based diets may be effective for the treatment of fibromyalgia, a painful condition suffered by millions.

Why the spike in antioxidant levels in our bloodstream after drinking apple juice might not be a good thing.

Human beings lost the ability to detoxify uric acid millions of years ago. What implications does this have for our health today?