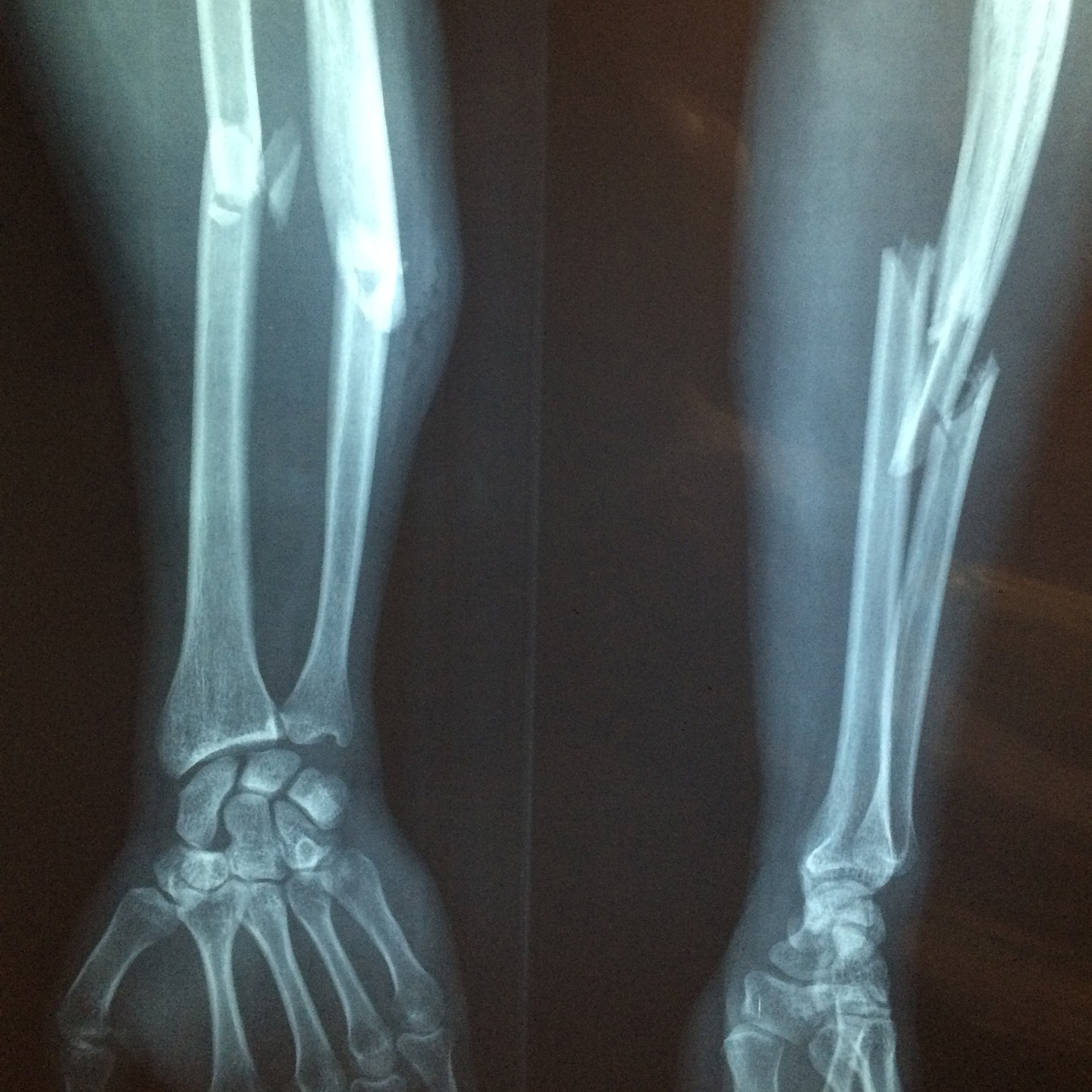
Bone Fractures
Bone Density
Bone mineral density screening is a billion-dollar industry, so it shouldn’t be that surprising that it is the focus of osteoporosis and treatment. Literally meaning porous bone, osteoporosis is characterized by reduced bone formation, excessive bone loss, or a combination of both, which leads to bone fragility and contributes to millions of fractures a year. Overall, the disease is estimated to affect 200 million people worldwide.
But, among women 65 and older, only 15 percent of low trauma fractures (meaning from a fall from no more than standing height) are due to osteoporosis. Between the ages of 60 and 80, hip fracture risk increases thirteenfold in men and women, whereas the age-related decline in bone mineral density accounted only for a twofold increased risk. So, 85 percent of the age-related rise in hip fracture risk has nothing to do with the measured density of your bones.
Fall Prevention
The primary cause of fractures—including vertebral fractures—are falls. The disparity between men and women in hip fracture rates seems primarily not because men have stronger bones but because women fall more often. Even a weak osteoporotic bone is strong enough to survive normal life activities without the excessive loading that comes from the impact of a fall or, in the case of the spine, bending with your back rather than your knees to lift something.
A number of associations have been made between increased fracture rates or weaker bones and intake of stomach acid–blocking “proton pump inhibitor” (PPI) drugs (with brand names like Prilosec, Prevacid, and Nexium), cigarette smoking, heavy cannabis use, and calcium supplementation, and consuming dairy milk products. However, the single most important thing we can do to prevent osteoporotic fractures is prevent injurious falls. And, based on dozens of randomized controlled trials, exercise is the single intervention most strongly associated with a reduction in falls rate. A recent meta-analysis found that exercise interventions—ones mostly using a combination of resistance exercise to improve lower limb muscle strength training and balance training—cut fracture rates nearly in half.
For substantiation of any statements of fact from the peer-reviewed medical literature, please see the associated videos below.
Image Credit: Manuel González Reyes / Pixabay. This image has been modified.
Popular Videos for Bone Fractures


Do Vitamin B12 Supplements Cause Bone Fractures and Lung Cancer?
What do randomized controlled trials of high-dose daily vitamin B12 supplementation show about the effects...
Vitamin D May Explain Higher Bone Fracture Risk in Vegans
A combination of low calcium intake and low vitamin D exposure may explain higher bone...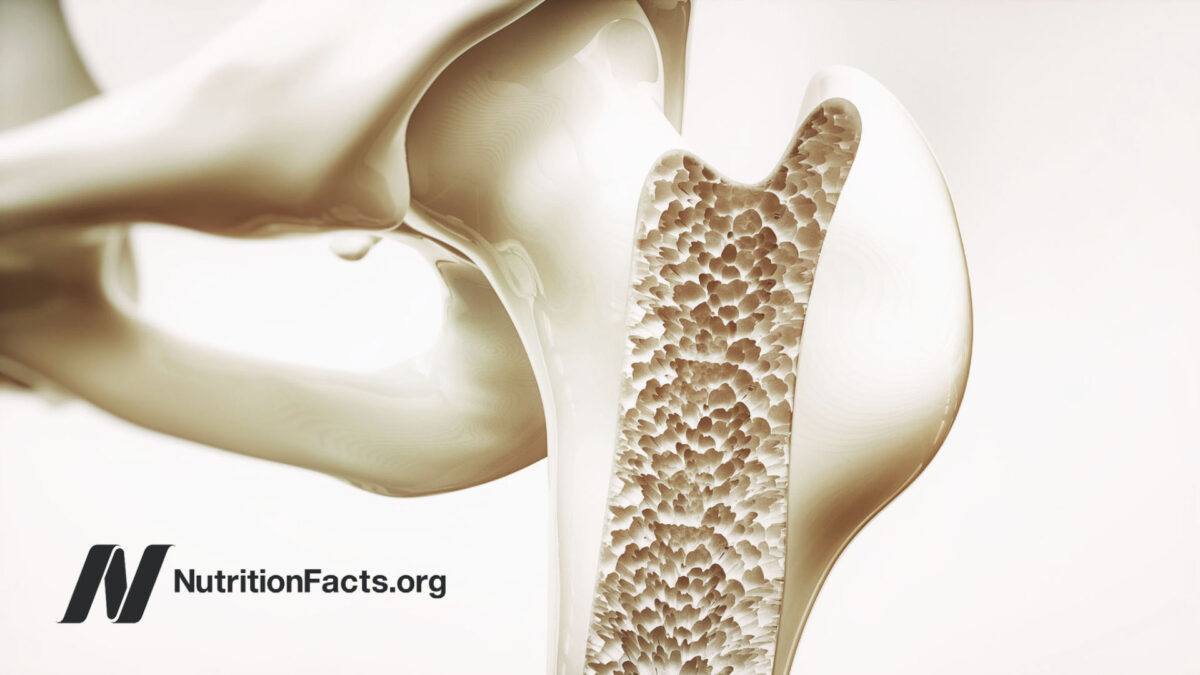
Do Vegans Have Lower Bone Density and More Fractures?
What are the bone fracture rates of omnivores vs. vegetarians vs. vegans?
Effects of Marijuana on Weight Gain and Bone Density
Are the apparent adverse effects of heavy cannabis use on bone just due to users...
Are Calcium Supplements Effective?
What is the optimal daily dietary calcium intake and might benefits for your bones outweigh...
Is Milk Good for Our Bones?
The galactose in milk may explain why milk consumption is associated with significantly higher risk...All Videos for Bone Fractures
-
Comparing the Benefits and Side Effects of Ozempic (Semaglutide)
Obesity can be so devastating to our health that the downsides of any effective drug would have to be significant to outweigh its weight-loss benefits.
-

The Best Exercise Type and Frequency for Bone Density
When it comes to bone health, it’s use it or lose it.
-

Onions and Tomatoes Put to the Test for Osteoporosis
Beyond the antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and alkaline-forming qualities of fruits and vegetables in general, are there extra benefits our bones can get from particular produce?
-

Three Reasons Fruits and Vegetables May Reduce Osteoporosis Risk
Even just a single extra serving of fruits and vegetables per day is associated with lower bone fracture risk.
-
Side Effects of Osteoporosis Medications Like Fosamax, Boniva, and Reclast
How rare are the bisphosphonate class of osteoporosis drugs’ devastating side effects, which ironically include bone fractures?
-
How Well Do Medicines Like Fosamax Work to Treat Osteoporosis?
Doctors and patients alike vastly overestimate the power of bisphosphonate drugs to prevent fractures.
-
Acid Reflux Medicine May Cause Osteoporosis
Stomach acid–blocking proton pump inhibitor drugs—PPIs with brand names like Prilosec, Prevacid, Nexium, Protonix, and AcipHex—appear to significantly increase the risk of bone fractures.
-

How Not To Age – Live Presentation
In this live lecture, Dr. Greger offers a sneak peek into his latest book, How Not to Age, a New York Times Best Seller.
-

Fall Prevention Is the Most Important Thing for Preventing Osteoporosis Bone Fractures
A combination of resistance exercise to improve lower limb muscle strength and balance training can beat out drugs for preventing osteoporotic bone fractures.
-

Vitamin D May Explain Higher Bone Fracture Risk in Vegans
A combination of low calcium intake and low vitamin D exposure may explain higher bone fracture rates in British vegans.
-
Do Vegans Have Lower Bone Density and More Fractures?
What are the bone fracture rates of omnivores vs. vegetarians vs. vegans?
-
Do Vegans Have Lower Bone Mineral Density and Higher Risk of Osteoporosis?
Those eating plant-based tend to be so much slimmer that their bone mass may suffer.
-

Do Vitamin B12 Supplements Cause Bone Fractures and Lung Cancer?
What do randomized controlled trials of high-dose daily vitamin B12 supplementation show about the effects on cancer risk, death, and longevity?
-

Effects of Marijuana on Weight Gain and Bone Density
Are the apparent adverse effects of heavy cannabis use on bone just due to users being skinnier?
-

Potential Pitfalls of Calorie Restriction
How to preserve bone and mass on a low calorie diet.
-

Keto Diets: Muscle Growth and Bone Density
Ketogenic diets found to undermine exercise efforts and lead to muscle shrinkage and bone loss.
-

Are Acid-Blocking Drugs Safe?
Do the benefits outweigh the risks for acid-blocker drugs (proton pump inhibitors like Nexium/Prilosec/Prevacid)? What about baking soda?
-

Pros and Cons of Gluten-Free, Casein-Free Diets for Autism
What did the most comprehensive double-blind study of diet for autism find, and what are the potential downsides?
-

Should Vitamin D Supplements Be Taken to Prevent Falls in the Elderly?
A daily dose of 4,000 IU of vitamin D is recommended for elders at high risk for falling to improve muscle strength and balance, though there is something that works even better.
-

Who Shouldn’t Eat Soy?
How can soy foods have it both ways with pro-estrogenic effects in some organs that can protect bones and reduce hot flash symptoms, yet also anti-estrogenic effects in others that protect against breast and endometrial cancer?
-

Could Lactose Explain the Milk and Parkinson’s Disease Link?
Neurotoxin contamination of the dairy supply doesn’t explain why the association between Parkinson’s and skim milk consumption is as strong as the disease’s association with whole milk.
-

HOW NOT TO DIE: The Role of Diet in Preventing, Arresting, & Reversing Our Top 15 Killers
In this “best-of” compilation of his last four year-in-review presentations, Dr. Greger explains what we can do about the #1 cause of death and disability: our diet.
-
Prunes for Osteoporosis
Vegetables and fruit, such as dried plums, may help build stronger bones.
-
The Risks and Benefits of Sensible Sun Exposure
We don’t have to choose between the lesser of two evils: skin cancer versus internal cancers from vitamin D deficiency.
-
Almonds for Osteoporosis
What happens when you take blood from people before and then again four hours after almond consumption, and drip that blood on bone cells?
-

When Drugs and Diets Don’t Lower Diabetes Deaths
Why do some drug-based strategies shorten the lives of diabetics and some diet-based strategies fail to decrease diabetes deaths?
-

Are Calcium Supplements Effective?
What is the optimal daily dietary calcium intake and might benefits for your bones outweigh the risks to your heart from taking calcium supplements?
-

Are Calcium Supplements Safe?
The unnaturally large, rapid, and sustained calcium levels in the blood caused by calcium supplements may explain why calcium from supplements, but not from food, appears to increase the risk of heart attacks.
-

Coffee and Mortality
What effect does coffee and tea consumption have on longevity, cancer risk, GERD reflux, bone fractures, glaucoma, sleep quality, and atrial fibrillation (irregular heartbeat)?
-

Food as Medicine: Preventing and Treating the Most Dreaded Diseases with Diet
Dr. Greger has scoured the world’s scholarly literature on clinical nutrition and developed this new presentation based on the latest in cutting edge research exploring the role diet may play in preventing, arresting, and even reversing some of our most feared causes of death and disability.
-

Diet and GERD Acid Reflux Heartburn
Which foods should we eat and avoid to prevent and treat acid reflux before it can place us at risk for Barrett’s esophagus and cancer?
-

Is Milk Good for Our Bones?
The galactose in milk may explain why milk consumption is associated with significantly higher risk of hip fractures, cancer, and premature death.
-

The Actual Benefit of Diet vs. Drugs
The medical profession oversells the benefits of drugs for chronic disease since so few patients would apparently take them if doctors divulged the truth.
-

Who Says Eggs Aren’t Healthy or Safe?
Freedom of Information Act documents reveal that the U.S. Department of Agriculture warned the egg industry that saying eggs are nutritious or safe may violate rules against false and misleading advertising.
-

Phytates for the Prevention of Osteoporosis
Women who consume the most high-phytate foods (whole grains, beans, and nuts) appear to have better bone density.
-

Phosphate Additives in Meat Purge and Cola
The consumption of phosphorus preservatives in junk food, and injected into meat, may damage blood vessels, accelerate the aging process, and contribute to osteoporosis.
-
Alkaline Diets, Animal Protein, and Calcium Loss
The decades-old dogma that the acid-forming quality of animal protein leads to bone loss has been called into question.