Osteoporosis
For substantiation of any statements of fact from the peer-reviewed medical literature, please see the associated videos below.
Popular Videos for Osteoporosis

Side Effects of Osteoporosis Medications Like Fosamax, Boniva, and Reclast
How rare are the bisphosphonate class of osteoporosis drugs’ devastating side effects, which ironically include...
How Well Do Medicines Like Fosamax Work to Treat Osteoporosis?
Doctors and patients alike vastly overestimate the power of bisphosphonate drugs to prevent fractures.
Acid Reflux Medicine May Cause Osteoporosis
Stomach acid–blocking proton pump inhibitor drugs—PPIs with brand names like Prilosec, Prevacid, Nexium, Protonix, and...
Fall Prevention Is the Most Important Thing for Preventing Osteoporosis Bone Fractures
A combination of resistance exercise to improve lower limb muscle strength and balance training can...
Are Calcium Supplements Safe?
The unnaturally large, rapid, and sustained calcium levels in the blood caused by calcium supplements...
Are Calcium Supplements Effective?
What is the optimal daily dietary calcium intake and might benefits for your bones outweigh...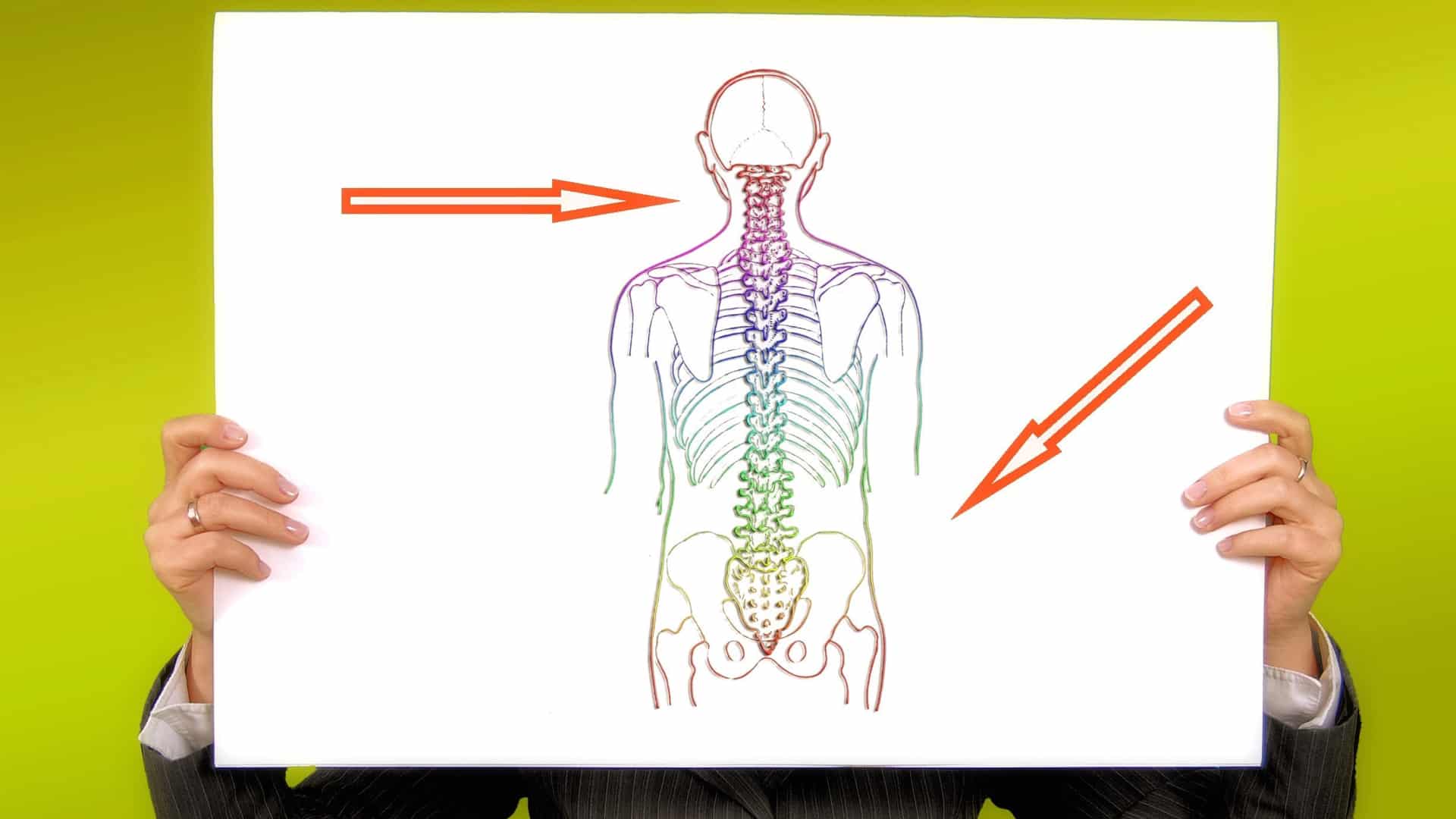
Prunes for Osteoporosis
Vegetables and fruit, such as dried plums, may help build stronger bones.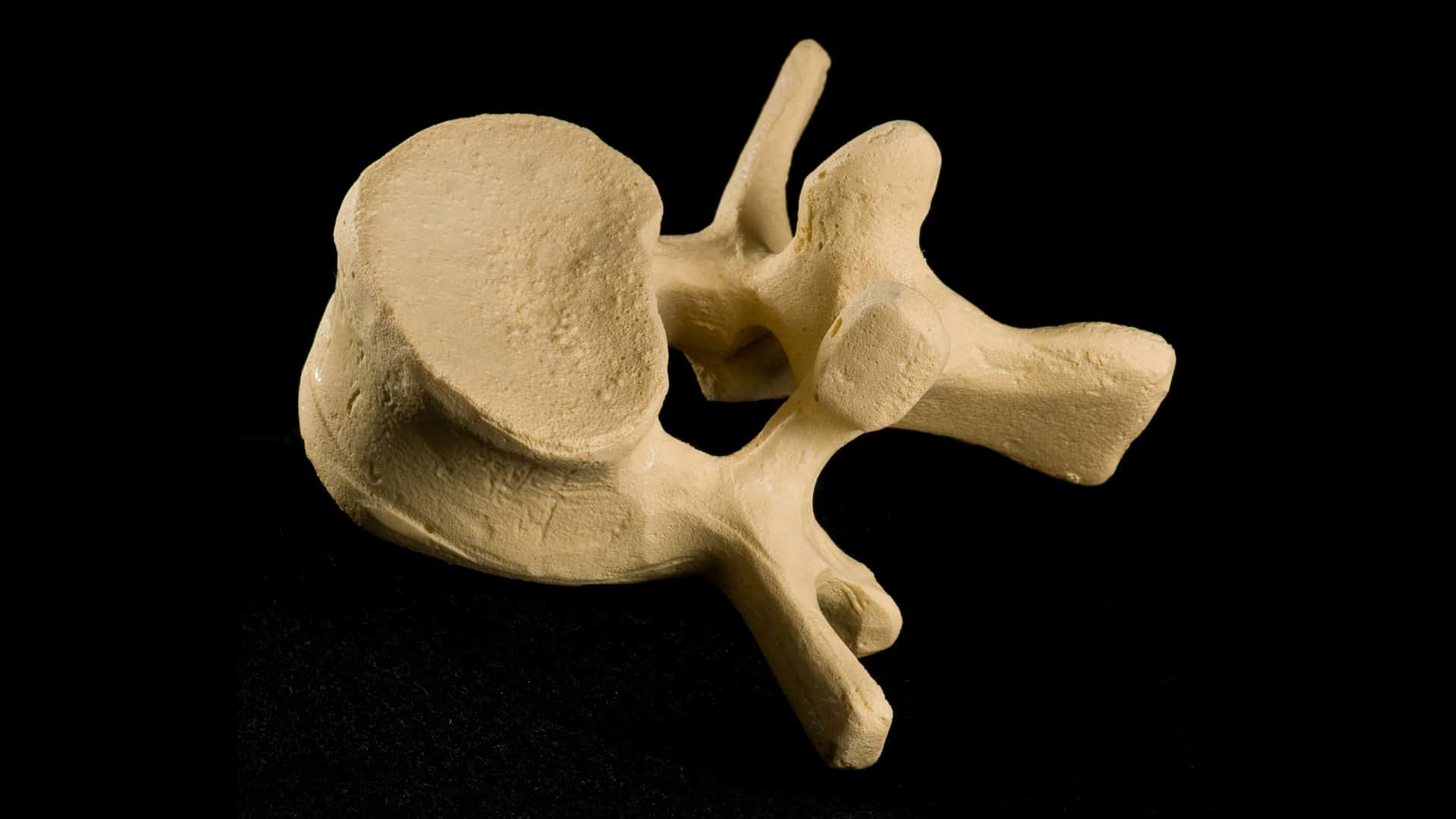
Almonds for Osteoporosis
What happens when you take blood from people before and then again four hours after...
Is Milk Good for Our Bones?
The galactose in milk may explain why milk consumption is associated with significantly higher risk...
Phytates for the Prevention of Osteoporosis
Women who consume the most high-phytate foods (whole grains, beans, and nuts) appear to have...
Are Onions Beneficial for Testosterone, Osteoporosis, Allergies, and Cancer?
What did randomized controlled human trials find about the ways we may—or may not—benefit from...
Fall Prevention Is the Most Important Thing for Preventing Osteoporosis Bone Fractures
A combination of resistance exercise to improve lower limb muscle strength and balance training can...
Yoga Put to the Test for IBS, Inflammatory Bowel, Menopause, and Osteoporosis
A study using sham acupuncture underscores the necessity of controlling for expectancy effects.All Videos for Osteoporosis
-

Pros and Cons of Raw Food Diets
Is there an advantage to eating a raw plant-based diet over a diet of raw and cooked whole plant foods?
-

The Best Exercise Type and Frequency for Bone Density
When it comes to bone health, it’s use it or lose it.
-

Resveratrol Tested for Alzheimer’s, Arthritis, and Osteoporosis
Resveratrol appears to triple the rate of age-related brain shrinkage.
-

Onions and Tomatoes Put to the Test for Osteoporosis
Beyond the antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and alkaline-forming qualities of fruits and vegetables in general, are there extra benefits our bones can get from particular produce?
-

Three Reasons Fruits and Vegetables May Reduce Osteoporosis Risk
Even just a single extra serving of fruits and vegetables per day is associated with lower bone fracture risk.
-
Side Effects of Osteoporosis Medications Like Fosamax, Boniva, and Reclast
How rare are the bisphosphonate class of osteoporosis drugs’ devastating side effects, which ironically include bone fractures?
-

Why Do Milk Drinkers Live Shorter Lives on Average?
How might we reduce the risk of premature death from dairy consumption?
-
How Well Do Medicines Like Fosamax Work to Treat Osteoporosis?
Doctors and patients alike vastly overestimate the power of bisphosphonate drugs to prevent fractures.
-

Preventing and Treating Osteoporosis (Webinar Recording)
I’m happy to share the recording of my webinar on osteoporosis, which includes 11 videos and a Q&A.
-
Acid Reflux Medicine May Cause Osteoporosis
Stomach acid–blocking proton pump inhibitor drugs—PPIs with brand names like Prilosec, Prevacid, Nexium, Protonix, and AcipHex—appear to significantly increase the risk of bone fractures.
-

Fall Prevention Is the Most Important Thing for Preventing Osteoporosis Bone Fractures
A combination of resistance exercise to improve lower limb muscle strength and balance training can beat out drugs for preventing osteoporotic bone fractures.
-

The Side Effects of Yoga
What is the rate of yoga injuries compared to other activities?
-

Yoga Put to the Test for IBS, Inflammatory Bowel, Menopause, and Osteoporosis
A study using sham acupuncture underscores the necessity of controlling for expectancy effects.
-

Vitamin D May Explain Higher Bone Fracture Risk in Vegans
A combination of low calcium intake and low vitamin D exposure may explain higher bone fracture rates in British vegans.
-
Do Vegans Have Lower Bone Density and More Fractures?
What are the bone fracture rates of omnivores vs. vegetarians vs. vegans?
-

The Purported Benefits of Vitamin K2: Should You Take Supplements?
Our body can make vitamin K2 from the K1 in green leafy vegetables.
-
Do Vegans Have Lower Bone Mineral Density and Higher Risk of Osteoporosis?
Those eating plant-based tend to be so much slimmer that their bone mass may suffer.
-

Are Onions Beneficial for Testosterone, Osteoporosis, Allergies, and Cancer?
What did randomized controlled human trials find about the ways we may—or may not—benefit from eating onions?
-

The Complications of Bariatric Weight-Loss Surgery
The extent of risk from bariatric weight-loss surgery may depend on the skill of the surgeon.
-

Effects of Marijuana on Weight Gain and Bone Density
Are the apparent adverse effects of heavy cannabis use on bone just due to users being skinnier?
-

Potential Pitfalls of Calorie Restriction
How to preserve bone and mass on a low calorie diet.
-

Keto Diets: Muscle Growth and Bone Density
Ketogenic diets found to undermine exercise efforts and lead to muscle shrinkage and bone loss.
-

The Rise in Blood Lead Levels at Pregnancy and Menopause
The lead trapped in our skeleton can leach back into our bloodstream when we temporarily or permanently lose bone due to pregnancy, weight loss, menopause, or osteoporosis.
-

What Are the Effects of the Hops Phytoestrogen in Beer?
When it comes to breast cancer risk, does the phytoestrogen in beer act more like the animal estrogens in Premarin or the protective phytoestrogens in soy?
-
Prunes for Osteoporosis
Vegetables and fruit, such as dried plums, may help build stronger bones.
-
Reductionism and the Deficiency Mentality
How the food, drug, and supplement industries have taken advantage of the field of nutrition’s reductionist mindset
-
Almonds for Osteoporosis
What happens when you take blood from people before and then again four hours after almond consumption, and drip that blood on bone cells?
-

Are Calcium Supplements Effective?
What is the optimal daily dietary calcium intake and might benefits for your bones outweigh the risks to your heart from taking calcium supplements?
-

Are Calcium Supplements Safe?
The unnaturally large, rapid, and sustained calcium levels in the blood caused by calcium supplements may explain why calcium from supplements, but not from food, appears to increase the risk of heart attacks.
-

What Are the Healthiest Foods?
Based on the Dietary Guidelines for Americans, which foods best supply shortfall nutrients while avoiding disease-promoting components?
-

Is Milk Good for Our Bones?
The galactose in milk may explain why milk consumption is associated with significantly higher risk of hip fractures, cancer, and premature death.
-

Beans, Beans, They’re Good for Your Heart
Legumes such as lentils, chickpeas, beans and split peas may reduce cholesterol so much that consumers may be able to get off their cholesterol-lowering statin drugs, but to profoundly alter heart disease risk we may have to more profoundly alter our diet.
-

Longer Life Within Walking Distance
Researchers find exercise often works just as well as drugs for the treatment of heart disease and stroke, and the prevention of diabetes. Exercise is medicine.
-

Phytates for the Treatment of Cancer
Do the anticancer effects of phytates in a petri dish translate out into clinical studies on cancer prevention and treatment?
-

Phytates for the Prevention of Osteoporosis
Women who consume the most high-phytate foods (whole grains, beans, and nuts) appear to have better bone density.
-

Phosphate Additives in Meat Purge and Cola
The consumption of phosphorus preservatives in junk food, and injected into meat, may damage blood vessels, accelerate the aging process, and contribute to osteoporosis.
-
Alkaline Diets, Animal Protein, and Calcium Loss
The decades-old dogma that the acid-forming quality of animal protein leads to bone loss has been called into question.
-

Chamomile Tea May Not Be Safe During Pregnancy
For the same reason aspirin should be avoided in pregnancy, chamomile has such powerful anti-inflammatory properties that regular consumption may result in a serious fetal heart problem—premature constriction of the fetal ductus arteriosus, which allows the fetus to “breathe” in the womb.
-

Glycotoxins
Advanced glycation end products (AGEs) in our diet are thought to accelerate the aging process.
-

Calcium Absorption: Soy Milk Versus Cow Milk
Soy milk should be shaken before pouring to get at the calcium that settles to the bottom.