Survival of the Firmest: Erectile Dysfunction and Death
Because penile arteries are only about half the size of the coronary arteries in the heart, erectile dysfunction can be a powerful predictor of cardiac events—such as sudden death.

Because penile arteries are only about half the size of the coronary arteries in the heart, erectile dysfunction can be a powerful predictor of cardiac events—such as sudden death.

Those eating a more plant-based diet may naturally have an enhanced antioxidant defense system to counter the DNA damage caused by free radicals produced by high-intensity exercise.

Two kiwi fruit an hour before bedtime may improve sleep quality and duration, without the side effects associated with sleeping pills.

Nearly 5,000 breast cancer deaths a year may be attributable to just light drinking (up to one drink a day).

The story behind the first U.S. dietary recommendations report explains why, to this day, the decades of science supporting a more plant-based diet have yet to fully translate into public policy.

Lignan intake is associated with improved breast cancer survival in three recent population studies following a total of thousands of women after diagnosis.
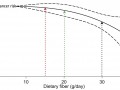
Inadequate fiber intake appears to be a risk factor for breast cancer, which can explain why women eating plant-based diets may be at lower risk.

A similar exponential increase in carotid artery plaque buildup was found for smokers and egg eaters.

The early onset of puberty in girls associated with animal protein consumption may be due to endocrine-disrupting chemical pollutants in the meat supply.

Vitamin D3—sourced from sunlight exposure, animal, and plant sources—may be preferable to vitamin D2 sourced from fungi.

Prolonged daily sitting is associated with a shorter lifespan, even in those who exercise regularly. Standing and treadmill desks are two potential solutions for office workers.

Congenital IGF-1 deficiency can lead to Laron Syndrome (a type of dwarfism); but with such low growth hormone levels, those with the condition have dramatically lower cancer rates. This raises the question of whether one can achieve the best of both worlds—by ensuring adequate IGF-1 levels during childhood, while then suppressing excess growth promotion in adulthood.

Insulin-like growth factor (IGF-1) is a natural human growth hormone instrumental in normal growth during childhood, but in adulthood can promote abnormal growth—the proliferation, spread (metastasis), and invasion of cancer.

Death in America is largely a foodborne illness. Focusing on studies published just over the last year in peer-reviewed scientific medical journals, Dr. Greger offers practical advice on how best to feed ourselves and our families to prevent, treat, and even reverse many of the top 15 killers in the United States.

One mechanism by which caloric restriction may extend one’s lifespan is by upregulating dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA), the most abundant steroid hormone in the human body. DHEA supplements are discouraged, but there may be a natural way to conserve levels as we age.

Though our life expectancy is improving, our health expectancy is not. In fact we are living fewer years without serious disease and disability.

A competing risks analysis of the Harvard Nurses’ Health Study compares the danger of smoking cigarettes to the danger of animal product consumption (cholesterol), and the benefits of plant foods (fiber) to the benefits of exercise.
Given how vascular our kidneys are, it should comes as no surprise that animal protein, animal fat, and cholesterol are associated with declining kidney function (microalbuminurea—loss of protein in the urine), which can be an early warning sign not only for kidney failure, but also for heart disease and a shortened lifespan.

Inadequate fruit and vegetable intake may help explain the loss of immune function associated with aging that is linked to an increased risk of dying from pneumonia and influenza.

The consumption of dark fish (such as salmon, swordfish, bluefish, mackerel, and sardines) may increase our risk of atrial fibrillation—an irregular heartbeat rhythm associated with stroke, dementia, heart failure, and a shortened lifespan.

Monday, March 12, 2012: The Harvard Health Professionals Follow-up Study and the Harvard Nurses’ Health Study concluded that red meat consumption was associated with living a significantly shorter life—increased cancer mortality, increased heart disease mortality, and increased overall mortality.

Harvard study found that men and women eating low carb diets live significantly shorter lives, but what about the “eco-Atkins diet,” a plant-based, low carbohydrate diet?

Why the current vitamin D recommendations may be too low, other expert recommendations may be too high, and 2000 international units a day may be just right.

People respond differently to the same level of vitamin D supplementation, making it difficult to formulate one-size-fits-all guidelines.

To reach the circulating (25-hydroxy) vitamin D levels associated with the lowest overall mortality, one may need to take supplements, given data suggesting suboptimal production from sun—even under optimal circumstances.

Vitamin D deficiency may shorten one’s lifespan, but getting too much vitamin D may also adversely affect longevity.

The Institute of Medicine’s conservative position on vitamin D is understandable, given the history of hyped vitamin supplements (vitamin A, beta carotene, folic acid, vitamin C, vitamin E) that turned out worthless—or worse.
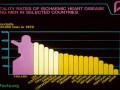
The success story in Finland shows that science-based dietary guidelines can save millions of lives.

Why does the medical establishment sometimes ignore highly efficacious therapies, such as plant-based diets, for heart disease prevention and treatment?
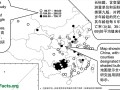
The China-Oxford-Cornell Diet and Health Project directed by T. Colin Campbell and colleagues showed that chronic diseases, such as heart disease, are not inevitable consequences of aging.

Dr. Dean Ornish proved decades ago that heart disease could be reversed solely with diet and lifestyle changes.

Medicare is now accepting for reimbursement the Dean Ornish Program for Reversing Heart Disease and the Pritikin Program, which, on a personal note, is what inspired me to go into medicine.

In a double-blind study, the spice saffron beat out placebo in the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease dementia symptoms.

Researchers discovered a dietary intervention that may slow the progression of cancer.