
How Much Does Chemotherapy Improve Survival?
If you put together all of the new chemo drugs that had been approved over a dozen years, the average overall survival benefit is only 2.1 months.

If you put together all of the new chemo drugs that had been approved over a dozen years, the average overall survival benefit is only 2.1 months.

The Mayo Clinic puts amygdalin to the test to see if it is an effective cancer treatment.

Shark cartilage supplements carry risks, but so do many cancer treatments. The question is, do they work?
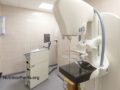
Various health organizations offer clashing mammogram recommendations that range from annual mammograms starting at age 40 to eliminating routine mammograms altogether. Who should you trust?

Most women are just being told what to do, rather than being given the facts needed to make a fully informed decision.

Polyomaviruses discovered in meat can survive cooking and pasteurization.

Shaving before applying underarm antiperspirants can increase aluminum absorption. Could this explain the greater number of tumors and the disproportionate incidence of breast cancer in the upper outer quadrant of the breast near the armpit?
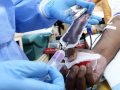
An extraordinary thing happened when those at high risk for heart disease were randomized to give blood—and it had nothing to do with their heart.

Perhaps dietary guidelines should stress fresh, frozen, and dried fruit—rather than canned.

If studies from the 1970s showed cancer patients treated with vitamin C lived 4 times longer and sometimes even 20 times longer, why isn’t it standard practice today?
Studies in the 1970s with terminal cancer patients appeared to show an extraordinary survival gain with vitamin C, a simple and relatively nontoxic therapy.

The movement to remove fast food operations from hospitals parallels the successful movement in the 80s to bar hospital tobacco sales.

Do the anticancer effects of phytates in a petri dish translate out into clinical studies on cancer prevention and treatment?

Less than a teaspoon a day of turmeric appears to significantly lower the DNA-mutating ability of cancer-causing substances.
Two theories about the buildup of subcutaneous fat, involving the chemical spermine and the hormone adiponectin, suggest a plant-based diet may help with cellulite.

Young women at high risk for breast cancer given just a teaspoon of ground flax seeds a day showed fewer precancerous changes.
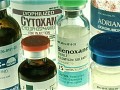
For decades, studies on Gerson therapy for cancer have questioned its safety and efficacy. But, what does the latest head-to-head trial of a Gerson-style regime, versus chemotherapy, show in terms of survival and quality of life for pancreatic cancer ?

The official National Cancer Institute report on the “unacceptable” burden of cancer stemming from industrial chemical pollutants is strongly worded, but lacks sufficient dietary guidance.

Death in America is largely a foodborne illness. Focusing on studies published just over the last year in peer-reviewed scientific medical journals, Dr. Greger offers practical advice on how best to feed ourselves and our families to prevent, treat, and even reverse many of the top 15 killers in the United States.
How meat scientists justify their promotion of foods associated with cancer risk.