
How to Reduce Your TMAO Levels
Should we be concerned about high-choline plant foods, such as broccoli, producing the same toxic TMAO that results from eating high-choline animal foods, such as eggs?

Should we be concerned about high-choline plant foods, such as broccoli, producing the same toxic TMAO that results from eating high-choline animal foods, such as eggs?

Those with certain autoimmune diseases such as Crohn’s disease should probably not eat nutritional yeast.

Do the medium-chain triglycerides in coconut oil and the fiber in flaked coconut counteract the negative effects on cholesterol and artery function?

After the trans fat oil ban, the only remaining major sources of trans fat will be from meat and dairy.

Polyomaviruses discovered in meat can survive cooking and pasteurization.

Whole plant sources of sugar and fat can ameliorate some of the postprandial (after-meal) inflammation caused by the consumption of refined carbohydrates and meat.
Eating meat during breastfeeding is associated with an increased risk of type 1 diabetes, perhaps a consequence of meat glycotoxins or paratuberculosis bacteria that may be passed though breast milk.

What is the baggage that comes along with the nutrients in your food?

As many as 37 percent of human breast cancer cases may be attributable to exposure to bovine leukemia virus.

The majority of U.S. dairy herds are infected with a cancer-causing virus, but until recently, human testing for exposure was not sufficiently sensitive.
Fiber isn’t the only thing our good gut bacteria can eat. Starch can also act as a prebiotic.

What can our nutrient requirements, metabolism, and physiology tell us about what we should be eating?

The highest levels of phthalates, hormone-disrupting plastics chemical pollutants, are found in meats, fats, and dairy.

Might appeals to masculinity and manhood help men with prostate cancer change their diet to improve their survival?

Anti-inflammatory drugs abolish the hyperfiltration and protein leakage response to meat ingestion, suggesting that animal protein causes kidney stress through an inflammatory mechanism.

Dr. Greger has scoured the world’s scholarly literature on clinical nutrition and developed this new presentation based on the latest in cutting edge research exploring the role diet may play in preventing, arresting, and even reversing some of our most feared causes of death and disability.

PBDE fire-retardant chemicals in the food supply may contribute to attention and cognitive deficits in children.

Decreasing animal protein and sodium intake appears more effective in treating calcium oxalate and uric acid kidney stones (nephrolithiasis) than restricting calcium or oxalates.

Heme iron, the type found predominantly in blood and muscle, is absorbed better than the non-heme iron that predominates in plants, but may increase the risk of cancer, stroke, heart disease, and metabolic syndrome.

Which plant and animal foods are associated with the development of multiple myeloma, and what effect might the spice turmeric have on the progression of monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance?
Sulfur dioxide preservatives in dried fruit, sulfites in wine, and the putrefaction of undigested animal protein in the colon can release hydrogen sulfide, the rotten egg gas associated with inflammatory bowel disease.

The negative impact of red meat on our cholesterol profile may be similar to that of white meat.
Advanced glycation end products in our diet may suppress sirtuin enzyme activity and play a role in age-related brain volume loss.

Plant-based diets appear to protect against renal cell carcinoma both directly and indirectly.

The deleterious effects of a Paleolithic diet appear to undermine the positive effects of a Crossfit-based high-intensity circuit training exercise program.

Neurotoxins in chicken, such as the beta-carboline alkaloid harman, may explain the link between meat consumption and hand tremor, the most common movement disorder.
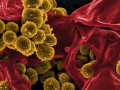
The level of multidrug antibiotic-resistant bacteria contamination is compared between meat from animals raised conventionally, and certified organic meat from animals raised without being fed antibiotics.

Eating meat or eggs before pregnancy may increase the risk of gestational diabetes.

How many months does it take to clear 99% of the mercury and other industrial toxins from one’s body, and what role might our fat stores play in holding on to fat-soluble pollutants?

The carotid arteries of those eating plant-based diets appear healthier than even those just as slim (long-distance endurance athletes who’ve run an average of 50,000 miles).
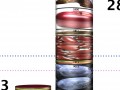
Even nine servings of fruits and vegetables a day may not reach the minimum recommended intake of antioxidants if one doesn’t make the right choices.

The consumption of phosphorus preservatives in junk food, and injected into meat, may damage blood vessels, accelerate the aging process, and contribute to osteoporosis.

Phytonutrients in certain plant foods may block the toxic effects of industrial pollutants, like dioxins, through the Ah receptor system.

Americans eating meat-free diets average higher intakes of nearly every nutrient, while maintaining a lower body weight—perhaps due, in part, to their higher resting metabolic rates.

The beef industry designed a study to show that a diet containing beef was able to lower cholesterol—if one cuts out enough poultry, pork, fish, and cheese to halve one’s total saturated fat intake.

Plant-based diets tend to be alkaline-forming. This may help protect muscle mass, and reduce the risk of gout and kidney stones. The pH of one’s urine can be estimated with natural pigments, using kitchen chemistry.
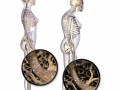
The decades-old dogma that the acid-forming quality of animal protein leads to bone loss has been called into question.

Simple changes in diet and lifestyle may quadruple a woman’s survival rate from breast cancer.

A plant-based diet may not only be the safest treatment for multiple sclerosis; it may also be the most effective.

Methionine restriction—best achieved through a plant-based diet—may prove to have a major impact on patients with cancer because, unlike normal tissues, many human tumors require the amino acid methionine to grow.