
Natural Ozempic Alternatives: Boosting GLP-1 with Diet and Lifestyle
Certain spices and the quinine in tonic water can boost GLP-1, but at what cost?
Topic summary contributed by volunteer(s): Emily and Linda
Blood clotting is healthy and necessary when it stops unwanted bleeding, but blood clots can form inside arteries, blood vessels, or the heart. If a clot travels to the heart or lungs, it could become dangerous.
Platelets play an important role in the clotting of our blood as well as the inflammatory process that brings additional aid to an injury site. But it is important to suppress the over-activity of platelets to avoid internal blood clots and the type of unwanted inflammation that can support heart disease, cancer, and other inflammatory diseases.
To reduce risk of blood clots, it is important to consume foods that suppress platelet activation. Garlic, tomatoes and berries may help with anti-platelet activation.
For substantiation of any statements of fact from the peer-reviewed medical literature, please see the associated videos below.
Image Credit: Wikimedia Commons. This image has been modified.

Certain spices and the quinine in tonic water can boost GLP-1, but at what cost?

Does soy food consumption explain why Japanese women appear to be so protected from hot flash symptoms?

What are the risks and benefits of getting an annual check-up from your doctor?

The aspirin compounds naturally found in plant foods may help explain the lower cancer rates among those eating plant-based diets.

The benefits of taking a daily aspirin must be weighed against the risk of internal bleeding.

How can soy foods have it both ways with pro-estrogenic effects in some organs that can protect bones and reduce hot flash symptoms, yet also anti-estrogenic effects in others that protect against breast and endometrial cancer?

Why should we wait ten minutes after chopping or crushing garlic before we cook it unless we’re going in for elective surgery within the next week?

What is the optimal daily dietary calcium intake and might benefits for your bones outweigh the risks to your heart from taking calcium supplements?

The unnaturally large, rapid, and sustained calcium levels in the blood caused by calcium supplements may explain why calcium from supplements, but not from food, appears to increase the risk of heart attacks.
We finally discovered why a single high-fat meal can cause angina chest pain.

The yellow fluid around tomato seeds appears to suppress platelet activation without affecting blood clotting. This anti-inflammatory effect may explain why eating tomato products is associated with lower cardiac mortality.

Flax seed consumption may play a role in preventing and treating breast cancer by blocking the inflammatory effects of interleukin-1.

The number one killer of Americans may be not eating enough fruit. Even if we just met the recommendations for fruit and vegetable intake we could save more than 100,000 people a year. One of the mechanisms by which plant foods protect us is by keeping our platelets from becoming activated.

The role white and pink (red) grapefruit may play in weight loss and cholesterol control, as well as the suppression of drug-clearance enzymes within the body.

By preventing the buildup of cholesterol in our bloodstream, we can prevent atherosclerosis in our coronary arteries—the leading cause of death in the United States for both men and women. This involves increasing our intake of fiber-containing plant foods, and decreasing our intake of trans fat, saturated fat, and cholesterol found in junk food and animal products.
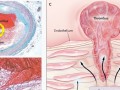
Atherosclerotic plaques in coronary arteries may be more aptly described as pimples, initiated by the infiltration of cholesterol into the lining of our arteries. The ending—should blood flow to our heart muscle be cut off by a clot formed by the rupture of one of these inflamed pockets of pus in our arterial lining—is a heart attack.

Mushrooms may help prevent breast cancer by acting as an aromatase inhibitor to block breast tumor estrogen production.