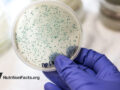
Antibiotic Resistance Genes in the Guts of Vegetarians vs. Meat-Eaters
Those eating plant-based have a reduced load of antibiotic resistance genes in their gut.
Topic summary contributed by volunteer(s): Miranda
Campylobacter is a bacteria that may be found in nearly 70% of poultry sold in the US. In most cases, people infected with Campylobacter may experience food poisoning and recover within several days. Some however, may develop irritable bowel syndrome, and others may develop Gullain-Barré Syndrome, a life-threatening auto-immune attack on the nervous system. Exposure to this pathogen occurs primarily via cross-contamination of other foods with raw poultry, rather than from cooked poultry. Disinfection of kitchen surfaces and utensils has been shown to be ineffective at eliminating Campylobacter, even using “extreme” cleaning methods (a five-minute soak in a bleach solution). Women handling poultry products have an increased risk of urinary tract infections and children who come into contact with raw poultry products while riding in a grocery cart have an 18 fold higher risk of bacterial infection.
What is the poultry industry doing to minimize customer exposure to Campylobacter? Meat products may be treated with bacteriophages (species specific viruses that attack bacteria), which may decrease bacterial contamination, but raises the possibility of exchange of genetic material between bacterial strains. The poultry industry also treats their meat with phosphates in order to enhance the color and minimize shrinkage of the product, which may have a one million fold increase in the amount of Campylobacter compared to phosphate free poultry.
What about the government? The meat industry won the right to sell contaminated meat, without the fear of governmental interference.
For substantiation of any statements of fact from the peer-reviewed medical literature, please see the associated videos below.

Those eating plant-based have a reduced load of antibiotic resistance genes in their gut.

What are the direct health implications of making clean meat—that is, meat without animals?

We need to reform the food system before it’s too late.

Can UTI-causing ExPEC E. coli bacteria be transferred human-to-human from those who eat chicken?

Poultry is the most common cause of serious food-poisoning outbreaks, followed by fish, then beef. But aren’t people more likely to order their burgers rarer than their chicken sandwiches? The primary location where outbreaks occur is the home, not restaurants.

In this “best-of” compilation of his last four year-in-review presentations, Dr. Greger explains what we can do about the #1 cause of death and disability: our diet.

Immunocompromised patients, such as those undergoing chemotherapy, are often denied fresh fruits and vegetables to ostensibly protect them against foodborne illness.

Organic food consumption appears to reduce exposure to pesticide residues and antibiotic-resistant bacteria.

The meat industry sued the federal government, winning the right to sell food known to be contaminated with food-poisoning bacteria.

The phosphorus preservatives injected into poultry may not just be an arterial toxin. They also appear to dramatically increase the growth of food poisoning Campylobacter bacteria.

Chronic red pepper powder ingestion may be an effective treatment for IBS and chronic dyspepsia (indigestion), both of which can arise from food poisoning.

Dr. Greger has scoured the world’s scholarly literature on clinical nutrition, and developed this brand-new live presentation on the latest in cutting-edge research on how a healthy diet can affect some of our most common medical conditions.

Handling chicken can lead to the colonization of one’s colon with antibiotic-resistant E. coli that may result in bladder infections in women.

This week Consumer Reports released a study showing the majority of retail pork tested was contaminated with antibiotic-resistant strains of the foodborne bacteria Yersinia enterocolitica.

Gerson Therapy is a largely diet-based alternative treatment for cancer. What have 65 years of medical research concluded about its efficacy and safety?
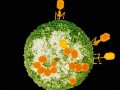
Bacteria-eating viruses (bacteriophages) have been approved as meat additives to reduce the risk of Listeria and Campylobacter found in processed meat and poultry products, but there’s a concern they could spread toxin genes between bacteria.

Exposure to meat packaging in the supermarket may lead to food poisoning in children placed in shopping carts.

The food-poisoning fecal bacteria found in 70% of U.S. retail poultry is destroyed by proper cooking, but contamination of the kitchen environment may place consumers at risk.
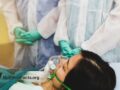
A neuropathic strain of the fecal bacteria Campylobacter, found in poultry, can trigger Guillain-Barré syndrome, a rapid and life-threatening paralysis.

An investigation finds 47% of U.S. retail meat tested is contaminated with staph (Staphylococcus) bacteria. Turkey appears most likely to harbor contagion.

How contaminated is the American meat supply with fecal matter?