Health Food Store Supplement Advice
Studies in the U.S. and Canada focus on what advice and supplements natural food store employees would offer a woman suffering from breast cancer.

Studies in the U.S. and Canada focus on what advice and supplements natural food store employees would offer a woman suffering from breast cancer.

The risk of glaucoma, the second leading cause of blindness, appears to be dramatically reduced by kale or collard greens consumption, thanks to the phytonutrient pigments lutein and zeaxanthin.

Dairy is considered a major cause of the acne epidemic, and other more serious chronic diseases in the Western world, due to the “abuse” of the mammalian postnatal signaling system by widespread cow milk consumption.

There are four common types of cinnamon: Vietnamese, Chinese (cassia), Indonesian, and Ceylon (true) cinnamon. Which is safest in terms of the level of coumarin, which may damage the liver at toxic doses?

Avian leukosis/sarcoma virus has been found in 14% of retail egg samples.

The largest study to date on poultry workers found a significantly increased risk of dying from penile cancer, thought to be due to exposure to oncogenic (cancer-causing) chicken viruses, which raise consumer concerns as well.

The association between poultry and cancer may be explained by the presence in chickens’ and turkeys’ flesh of industrial carcinogens such as dioxins, oncogenic (cancer-causing) viruses, and/or the drugs that were fed to the birds.

In a study of a half million people, which was most associated with the risk of developing lymphoma? Red meat, processed meat, poultry, offal, eggs, or milk?

Even after controlling for a variety of dietary and nondietary factors, those eating plant-based diets appear to have lower overall cancer rates.
Caffeine has positive cognitive and physiological effects at moderate doses.

Coffee consumption is associated with a modest reduction of total cancer incidence.

All three human studies on soy and breast cancer survival suggest that soy in sufficient amounts may improve survival in women diagnosed with breast cancer.
One teaspoon of flax seeds may double one’s daily production of lignans—phytonutrients that appear to play a role in both breast cancer prevention and survival.

Breast cancer survivors may reduce their chances of survival if they eat too much trans fat, found primarily in the American diet in junk food and animal products.

Breast cancer survivors may reduce their chances of survival if they eat too much saturated fat, found primarily in the American diet in cheese, chicken, and junk food.

The effect of raw and cooked broccoli consumption on survival rates of bladder cancer patients.

The anti-proliferative effects of cruciferous vegetable phytonutrients may decrease the metastatic potential of lung cancer, the number one cancer killer of women.

6,000 cups of broccoli a year is probably too much.

Monday, March 12, 2012: The Harvard Health Professionals Follow-up Study and the Harvard Nurses’ Health Study concluded that red meat consumption was associated with living a significantly shorter life—increased cancer mortality, increased heart disease mortality, and increased overall mortality.

In a test tube, the broccoli phytonutrient sulforaphane appears to target breast cancer stem cells. But how do we know it’s even absorbed into the body? Have women undergoing breast reduction surgery eat some an hour before their operation, and directly measure the level in their tissues.
A new theory of cancer biology—cancer stem cells—and the role played by sulforaphane, a phytonutrient produced by cruciferous vegetables.
How meat scientists justify their promotion of foods associated with cancer risk.

In the context of a healthy, plant-based diet, the nitrates in vegetables can safely be converted into nitric oxide, which can boost athletic performance, and may help prevent heart disease.

The addition of vitamin C to processed (cured) meats such as bacon may actually make them more carcinogenic.

Frying bacon outdoors decreases the concentration of airborne nitrosamine carcinogens.

Phytonutrients, such as vitamin C, prevent the formation of nitrosamines from nitrites—which explains why adding nitrite preservatives to processed meat can be harmful, but adding more vegetables, with their nitrite-forming nitrates, to our diet can be helpful.

The nitrite preservatives in processed meats such as bologna, bacon, ham, and hot dogs form carcinogenic nitrosamines, but also reduce the growth of botulism bacteria—forcing regulators to strike a balance between consumers risking cancer, or a deadly form of food poisoning.

Nitrites in processed meat form nitrosamines, a class of potent carcinogens found in cigarette smoke, which may explain why hot dog consumption has been associated with the two leading pediatric cancers, brain tumors and childhood leukemia.

Even when fiber and fruit and vegetable intake are kept constant, choosing foods richer in antioxidants may increase stool size, which is associated with lower cancer risk.

The four most antioxidant-packed natural substances so far tested are cloves, amla (Indian gooseberries), triphala (a combination of amla, bibhitaki, and haritaki fruits), and dragon’s blood.

Triphala, a combination of three fruits—amla, bibhitaki, and haritaki—is the most commonly used herbal formulation in Ayurvedic medicine, and may have powerful anticancer properties. Unfortunately, one in five Ayurvedic herbal dietary supplements were found contaminated with lead, mercury, and/or arsenic.

Indian gooseberries (amla) block breast cancer cell growth and metastasis potential in vitro.

Indian gooseberries (amla), an important plant in Ayurvedic medicine, may have anticancer properties, as well as cough-, fever-, pain-, stress-, and diarrhea-suppressing effects.

Vitamin D deficiency may shorten one’s lifespan, but getting too much vitamin D may also adversely affect longevity.

The Institute of Medicine’s conservative position on vitamin D is understandable, given the history of hyped vitamin supplements (vitamin A, beta carotene, folic acid, vitamin C, vitamin E) that turned out worthless—or worse.

The USDA Dietary Guidelines Committee stands accused of ignoring the science to justify its recommendation to eat meat.
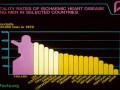
The success story in Finland shows that science-based dietary guidelines can save millions of lives.

The insecticide and fungicide compound found naturally in avocados (persin) may damage the DNA of normal cells, as well as cancer cells.

Persin, a natural toxin found in avocados, appears so effective at killing breast cancer cells that it is being considered as a chemotherapy agent.

Major fish oil manufacturers and drug stores are being sued for failing to disclose the PCB pollutants in fish oil supplements.