
Is Shrimp Bad for Cholesterol and Heart Disease?
Might asymptomatic food sensitivities to gluten, milk, peanuts, eggs, or shrimp increase the risk of premature death for those who eat these foods?
Topic summary contributed by volunteer(s): Crystal
Most Americans suffer an acute diarrheal illness every year. Certain foods may increase our risk of getting diarrhea such as meat, gluten if we have a gluten sensitivity, and fish. Diarrhea can also be an unwanted side effects for many medications including metformin, an antidiabetes drug, antibiotics, and the diet drug, alli.
Some foods that may help prevent diarrhea include foods high in fiber, probiotics, chamomile tea, and amla. Good gut flora is one key to preventing diarrhea.
For substantiation of any statements of fact from the peer-reviewed medical literature, please see the associated videos below.

Might asymptomatic food sensitivities to gluten, milk, peanuts, eggs, or shrimp increase the risk of premature death for those who eat these foods?

I compare the cost, convenience, and safety of various plant, animal, and supplement sources of taurine.

Particular caution should be used for NAD+-boosting supplements by those with cancer, a personal or strong family history of cancer and perhaps also by those with inflammatory disorders and certain active infections.

What are the pros, cons, and efficacy of dihydronicotinamide riboside (reduced NR), perhaps the most potent NAD+ precursor, as well as reduced NMN, taking NAD+ directly, or making it from scratch from tryptophan?

Given niacin’s decades of use as a cholesterol drug, we have a good idea of its safety profile.

What is NAD+ and what role does it play in the aging process?
Obesity can be so devastating to our health that the downsides of any effective drug would have to be significant to outweigh its weight-loss benefits.
How common are serious potential side effects of GLP-1 weight-loss drugs, such as suicide, pancreatitis, bowel obstruction, thyroid cancer, and pancreatic cancer?

How might we mitigate the gastrointestinal and muscle loss side effects of GLP-1 weight-loss drugs?

The pros and cons of all the NAD+ supplements and what are the ways to boost NAD+ naturally with diet and lifestyle?

Probiotics can actually interfere with microbiome recovery after antibiotics, rather than facilitate it.
As a mild mitochondrial poison, metformin carries a variety of downsides.
I go over randomized, controlled trials and case reports of stool transplants for various clinical conditions.

What are the maximum acute and daily doses for adults and children to avoid gastrointestinal effects?

How safe are fourth-generation sweeteners, such as the rare sugar allulose?

Are yellow-fleshed potatoes healthier than white? And, what about the glycoalkaloid toxins?

Prunes, figs, and exercise are put to the test as natural home remedies for constipation.

The extent of risk from bariatric weight-loss surgery may depend on the skill of the surgeon.

More than half of IBS sufferers appear to have a form of atypical food allergy.

It may not be the number of bacteria growing in your small intestine, but the type of bacteria, which can be corrected with diet.

Plant-based diets can be 98 percent effective in keeping ulcerative colitis patients in remission, blowing away other treatments.

What does the clinical course of COVID-19 look like for both those who survive and those who don’t?

Vitamin C, turmeric, beta-glucan fiber, and vitamin B12 are put to the test for recurring canker sores (aphthous ulcers).

From a case report to a randomized controlled trial, aloe is put to the test against cancer.

What role do antibiotics play in the development and treatment of autism spectrum disorder?

Might lectins help explain why those who eat more beans and whole grains have less cancer?

Those with certain autoimmune diseases such as Crohn’s disease should probably not eat nutritional yeast.

Less than half of herbal supplements tested from a dozen companies were found to be authentic.

Fennel seeds can work as effectively as drugs like ibuprofen for painful periods, and an eighth of a teaspoon of ginger powder three times a day can cut menstrual bleeding in half.
Why does our immune system confuse unhealthy diets with dysbiosis—an overrun of bad bacteria in our colon?

Most people have between 3 bowel movements a day and 3 a week, but normal doesn’t necessarily mean optimal.

Freedom of Information Act documents show drug companies hid critical findings from doctors and the public.

The majority of polyphenol phytonutrients may be bound to fiber, helping to explain the marked difference in health impacts between whole fruit and fruit juice.

Approximately 1 in 3 Americans have prediabetes, but only about 1 in 10 knows it. What works better at preventing it from turning into full-blown diabetes—drugs or diet and exercise?

For more than 30 years, the medical profession has debated the existence of an intolerance to the wheat protein, gluten, unrelated to allergy or celiac disease. What is the evidence pro and con?

There’s a cheap concoction one can make at home that safely wipes out cavity-forming bacteria on our teeth better than chlorhexidine mouthwash and also reduces their plaque-forming ability.

Though prebiotics may be preferable, probiotics may reduce the risk of upper respiratory tract infections.
Probiotics may help prevent antibiotic-associated diarrhea, and appear to speed recovery from acute gastroenteritis.

For the same reason aspirin should be avoided in pregnancy, chamomile has such powerful anti-inflammatory properties that regular consumption may result in a serious fetal heart problem—premature constriction of the fetal ductus arteriosus, which allows the fetus to “breathe” in the womb.
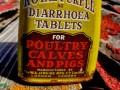
In a national survey, fewer than half of the participants realized meat contaminated with fecal food-poisoning bacteria, such as Salmonella, can still legally be sold. Rather than producing safe products, the meat industry shifts the responsibility for safety onto the consumer.