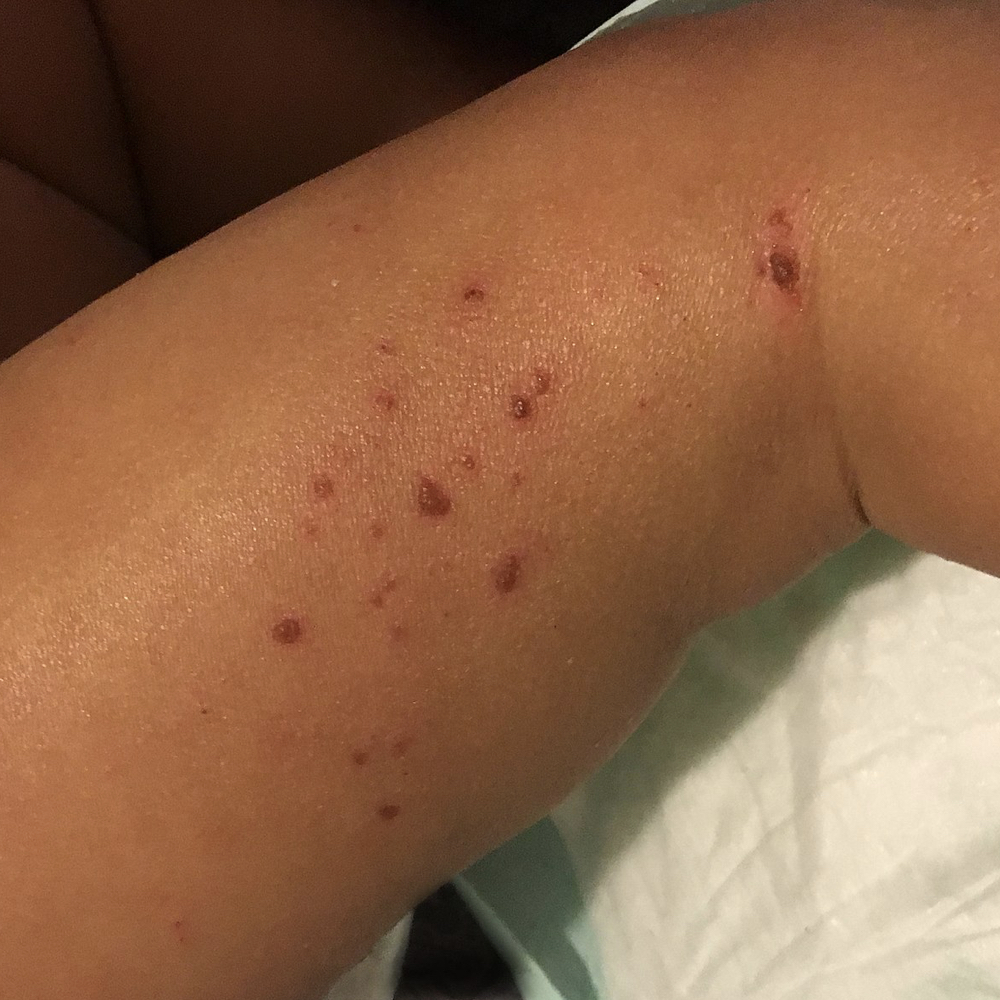
Eczema
Eczema, also known as atopic dermatitis, is a chronic inflammatory skin disease affecting about one in ten kids and about 3 percent of adults. It is more than just an itchy rash that can be exhausting and make us feel self-conscious. Eczema is associated with other diseases, too. It may increase risk for ADHD in children, though perhaps just from the sleep deprivation, and may increase risk of major depression in adults. What’s more, eczema is on the rise.
Might diet play a role? The original randomized, double-blind, controlled trial of diet and eczema found that cutting out eggs, chicken, milk, and beef significantly improved eczema in 70 percent of the kids who completed the study. Subsequent studies found similar results. In fact, out of 13 studies on avoiding milk, eggs, or both, 10 studies documented overall clinical improvement.
Topical steroids, like cortisone creams, are commonly used as first-line therapy, and there are immunosuppressants, as well, with more drugs in the pipeline. What about natural treatments?
Reviews have found there is no convincing evidence that taking oral supplements, such as evening primrose oil, borage oil, and hempseed oil, improves eczema compared to placebo, researchers concluded that licorice extracts applied topically could be considered an effective eczema treatment agent. St. John’s wort cream has also been found to reduce eczema severity scores better than placebo.
Regardless of what topical agent is used, steroid or otherwise, it is critical that the skin barrier is protected and maintained with the use of emollients, ideally once or twice a day, especially right after showering, to lock in the moisture. Based on 77 studies of moisturizers for eczema, researchers determined there was no reliable evidence that one moisturizer was better than another, though a consensus of experts found that petroleum jelly, like Vaseline, may be best for skin barrier function protection.
For substantiation of any statements of fact from the peer-reviewed medical literature, please see the associated videos below.
Image Credit: National Institutes of Health / Flickr. This image has been modified.
Popular Videos for Eczema

Eczema Treatment with Evening Primrose Oil, Borage Oil vs. Hempseed Oil
Are there dietary supplements that can help with atopic dermatitis?
Best Foods to Avoid for Eczema
Randomized, double-blind, controlled trials suggest that excluding certain foods, such as eggs and chicken, can...
Exclusion Diets for Eczema
Infants of mothers randomized to cut out eggs, milk, and fish were significantly less likely...
Treating Asthma and Eczema with Plant-Based Diets
Pilot studies on treating allergic eczema and severe asthma with dietary interventions have shown remarkable...All Videos for Eczema
-

Topical Apple Cider Vinegar for Treating Varicose Veins
What are the results of a randomized controlled trial on the effect of topical apple cider vinegar on varicose veins?
-

The World’s Largest Fasting Study
Buchinger modified fasting is put to the test.
-

Exclusion Diets for Eczema
Infants of mothers randomized to cut out eggs, milk, and fish were significantly less likely to have eczema even years later.
-

Best Foods to Avoid for Eczema
Randomized, double-blind, controlled trials suggest that excluding certain foods, such as eggs and chicken, can significantly improve atopic dermatitis.
-

Eczema Treatment with Coconut Oil, Mineral Oil vs. Vaseline
Natural topical remedies for eczema, including licorice root gel, St. John’s Wort cream, and emollients such as coconut oil, mineral oil, and petroleum jelly, are put to the test.
-

Eczema Treatment with Evening Primrose Oil, Borage Oil vs. Hempseed Oil
Are there dietary supplements that can help with atopic dermatitis?
-

Childhood Constipation and Cow’s Milk
The elimination of all dairy products was found to cure constipation in up to 100% of kids tested, leading to a resolution of rectal inflammation and complications such as anal fissures.
-
Treating Asthma and Eczema with Plant-Based Diets
Pilot studies on treating allergic eczema and severe asthma with dietary interventions have shown remarkable results.
-

Treating Asthma with Fruits and Vegetables
Increasing fruit and vegetable consumption to seven servings a day appears to cut asthma exacerbation rates in half, whereas restricting consumption to Standard American Diet levels leads to a significant worsening of lung function and asthma control.
-

Preventing Asthma with Fruits and Vegetables
A study involving more than a million kids suggests the striking worldwide variation in childhood rates of allergies, asthma, and eczema is related to diet.
-

Dietary Sources of Alkylphenol Endocrine Disruptors
Foods of animal origin (especially fish) appear to be the most important source of human exposure to industrial pollutants such as alkylphenol xenoestrogens.
-

Alkylphenol Endocrine Disruptors and Allergies
The dramatic rise of allergic diseases such as eczema and seasonal allergies may be related to dietary exposure to endocrine-disruptor xenoestrogens, such as alkylphenol industrial pollutants.
-

Chamomile Tea May Not Be Safe During Pregnancy
For the same reason aspirin should be avoided in pregnancy, chamomile has such powerful anti-inflammatory properties that regular consumption may result in a serious fetal heart problem—premature constriction of the fetal ductus arteriosus, which allows the fetus to “breathe” in the womb.
-

Throw Household Products off the Scent
Volatile chemicals in consumer products such as air fresheners, laundry detergents, fabric softeners, and dryer sheets may be hazardous.
-

Preventing Childhood Allergies
What is responsible for the rising prevalence of atopic diseases, such as food allergies, asthma, hay fever, and eczema?