
Studies on Millet Nutrition: Is It a Healthy Grain?
Millet isn’t the name of a specific grain, but a generic term that applies to a number of totally different plants. Which is the most healthful?
Topic summary contributed by volunteer(s): Linda
In the last three decades, the incidence of esophageal cancer in the US has increased sixfold–an increase greater than that of melanoma, breast, or prostate cancer.
This is likely because acid reflux is on the rise, and acid reflux can lead to inflammation, then esophagitis, then Barrett’s esophagus, and then, possibly, cancer. Numerous studies have been published on the association between Barrett’s esophagus, esophageal cancer, and diet. They found that meat and high-fat meals may increase cancer risk. Specific foods that have been shown to be associated with esophageal cancer include cured meats—like bologna, bacon, ham, and hot dogs—and eggs, because of frequent dioxin contamination. High intake of folic acid from supplements may also be associated with a significantly elevated risk of Barrett’s esophagus with precancerous changes.
A higher intake of fiber may have highly protective effects against esophageal cancer. Individuals with the highest fiber intakes appear to have an approximately 30% lower risk of cancer. Clinical trials have demonstrated the effectiveness of strawberries in reversing the progression of esophageal cancer in the majority of patients.
For substantiation of any statements of fact from the peer-reviewed medical literature, please see the associated videos below.

Millet isn’t the name of a specific grain, but a generic term that applies to a number of totally different plants. Which is the most healthful?

How does sorghum compare with other grains in terms of protein, antioxidants, and micronutrients? And the benefits of red sorghum compared to black and white varieties.

Losing weight can reduce sciatica, hypertension, and cancer risk, and reverse type 2 diabetes.

A review of reviews on the health effects of tea, coffee, milk, wine, and soda.

If even light drinking can cause cancer, why don’t doctors warn their patients about it?

Avocado consumption can improve artery function, but what effect might guacamole have on cancer risk?
Straining at stool over time may force part of the stomach up into the chest, contributing to GERD acid reflux disease. This may explain why hiatal hernia is extremely rare among populations eating high-fiber diets.

Which foods should we eat and avoid to prevent and treat acid reflux before it can place us at risk for Barrett’s esophagus and cancer?

There appear to be no consistent differences in the level of vitamins and minerals in organic versus conventionally grown produce, but organic fruits and vegetables have more phenolic phytonutrients.

American Institute for Cancer Research recommendation compliance associated not only with cancer prevention and survival but less heart and respiratory disease mortality and a longer lifespan.

The association between cancer and the consumption of deep-fried foods may be due to carcinogens formed at high temperatures in animal foods (heterocyclic amines and polycyclic hydrocarbons) and plant foods (acrylamide).

Dr. Greger has scoured the world’s scholarly literature on clinical nutrition, and developed this brand-new live presentation on the latest in cutting-edge research on how a healthy diet can affect some of our most common medical conditions.

Modest lifestyle changes that include the avoidance of alcohol may cut the odds of breast cancer in half, but certain grapes appear to contain natural aromatase inhibitors that may undermine the ability of breast tumors to produce their own estrogen.
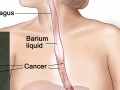
A randomized phase II clinical trial on the ability of strawberries to reverse the progression to esophageal cancer.

People taking dietary supplements may, in some cases, be paying to make themselves sick. This video covers folic acid, beta carotene, and green tea supplements.

The largest study to date on poultry workers found a significantly increased risk of dying from penile cancer, thought to be due to exposure to oncogenic (cancer-causing) chicken viruses, which raise consumer concerns as well.

Coffee consumption is associated with a modest reduction of total cancer incidence.

The nitrite preservatives in processed meats such as bologna, bacon, ham, and hot dogs form carcinogenic nitrosamines, but also reduce the growth of botulism bacteria—forcing regulators to strike a balance between consumers risking cancer, or a deadly form of food poisoning.