
Zeranol Use in Meat and Breast Cancer
Anabolic growth-promoting drugs in meat production are by far the most potent hormones found in the food supply.
Topic summary contributed by volunteer(s): Mary
The FDA issued voluntary guidance to remove antibiotics from farm animal feed, however, it is non-binding and legally non-enforceable, so 80% of available antibiotics may still be squandered on farm animals. Mass feeding of antibiotics to livestock is directly linked to antibiotic resistant bacteria infections in humans. Clostridium difficile is one of the superbugs found in the U.S. meat supply (including up to 42% of poultry sampled), and may be even more dangerous than MRSA.
Dioxins are highly toxic pollutants that may be found in contaminated feed fed to chickens and farm-raised fish. Canthoxanthine feed additives given to farmed fish may be linked to gold dust retinopathy. The poultry industry feeds their birds millions of pounds of arsenic-containing drugs every year, ending up in chickens and feathers (which is used along other unusable chicken parts to feed back to farm animals). Estrogen levels found in this chicken litter fed back to chickens may trigger premature development in consumers. Researchers in Greece fed infected cow brains to farm fish and found evidence mad cow-like changes in the fish.
Bacteria-eating viruses have been approved as meat additives to reduce the risk of Listeria and Campylobacter found in processed meat and poultry products. Most GMO soy grown in the US is fed to farm animals. The egg industry is attempting to improve the fatty acid lipid profile of eggs by feeding blubber from the Canadian harp seal hunt to laying hens to lower their arachidonic acid level. Government subsidies of livestock feed keep these unhealthy products so cheap.
For substantiation of any statements of fact from the peer-reviewed medical literature, please see the associated videos below.

Anabolic growth-promoting drugs in meat production are by far the most potent hormones found in the food supply.

Dr. Greger has scoured the world’s scholarly literature on clinical nutrition and developed this new presentation based on the latest in cutting edge research exploring the role diet may play in preventing, arresting, and even reversing some of our most feared causes of death and disability.

PBDE fire-retardant chemicals in the food supply may contribute to attention and cognitive deficits in children.

The sex steroids found naturally in animal products likely exceed the hormonal impacts of endocrine-disrupting chemical pollutants.

The hormonal effects of the Roundup pesticide on GMO soy put into perspective.

The FDA’s suggestion that the meat industry voluntarily stop feeding antibiotics by the ton to farm animals to fatten them faster falls short of the changes needed to forestall the epidemic of antibiotic resistance.

Feed contaminated with toxic pollutants thought to originate from sewer sludge fed to chickens and fish results in human dioxin exposure through poultry, eggs, and catfish.
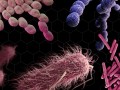
The emergence of pathogens resistant to even our antibiotics of last resort has raised the specter of a “post-antibiotic age” in which drugs to fight infections may be useless. This has focused attention on the mass use of antibiotics in farm animal feed to promote growth and prevent infection in high density production.

By testing chicken feathers for chemical residues, researchers aim to find out what the poultry industry is feeding their birds. The presence of banned drugs and a broad range of pharmaceuticals raises concern, recalling the time in which DES was fed to chickens for years after it was shown to cause human vagina cancer.

What if billions in tax dollars were invested in healthier options, rather than given to corporations to subsidize the very foods that are making us sick?

Meat industry public relations campaign to “crush” myths makes false claim about the millions of pounds of antibiotics fed to farm animals.
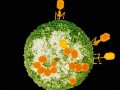
Bacteria-eating viruses (bacteriophages) have been approved as meat additives to reduce the risk of Listeria and Campylobacter found in processed meat and poultry products, but there’s a concern they could spread toxin genes between bacteria.

The egg industry is attempting to improve the fatty acid lipid profile of eggs by feeding blubber from the Canadian harp seal hunt to laying hens.