
How Long to Detox from Fish Before Pregnancy?
How many months does it take to clear 99% of the mercury and other industrial toxins from one’s body, and what role might our fat stores play in holding on to fat-soluble pollutants?

How many months does it take to clear 99% of the mercury and other industrial toxins from one’s body, and what role might our fat stores play in holding on to fat-soluble pollutants?

The carotid arteries of those eating plant-based diets appear healthier than even those just as slim (long-distance endurance athletes who’ve run an average of 50,000 miles).

To stay out of oxidative debt, we need to take in more antioxidants than we use up.
Even nine servings of fruits and vegetables a day may not reach the minimum recommended intake of antioxidants if one doesn’t make the right choices.

Risk/benefit analysis of 33 fish species contrasts the brain-boosting effects of DHA with the brain-damaging effects of mercury, to determine the net effect on intelligence (IQ).

Exposure to mercury during pregnancy appears to influence fetal brain development, as detected by decreased size of a newborn’s brain.

Phytonutrients in certain plant foods may block the toxic effects of industrial pollutants, like dioxins, through the Ah receptor system.

Americans eating meat-free diets average higher intakes of nearly every nutrient, while maintaining a lower body weight—perhaps due, in part, to their higher resting metabolic rates.

Too much choline—a compound concentrated in eggs and other animal products—can make bodily secretions smell like rotting fish, and may increase the risk of heart disease, due to conversion in the gut to trimethylamine.

The beef industry designed a study to show that a diet containing beef was able to lower cholesterol—if one cuts out enough poultry, pork, fish, and cheese to halve one’s total saturated fat intake.

Plant-based diets tend to be alkaline-forming. This may help protect muscle mass, and reduce the risk of gout and kidney stones. The pH of one’s urine can be estimated with natural pigments, using kitchen chemistry.
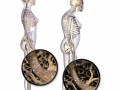
The decades-old dogma that the acid-forming quality of animal protein leads to bone loss has been called into question.

Methionine restriction—best achieved through a plant-based diet—may prove to have a major impact on patients with cancer because, unlike normal tissues, many human tumors require the amino acid methionine to grow.

A higher rate of cancer deaths among those that handle and process meat is attributed to infection with viruses, and chronic exposure to animal proteins.

Those eating a more plant-based diet may naturally have an enhanced antioxidant defense system to counter the DNA damage caused by free radicals produced by high-intensity exercise.

Dr. Greger has scoured the world’s scholarly literature on clinical nutrition, and developed this brand-new live presentation on the latest in cutting-edge research on how a healthy diet can affect some of our most common medical conditions.

Dioxins, endocrine disrupting pollutants, heavy metals, saturated fat, and steroids in the meat supply may be affecting sperm counts, semen quality, and the ability of men to conceive.

Based on studies of atomic bomb survivors, Chernobyl victims, and airline pilots exposed to more cosmic rays at high altitudes, it appears that fruits and vegetables may decrease radiation-induced chromosome damage.

The majority of radioactive fallout from the Fukushima nuclear power plant tragedy was absorbed by the Pacific Ocean. What does that mean for seafood safety?
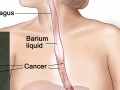
A randomized phase II clinical trial on the ability of strawberries to reverse the progression to esophageal cancer.
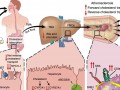
Expanding on the subject of my upcoming appearance on The Dr. Oz Show, a landmark new article in the New England Journal of Medicine shows that choline in eggs, poultry, dairy, and fish produces the same toxic TMAO as carnitine in red meat—which may help explain plant-based protection from heart disease and prostate cancer.
Plant-based diets appear to offer relief from a variety of menstrual symptoms, including cramping, bloating, and breast pain (cyclical mastalgia).

Longstanding concerns about certain isolated components of the spice tarragon have broadened into questions about the safety of even the leaves themselves.

The story behind the first U.S. dietary recommendations report explains why, to this day, the decades of science supporting a more plant-based diet have yet to fully translate into public policy.
Hundreds of thousands of Americans are Salmonella-poisoned by poultry every year—yet it remains legal to sell meat proven to be contaminated.

Plant-based diets in general, and certain plant foods in particular, may be used to successfully treat Parkinson’s disease—in part, by boosting L-DOPA levels.

The early onset of puberty in girls associated with animal protein consumption may be due to endocrine-disrupting chemical pollutants in the meat supply.

People eating conventional diets may ingest a trillion microparticles of the food-whitening additive, titanium dioxide, every day. What implication might this have for inflammation in the gut?

The polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the vapors released from cooking meat may be hazardous for fetal development, and increase the risk of cancer.

The boost in detoxifying enzymes triggered by cruciferous vegetable consumption may last for weeks!
Garlic and flavonoid phytonutrients found in fruits, vegetables, nuts, and grains appear to protect against DNA damage induced by mutagenic chemicals found in cooked meat.
Using the cooked meat carcinogen PhIP to turn normal breast cells cancerous, researchers explore the use of green tea to interrupt this malignant transformation.

Even vegetarians could potentially be exposed to the carcinogens typically formed by cooking meat through eggs, cheese, creatine sports supplements, and cigarette smoke.

Those who eat meat risk food poisoning from undercooked meat, but also exposure to cooked meat carcinogens in well-cooked meat. By boiling meat, non-vegetarians can mediate their risk of both.

The cooked meat carcinogen PhIP—found in fried bacon, fish, and chicken—may not only trigger cancer and promote tumor growth, but also increase its metastatic potential, by increasing its invasiveness.

DNA-damaging chemicals, formed when meat is cooked, stimulate breast cancer cells almost as much as pure estrogen, and can infiltrate the ducts where most breast cancers arise.

Meat and sugar increase uric acid levels, which are associated with increased risk of gout, hypertension (high blood pressure), obesity, prediabetes, diabetes, kidney disease and cardiovascular disease.

Where do DDT, hexachlorobenzene, PCBs, and perfluorochemicals (linked to thyroid disease) concentrate in the food supply?
Are pregnant women who eat fish, other meat, and dairy still passing along the pesticide DDT—even decades after it was banned?

Other than pet food and fish (which may be most contaminated), how do fire-retardant chemicals (PBDEs) and polychlorinated naphthalenes (PCNs) concentrate in the American food supply?