
Are Keto Diets Safe?
The effects of ketogenic diets on nutrient sufficiency, gut flora, and heart disease risk.

The effects of ketogenic diets on nutrient sufficiency, gut flora, and heart disease risk.

Dairy is compared to other foods for cardiovascular (heart attack and stroke) risk.

The secret to unlocking the benefits of chia seeds may be grinding them up.

Do legumes—beans, chickpeas, split peas, and lentils—work only to prevent disease, or can they help treat and reverse it as well?

Does excluding dairy products, food additives, and gluten-containing grains from one’s diet help those with recurring canker sores (aphthous ulcers)?

Certain gut bacteria can supercharge the benefits of soy foods, resulting in even more bone protection, better control of menopausal symptoms, and lower prostate cancer risk, but how can we foster the growth of these good bacteria?

Is the exaggerated reaction of many Crohn’s disease patients to baker’s, brewer’s, and nutritional yeast just a consequence of their inflamed leaky gut, or might the yeast be a contributing cause?

Do the medium-chain triglycerides in coconut oil and the fiber in flaked coconut counteract the negative effects on cholesterol and artery function?

I recommend people switch away from using rice milk.

Soy is put to the test for the treatment of prostate cancer.

What is the optimal source and amount of protein for senior citizens?

Only about 1 in 10,000 people live to be 100 years old. What’s their secret?

In this “best-of” compilation of his last four year-in-review presentations, Dr. Greger explains what we can do about the #1 cause of death and disability: our diet.

The myth that plant proteins are incomplete, necessitating protein combining, was debunked by the scientific nutrition community decades ago.
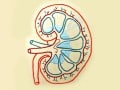
Dietary Acid Load is determined by the balance of acid-inducing food, such as meats, eggs, and cheeses, offset by base-inducing (“alkaline”) foods, such as fruits and vegetables.

Anti-inflammatory drugs abolish the hyperfiltration and protein leakage response to meat ingestion, suggesting that animal protein causes kidney stress through an inflammatory mechanism.

While epidemics of chronic disease are currently by far our leading causes of death, global warming is considered a looming public health threat. How can we eat to combat dietary diseases and greenhouse gas emissions at the same time?

Decreasing animal protein and sodium intake appears more effective in treating calcium oxalate and uric acid kidney stones (nephrolithiasis) than restricting calcium or oxalates.

Which foods should we eat and avoid to prevent and treat acid reflux before it can place us at risk for Barrett’s esophagus and cancer?
Sulfur dioxide preservatives in dried fruit, sulfites in wine, and the putrefaction of undigested animal protein in the colon can release hydrogen sulfide, the rotten egg gas associated with inflammatory bowel disease.

The negative impact of red meat on our cholesterol profile may be similar to that of white meat.

Does just reducing one’s intake of meat, dairy, and eggs significantly reduce mortality?
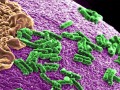
The toxic rotten egg gas hydrogen sulfide may explain why animal protein is associated with inflammatory bowel disease.

American Institute for Cancer Research recommendation compliance associated not only with cancer prevention and survival but less heart and respiratory disease mortality and a longer lifespan.

How do the blood-pressure lowering effects of hibiscus tea compare to the DASH diet, a plant-based diet, and a long-distance endurance exercise?

Nutritional quality indices show plant-based diets are the healthiest, but do vegetarians and vegans reach the recommended daily intake of protein?

Our immune response against a foreign molecule present in animal products may play a role in some allergic, autoimmune, and inflammatory disorders. This reaction is thought to underlie tick bite-triggered meat allergies.

A study involving more than a million kids suggests the striking worldwide variation in childhood rates of allergies, asthma, and eczema is related to diet.

The lifespan extension associated with dietary restriction may be due less to a reduction in calories, and more to a reduction in animal protein (particularly the amino acid leucine, which may accelerate aging via the enzyme TOR).
Blood flow within the hearts of those eating low-carb diets was compared to those eating plant-based diets.
The DNA of those cooking with spices such as ginger, rosemary, and turmeric appears less susceptible to breakage.

Coronary heart disease, our #1 cause of death, was found to be almost non-existent in a population eating a diet centered around whole plant foods.

Canned beans are convenient, but are they as nutritious as home-cooked? And, if we do use canned, should we drain them or not?

One reason why soy consumption is associated with improved survival and lower recurrence rates in breast cancer patients may be because soy phytonutrients appear to improve the expression of tumor-suppressing BRCA genes.

The beef industry designed a study to show that a diet containing beef was able to lower cholesterol—if one cuts out enough poultry, pork, fish, and cheese to halve one’s total saturated fat intake.

Plant-based diets tend to be alkaline-forming. This may help protect muscle mass, and reduce the risk of gout and kidney stones. The pH of one’s urine can be estimated with natural pigments, using kitchen chemistry.

Reducing the ratio of animal to plant protein in men’s diets may slow the progression of prostate cancer.

Plant-based diets may prove to be a useful nutrition strategy in both cancer growth control as well as lifespan extension, because these diets are naturally lower in methionine.

Changing food perceptions and incorporating puréed vegetables into entrees can improve the dietary quality of kids and grown-ups.

Dr. Greger has scoured the world’s scholarly literature on clinical nutrition, and developed this brand-new live presentation on the latest in cutting-edge research on how a healthy diet can affect some of our most common medical conditions.