
Diet and Caloric Restriction for Longevity—The Monkey Trials
How can we make sense of the disparate results from the four primate studies on caloric restriction and lifespan?
Topic summary contributed by volunteer(s): Mariana
Caloric restriction may improve memory in seniors. It also may increases lifespan by different mechanisms such as increasing the levels of dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA), through xenohormesis, a process where plants pass on their stress-resilient phytonutrients, and/or through the inhibition of the enzyme TOR, which also protect from some invasive cancers and have positive effects on the reduction of metabolic syndrome and blood sugar levels. Since the effects of caloric restriction seem to correlate more with protein intake than calorie restriction itself, the adoption of a low protein diet can potentially include all the benefits of caloric restriction without the side effects of starvation. A severely calorie restricted diet is difficult to sustain and might carry unwanted side-effects, but a plant-based diet was shown to have similar effects on DHEA levels as caloric restriction. Plant-based diets have also been linked to increased longevity due to their naturally low amounts of methionine and leucine, two amino acids associated with aging and tumor development that tend to be more concentrated in animal protein. Plant-based diets may also be as effective as calorie restriction for weight loss.
For substantiation of any statements of fact from the peer-reviewed medical literature, please see the associated videos below.

How can we make sense of the disparate results from the four primate studies on caloric restriction and lifespan?

How might we help flush the pollutants stored in our fat that come spilling out into our bloodstream during weight loss?

Plant-based diets improve the performance of athletes and nonathletes alike.

Losing weight without rearranging your gastrointestinal anatomy carries advantages beyond just the lack of surgical risk.

The spice cumin can work as well as orlistat, the “anal leakage” obesity drug.

How can we use sensory-specific satiety to our advantage?

Big Food uses our hard-wired drive for dietary diversity against us.

I debunk the myth of protein as the most satiating macronutrient.

I dive into one of the most fascinating series of studies I’ve ever come across.

Fasting and exercise can raise BDNF levels in our brain, but this can also be achieved by eating and avoiding certain foods.

Breakthroughs in the field of chronobiology—the study of our circadian rhythms—help solve the mystery of the missing morning calories in breakfast studies.
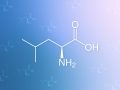
Why we may want to strive not to exceed the recommended intake of protein.

Calories eaten in the morning count less and are healthier than calories eaten in the evening.

Are there benefits to giving yourself a bigger daily break from eating?

17 ingredients to an ideal weight-loss diet and the 21 tweaks to accelerate the further loss of excess body fat.

The effects of eating only 5 days a week or a fasting-mimicking diet 5 days a month.

Alternate-day modified fasting is put to the test for lifespan extension.

Eating every other day can raise your cholesterol.
Does every-other-day-eating prevent the metabolic slowing that accompanies weight loss or improve compliance over constant day-to-day calorie restriction?

The reasons why fasting longer than 24 hours, and particularly three or more days, should only be done under the supervision of a health professional and preferably in a live-in clinic.

Fasting for a week or two is like the keto diet—it can actually slow body fat loss rather that accelerating it.

For more than a century, fasting—up to 382 days without calories—has been used a weight-loss treatment.

How to preserve bone and mass on a low calorie diet.

Though a bane for dieters, a slower metabolism may actually be a good thing.

Losing a pound of fat can take as few as 10 calories a day or as many as 55, depending on whether you’re improving food quality or just restricting food quantity.

Understanding the metabolic and behavioral adaptations that slow weight loss.

How many fewer calories do you have to eat every day to lose one pound of body fat?

Keto diets put to the test for diabetes reversal.

Ketogenic diets found to undermine exercise efforts and lead to muscle shrinkage and bone loss.

The effects of ketogenic diets on nutrient sufficiency, gut flora, and heart disease risk.

Might the appetite-suppressing effects of ketosis improve dietary compliance?

Ketogenic diets and the $33-billion diet gimmick.

What is the return on investment for educating employees about healthy eating and living?

The most well-published community-based lifestyle intervention in the medical literature is also one of the most effective.

The reason greens are associated with a significantly longer lifespan may be because, like caloric restriction, they improve our energy efficiency.

Even when study subjects were required to eat so much that they didn’t lose any weight, a plant-based diet could still reverse type 2 diabetes in a matter of weeks.

Type 2 diabetes can be reversed with severe calorie restriction—whether by surgery or starvation—but did you know it can also be reversed simply by eating healthier?

When type 2 diabetes is reversed after gastric bypass surgery, is it due to the actual operation or just the severely restrictive diet required for recovery?

Why do some drug-based strategies shorten the lives of diabetics and some diet-based strategies fail to decrease diabetes deaths?

When placed head-to-head against the American Diabetes Association diet, how do plant-based diets fare in terms of not only blood sugar, body weight, and cholesterol control, but also mood and quality of life?