How to Avoid Phosphate Additives
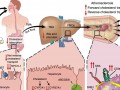
The vast majority of chicken and poultry products are injected with phosphorus preservatives, which are often not listed in the ingredients. Reducing one’s intake of meat, junk food, fast food, and processed cheese may help lower intake until labeling is mandated.