
Is It Safe to Eat Raw Mushrooms?
Microwaving is probably the most efficient way to reduce agaritine levels in fresh mushrooms.
Topic summary contributed by volunteer(s): Linda
A small number of food additives have been found to be harmless or even healthy. Those in the “harmless” category include MSG, citric acid, and stevia (in limited amounts). Of all added sweeteners, only date sugar and molasses are considered to be health-promoting. Black pepper and gum arabic appear to offer health benefits.
Many food additives may be harmful to human health such as nitrate, a carcinogenic substance found abundantly in hot dogs and cured meats. Another dangerous additive is phosphate, found mostly in chicken meat. Other harmful additives include the preservatives sodium benzoate, potassium sorbate, sulfites, sulfur dioxide, formaldehyde, arsenic compounds, and coumarin (which has been banned). Diacetyl, an artificial flavoring for popcorn, and most types of artificial coloring (found in farmed fish as well) have been linked to disease risk. Red dye number 3 has been associated with ADHD symptoms in children, cancer, and liver and thyroid diseases. Aluminum, found in many cheeses, the “fortifying” nutrient folic acid, and flavor additives salt, corn syrup, and NutraSweet also introduce health risks.
Some additives have themselves been found to be contaminated with mercury. The meat industry is currently considering additives to try to make meat safer.
For substantiation of any statements of fact from the peer-reviewed medical literature, please see the associated videos below.

Microwaving is probably the most efficient way to reduce agaritine levels in fresh mushrooms.

Emulsifiers are the most widely used food additive. What are they doing to our gut microbiome?

The industry’s response to the charge that breakfast cereals are too sugary.

The majority of dietary supplement facilities tested were found noncompliant with good manufacturing practices guidelines.
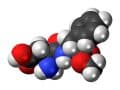
How should we parse the conflicting human data on intake of aspartame (Nutrasweet) and non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma, multiple myeloma, leukemia, and pancreatic cancer?

Anabolic growth-promoting drugs in meat production are by far the most potent hormones found in the food supply.

How many cola cancer cases are estimated to be caused by Coke and Pepsi in New York versus California, where a carcinogen labeling law (Prop 65) exists?

What effect do artificial sweeteners such as sucralose (Splenda), saccharin (Sweet & Low), aspartame (Nutrasweet), and acesulfame K (Sweet One) have on our gut bacteria?
Sulfur dioxide preservatives in dried fruit, sulfites in wine, and the putrefaction of undigested animal protein in the colon can release hydrogen sulfide, the rotten egg gas associated with inflammatory bowel disease.

The reason artificially sweetened beverages have been associated with depression may be because of psychological disturbances recently tied to aspartame (“Equal” or “NutraSweet”).
How can we protect our tooth enamel from the erosive natural acids found in sour foods and beverages?
Arsenic-containing drugs intentionally added to poultry feed to reduce the parasite burden and pinken the meat are apparently converted by cooking into carcinogenic inorganic arsenic compounds.

Unlike most other anticancer agents, the phytates naturally found in whole plant foods may trigger cancer cell differentiation, causing them to revert back to behaving more like normal cells.

The artificial food coloring Red No. 3 has yet to be banned—despite its purported role in causing thousands of cases of thyroid cancer.

Concern that one of the most commonly-consumed food colorings may cause cancer has led to changes in soft drink formulation in California.

The vast majority of chicken and poultry products are injected with phosphorus preservatives, which are often not listed in the ingredients. Reducing one’s intake of meat, junk food, fast food, and processed cheese may help lower intake until labeling is mandated.

The phosphorus preservatives injected into poultry may not just be an arterial toxin. They also appear to dramatically increase the growth of food poisoning Campylobacter bacteria.

The consumption of phosphorus preservatives in junk food, and injected into meat, may damage blood vessels, accelerate the aging process, and contribute to osteoporosis.

In response to definitive evidence showing artificial colors may increase inattentiveness, impulsivity, and hyperactivity among young children, a call has been made by consumer groups to ban food dyes.

The artificial butter flavoring diacetyl has been linked not only to deaths of workers handling the chemical, but also to serious lung disease in consumers of microwave popcorn.

Carrageenan is a food additive used as a thickener and fat substitute in a variety of dairy and nondairy products. Concerns about potential intestinal tract damage are placed in the context of dietary consequences.

People eating conventional diets may ingest a trillion microparticles of the food-whitening additive, titanium dioxide, every day. What implication might this have for inflammation in the gut?

Human beings lost the ability to detoxify uric acid millions of years ago. What implications does this have for our health today?

Case reports of fibromyalgia chronic pain sufferers cured, by removing the artificial sweetener aspartame (Nutrasweet®) from their diets.

Death in America is largely a foodborne illness. Focusing on studies published just over the last year in peer-reviewed scientific medical journals, Dr. Greger offers practical advice on how best to feed ourselves and our families to prevent, treat, and even reverse many of the top 15 killers in the United States.

Given their inherent resistance to food-poisoning bacteria, maggots can be used to create an antibacterial food additive to increase the safety of the meat supply.
Bacteria-eating viruses (bacteriophages) have been approved as meat additives to reduce the risk of Listeria and Campylobacter found in processed meat and poultry products, but there’s a concern they could spread toxin genes between bacteria.
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease is now the third leading cause of death. The good news is that. in addition to smoking cessation, there are dietary interventions that can help prevent COPD.

There are four common types of cinnamon: Vietnamese, Chinese (cassia), Indonesian, and Ceylon (true) cinnamon. Which is safest in terms of the level of coumarin, which may damage the liver at toxic doses?
How meat scientists justify their promotion of foods associated with cancer risk.

The addition of vitamin C to processed (cured) meats such as bacon may actually make them more carcinogenic.

The levels of nitrosamines—considered the most carcinogenic agents in cigarette smoke—were recently measured in an array of processed meats including chicken, turkey, and pork.

Phytonutrients, such as vitamin C, prevent the formation of nitrosamines from nitrites—which explains why adding nitrite preservatives to processed meat can be harmful, but adding more vegetables, with their nitrite-forming nitrates, to our diet can be helpful.

The nitrite preservatives in processed meats such as bologna, bacon, ham, and hot dogs form carcinogenic nitrosamines, but also reduce the growth of botulism bacteria—forcing regulators to strike a balance between consumers risking cancer, or a deadly form of food poisoning.

Nitrites in processed meat form nitrosamines, a class of potent carcinogens found in cigarette smoke, which may explain why hot dog consumption has been associated with the two leading pediatric cancers, brain tumors and childhood leukemia.
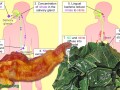
If the nitrates in vegetables such as greens are health-promoting because they can be turned into nitrites, and then nitric oxide, inside our bodies, what about the nitrites added to cured meats—such as bacon, ham, and hot dogs?