
Dietary Treatment of Glaucoma
Blueberries may help protect against age-related macular degeneration, and black currants may help halt the progression of glaucoma.

Blueberries may help protect against age-related macular degeneration, and black currants may help halt the progression of glaucoma.
Kale and collard greens contain vision-protecting plant nutrients, such as zeaxanthin, that may significantly lower the risk of glaucoma—a leading cause of blindness.

Blueberry consumption may double the population of our cancer-fighting immune cells, and the spices cardamom and black pepper may boost their activity.

To stay out of oxidative debt, we need to take in more antioxidants than we use up.
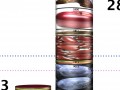
Even nine servings of fruits and vegetables a day may not reach the minimum recommended intake of antioxidants if one doesn’t make the right choices.
How many antioxidant-rich foods do we need to eat every day just to stay out of oxidative debt?

Coronary heart disease, our #1 cause of death, was found to be almost non-existent in a population eating a diet centered around whole plant foods.

Evidence from PET scans suggests brain activity changes from the overconsumption of sugar may parallel that of drug addiction. Diminished “pleasure center” dopamine pathway sensitivity in obese individuals may be analogous to that found in cocaine addicts and alcoholics.

Phytonutrients in certain plant foods may block the toxic effects of industrial pollutants, like dioxins, through the Ah receptor system.

Might the antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties of plant-based diets undermine some of the benefits of exercise?

The role white and pink (red) grapefruit may play in weight loss and cholesterol control, as well as the suppression of drug-clearance enzymes within the body.

Plant-based diets tend to be alkaline-forming. This may help protect muscle mass, and reduce the risk of gout and kidney stones. The pH of one’s urine can be estimated with natural pigments, using kitchen chemistry.
The decades-old dogma that the acid-forming quality of animal protein leads to bone loss has been called into question.

Simple changes in diet and lifestyle may quadruple a woman’s survival rate from breast cancer.

Reducing the ratio of animal to plant protein in men’s diets may slow the progression of prostate cancer.

Methionine restriction—best achieved through a plant-based diet—may prove to have a major impact on patients with cancer because, unlike normal tissues, many human tumors require the amino acid methionine to grow.

Public health campaigns can use vanity to improve fruit and vegetable consumption, since experiments show carotenoid phytonutrients improve the physical attractiveness of African, Asian, and Caucasian faces.

Tips like cutting vegetables into shapes, covertly puréeing greens into sauces, and modeling healthy behaviors can improve our children’s diets.

Interventions to improve child nutrition at school have included everything from reducing cookie size, adding fruit to classroom cupcake celebrations, and giving vegetables attractive names, to more comprehensive strategies such as “veggiecation” curricula, and transforming school cafeterias.

Since both coronary heart disease and impotence can be reversed with a healthy diet, sexual dysfunction can be used as a motivator to change poor lifestyle habits.

Nori seaweed snacks may favorably alter estrogen metabolism by modulating women’s gut flora, resulting in decreased breast cancer risk.
Anti-inflammatory phytonutrients in berries may explain why cherries can speed recovery after a marathon—by reducing muscle pain in long-distance runners.

Daily citrus fruit consumption during athletic training may reduce muscle fatigue, as evidenced by lower blood lactate concentrations.

Phytonutrients in citrus, such as hesperidin, may increase blood flow sufficient to warm the hands and feet of those with cold sensitivity.

The melatonin content in certain plant foods such as almonds, raspberries, and goji berries may explain the improvement in sleep quality associated with tart cherry consumption.

Two kiwi fruit an hour before bedtime may improve sleep quality and duration, without the side effects associated with sleeping pills.

Natural monoamine oxidase enzyme inhibitors in fruits and vegetables may help explain the improvement in mood associated with switching to a plant-based diet.

Dr. Greger has scoured the world’s scholarly literature on clinical nutrition, and developed this brand-new live presentation on the latest in cutting-edge research on how a healthy diet can affect some of our most common medical conditions.

Cancer cells are commonly present in the body, but cannot grow into tumors without hooking up a blood supply. Angiogenesis inhibitors in plant foods may help prevent this from happening.
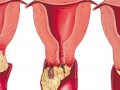
Most young women get infected with human papilloma virus, the cause of cervical cancer, but most are able to clear the infection before the virus causes cancer. What dietary changes can improve viral clearance?

Dioxins, endocrine disrupting pollutants, heavy metals, saturated fat, and steroids in the meat supply may be affecting sperm counts, semen quality, and the ability of men to conceive.

Based on studies of atomic bomb survivors, Chernobyl victims, and airline pilots exposed to more cosmic rays at high altitudes, it appears that fruits and vegetables may decrease radiation-induced chromosome damage.
Green tea consumption may help prevent cavities, but excessive consumption among young children may lead to dental fluorosis, due to the natural fluoride content of the plant.
Cranberries may reduce the recurrence of urinary tract infections, but their role in treating infections is limited.
A more plant-based diet may help prevent vaginal infections, one of the most common gynecological problems of young women.

Though prebiotics may be preferable, probiotics may reduce the risk of upper respiratory tract infections.

Modest lifestyle changes that include the avoidance of alcohol may cut the odds of breast cancer in half, but certain grapes appear to contain natural aromatase inhibitors that may undermine the ability of breast tumors to produce their own estrogen.

Black raspberries may cause complete clinical regression of precancerous oral lesions (oral intraepithelial neoplasia).
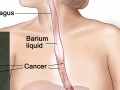
A randomized phase II clinical trial on the ability of strawberries to reverse the progression to esophageal cancer.

Drug companies and supplement manufacturers have yet to isolate the components of cranberries that suppress cancer cell growth.