
Getting Starch to Take the Path of Most Resistance
How might beans, berries, and intact (not just whole) grains reduce colon cancer risk?

How might beans, berries, and intact (not just whole) grains reduce colon cancer risk?
Fiber isn’t the only thing our good gut bacteria can eat. Starch can also act as a prebiotic.

What happens when Paleolithic-type diets are put to the test?

Why is the field of nutrition often more about marketing products than educating people about the fundamentals of healthy eating?

Despite less education on average, a higher poverty rate, and more limited access to health care, U.S. Hispanics tend to live the longest. Why?

How extreme was Dr. Kempner’s rice diet compared to traditional surgical approaches? Is there a safer alternative?

What happens when brown rice is put to the test in a randomized controlled crossover trial?
Avoid sugary and cholesterol-laden foods to reduce the risk of our most common cause of chronic liver disease.

Does vinegar work by slowing stomach emptying, acting as a starch blocker, or improving insulin sensitivity? What might be the downsides?

Before drugs came along, the consumption of vinegar with meals was used as a folk remedy for diabetes, but it wasn’t put to the test until recently.

White rice is missing more than fiber, vitamins, and minerals. Phytonutrients such as gamma oryzanol in brown rice may help explain the clinical benefits, and naturally pigmented rice varieties may be even healthier.
What happens when you take blood from people before and then again four hours after almond consumption, and drip that blood on bone cells?

If copper is associated with Alzheimer’s disease, what about healthy, whole plant food sources such as nuts, seeds, beans, and whole grains?

Even when study subjects were required to eat so much that they didn’t lose any weight, a plant-based diet could still reverse type 2 diabetes in a matter of weeks.

Type 2 diabetes can be reversed with severe calorie restriction—whether by surgery or starvation—but did you know it can also be reversed simply by eating healthier?

Energy density explains how a study can show participants lose an average of 17 pounds within 21 days while eating a greater quantity of food.

The extraordinarily low rates of chronic disease among plant-based populations have been attributed to fiber, but reductionist thinking may lead us astray.

A guideline is suggested for how to read food labels for grain products such as bread and breakfast cereals.
What happens to our gut flora microbiome when we’re on plant-based versus animal-based diets?
Diet and lifestyle improvements started even late in life can offer dramatic benefits.

When placed head-to-head against the American Diabetes Association diet, how do plant-based diets fare in terms of not only blood sugar, body weight, and cholesterol control, but also mood and quality of life?
If depression can be induced with pro-inflammatory drugs, might an anti-inflammatory diet be effective in preventing and treating mood disorders?

Why does the leading cancer and diet authority recommend we avoid bacon, ham, hot dogs, sausage, and all other processed meats—including chicken and turkey?

What happens inside the arteries going to the hearts and brains of those who add nuts or extra virgin olive oil to their diet?

While epidemics of chronic disease are currently by far our leading causes of death, global warming is considered a looming public health threat. How can we eat to combat dietary diseases and greenhouse gas emissions at the same time?

Eating intact grains, beans, and nuts (as opposed to bread, hummus, and nut butters) may have certain advantages for our gut flora and blood sugar control, raising questions about blending fruits and vegetables.

Causes of dry eye disease include LASIK laser eye surgery, but there are dietary approaches to prevention and treatment.

Does extra virgin olive oil have the same adverse effect on arterial function as refined oils and animal fats?

Big Candy boasts studies showing that those who eat chocolate weigh less than those who don’t, but what does the best science show?

Eating a diet low enough in sodium (salt) can prevent the rise in hypertension risk as we age.

Dr. Greger has scoured the world’s scholarly literature on clinical nutrition and developed this new presentation based on the latest in cutting edge research exploring the role diet may play in preventing, arresting, and even reversing some of our most feared causes of death and disability.

The lignans in rye could explain why rye intake is associated with lower breast and prostate cancer risk.
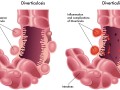
More than two-thirds of Americans over age 60 have diverticulosis, but it was nearly unknown a century ago, and remained extremely rare among populations eating whole food plant-based diets.
The reversal of blindness due to hypertension and diabetes with Dr. Kempner’s rice and fruit diet demonstrates the power of diet to exceed the benefits of the best modern medicine and surgery have to offer.

What happened when the World Health Organization had the gall to recommend a diet low in saturated fat, sugar, and salt and high in fruit and vegetables?

Decreasing animal protein and sodium intake appears more effective in treating calcium oxalate and uric acid kidney stones (nephrolithiasis) than restricting calcium or oxalates.

Heme iron, the type found predominantly in blood and muscle, is absorbed better than the non-heme iron that predominates in plants, but may increase the risk of cancer, stroke, heart disease, and metabolic syndrome.

Less than 3% of Americans meet the daily recommended fiber intake, despite research suggesting high-fiber foods such as whole grains can affect the progression of coronary heart disease.

What is the contemporary relevance of Dr. Kempner’s rice and fruit protocol for the reversal of chronic disease?

High blood pressure, the #1 killer risk factor in the world, may be eliminated with a healthy enough diet.