Survival of the Firmest: Erectile Dysfunction and Death
Because penile arteries are only about half the size of the coronary arteries in the heart, erectile dysfunction can be a powerful predictor of cardiac events—such as sudden death.

Because penile arteries are only about half the size of the coronary arteries in the heart, erectile dysfunction can be a powerful predictor of cardiac events—such as sudden death.

Those eating a more plant-based diet may naturally have an enhanced antioxidant defense system to counter the DNA damage caused by free radicals produced by high-intensity exercise.
Anti-inflammatory phytonutrients in berries may explain why cherries can speed recovery after a marathon—by reducing muscle pain in long-distance runners.

Carrageenan is a food additive used as a thickener and fat substitute in a variety of dairy and nondairy products. Concerns about potential intestinal tract damage are placed in the context of dietary consequences.
Women suffering with dysmenorrhea who switch to a plant-based diet experience significant relief in menstrual pain intensity and duration.

Chronic red pepper powder ingestion may be an effective treatment for IBS and chronic dyspepsia (indigestion), both of which can arise from food poisoning.

The melatonin content in certain plant foods such as almonds, raspberries, and goji berries may explain the improvement in sleep quality associated with tart cherry consumption.

Natural monoamine oxidase enzyme inhibitors in fruits and vegetables may help explain the improvement in mood associated with switching to a plant-based diet.

Cooked white mushroom consumption stimulates antibody production, while potentially still playing an anti-inflammatory role.
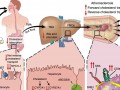
Expanding on the subject of my upcoming appearance on The Dr. Oz Show, a landmark new article in the New England Journal of Medicine shows that choline in eggs, poultry, dairy, and fish produces the same toxic TMAO as carnitine in red meat—which may help explain plant-based protection from heart disease and prostate cancer.

Instead of treating sensitive skin topically, with lotions and creams, why not treat it from the inside out—with diet?
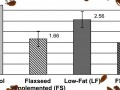
Researchers set out to find out what it was about a flax seed-supplemented, lower-fat diet that so effectively appeared to decrease prostate cancer growth.

A comparison of the cholesterol-lowering potential of four dried fruits—apples, dates, figs, and plums.

People eating conventional diets may ingest a trillion microparticles of the food-whitening additive, titanium dioxide, every day. What implication might this have for inflammation in the gut?

Plant-based diets may help protect against oral cancer and periodontal (gum) disease, a leading cause of tooth loss.

Plant-based diets may be effective for the treatment of fibromyalgia, a painful condition suffered by millions.
Plant-based diets appear to decrease inflammation via a variety of mechanisms—including boosting our adrenal gland function, due to the consumption of potassium rich foods.
The foreign meat molecule Neu5Gc builds up in human tumors and atherosclerotic plaques, and may play an inflammatory role in the progression of both diseases.
Cancer may use a molecule found in animal products to trick our immune system into feeding it with inflammation.
Plant-based diets may help rheumatoid arthritis by decreasing exposure to an inflammatory compound found in animal products.

Plant-based diets may be protective against multiple sclerosis because IGF-1 can prevent our immune system from eliminating autoimmune cells.
Because certain tumors such as breast cancers thrive in settings of low-grade inflammation, our immune response can sometimes facilitate tumor growth.

This week Consumer Reports released a study showing the majority of retail pork tested was contaminated with antibiotic-resistant strains of the foodborne bacteria Yersinia enterocolitica.

Some foods appear protective against the development of skin wrinkles—while others may make them worse.

Phytonutrients found in certain foods may protect against the toxic effects of industrial pollutants such as dioxin and DDT, suggesting a dual role for plant-based diets to reduce both exposure and subsequent damage.

Since chronic inflammation underlines many disease processes, and saturated fat appears to facilitate the endotoxic inflammatory reaction to animal products, researchers have looked to wild animals for less unhealthy meat options.

Within a matter of weeks, participants placed on the vegan diet outlined by the prophet Daniel experienced improvements in blood pressure, cholesterol and insulin levels, insulin resistance, and C-reactive protein levels, a marker of inflammation within the body.

Certain good bacteria in our gut can turn the fiber we eat into an anti-inflammatory, anti-cancer compound—called butyrate—that we absorb back into our system. We may be able to boost the number of butyrate-producing bacteria by eating a plant-based diet.

A dramatic difference exists between the anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects of black walnuts versus English walnuts.

Despite promising autopsy and population data suggesting that inadequate magnesium intake is a risk factor for sudden cardiac death, it wasn’t until recently that this was demonstrated in prospective studies.

Iron is a double-edged sword. If we don’t absorb enough, we risk anemia; but if absorb too much, we may increase our risk of cancer, heart disease, and a number of inflammatory conditions. Because the human body has no mechanism to rid itself of excess iron, one should choose plant-based (non-heme) sources, over which our body has some control.

Death in America is largely a foodborne illness. Focusing on studies published just over the last year in peer-reviewed scientific medical journals, Dr. Greger offers practical advice on how best to feed ourselves and our families to prevent, treat, and even reverse many of the top 15 killers in the United States.
The high bacteria load in raw or cooked animal foods and fermented foods may trigger an endotoxemic surge of inflammation, which may be exacerbated by the presence of saturated animal fat.

The endotoxemia (bacterial toxins in the bloodstream) that follows a meal of animal products and results in inflammation and stiffened arteries may come from the food itself, rather than from one’s own gut bacteria.
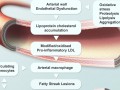
A single meal of meats, eggs, and dairy can cause a spike of inflammation within hours that can stiffen one’s arteries. Originally, this was thought to be the result of saturated animal fat causing our gut lining to leak bacterial toxins into our bloodstream, leading to endotoxemia.

Meat (including fish), cheese, and animal protein intake in general have been associated with an increased risk of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). In the meantime, plant-based diets may not only help prevent such conditions, but treat them as well, resulting in the longest recorded remission rates for Crohn’s disease.

The equivalent of eating a single walnut half per day appeared to cut the risk of dying from inflammatory disease about in half, whereas fish did not appear to play a protective role. That may be why those eating vegetarian foods have lower levels of inflammation and chronic disease risk.

Antioxidant, anti-inflammatory properties of white compared to yellow and purple potatoes. Purple potatoes may also help lower high blood pressure.

For the same reason aspirin should be avoided in pregnancy, chamomile has such powerful anti-inflammatory properties that regular consumption may result in a serious fetal heart problem—premature constriction of the fetal ductus arteriosus, which allows the fetus to “breathe” in the womb.

Mushrooms appear to have an anti-inflammatory effect on human arterial lining cells in vitro, which may help stop the inflammatory cascade, thought to be integral to the progression of atherosclerotic (artery-clogging) heart disease. The effects of shitake, crimini, oyster, maitake, and plain white button mushrooms are compared.