
The Best Source and Dose of Plant Sterols for Lowering Cholesterol
Lower LDL cholesterol with 2 to 3 grams a day of phytosterols taken with meals from healthy, fortified foods or safe supplements.
According to William C. Roberts, editor in chief of the American Journal of Cardiology, the only critical risk factor for atherosclerotic plaque buildup is cholesterol, specifically elevated LDL cholesterol in our blood. Indeed, LDL is called “bad” cholesterol because it’s the vehicle by which cholesterol is deposited into our arteries. Autopsies of thousands of young accident victims have shown that blood cholesterol levels were closely correlated with the amount of atherosclerosis in their arteries. To drastically reduce LDL cholesterol levels, we need to drastically reduce our intake of trans fat, which comes from processed foods and naturally from meat and dairy; saturated fat, found mainly in animal products and junk foods; and dietary cholesterol, found exclusively in animal-derived foods, especially eggs.
The optimal LDL cholesterol level is probably 50 or 70 mg/dL, and apparently, the lower, the better. That’s where we start out at birth, that’s the level seen in populations largely free of heart disease, and that’s the level at which the progression of atherosclerosis appears to stop in cholesterol-lowering trials. An LDL around 70 mg/dL corresponds to a total cholesterol reading of about 150, the level below which no deaths from coronary heart disease were reported in the famous Framingham Heart Study, a generations-long project to identify risk factors for heart disease. The population target should therefore be a total cholesterol level under 150 mg/dL.
To become virtually heart-attack proof, we need to get our LDL cholesterol at least under 70 mg/dL. Plant-based diets have been shown to lower cholesterol just as effectively as first-line statin drugs, but without the risks. In fact, the “side effects” of healthy eating tend to be good—less cancer and diabetes risk and protection of the liver and brain.
For substantiation of any statements of fact from the peer-reviewed medical literature, please see the associated videos below.

Lower LDL cholesterol with 2 to 3 grams a day of phytosterols taken with meals from healthy, fortified foods or safe supplements.

Safety concerns regarding phytosterolemia, red blood cell fragility, oxysterols, and the absorption of fat-soluble nutrients are addressed.

Even if we eat little or no cholesterol, phytosterols can block the reabsorption of the excess cholesterol our liver dumps into our intestines.

Can a plant-based Portfolio Diet lower LDL cholesterol as effectively as statin drugs?

Dozens of human trials reveal where turmeric delivers—and where it doesn’t.

Are there natural treatments for hypothyroidism?

If the only ultra-processed food that appears to be killing people is meat, then plant-based meats may be the solution to the ultra-processed foods problem.

Might asymptomatic food sensitivities to gluten, milk, peanuts, eggs, or shrimp increase the risk of premature death for those who eat these foods?

Weight loss isn’t necessarily required for type 2 diabetes remission, but what is?

Which is the safest and most effective statin?
Since there is benefit to getting our LDL cholesterol as low as possible, why aren’t statins prescribed for everyone even if we start out with optimal levels?

A meta-analysis of low-carb diets for diabetes remission found little to no effect at 12 months, clinically important harms to quality of life, and the deal-killer––an increase in LDL cholesterol.

How can we plan well-balanced plant-based diets for infants and kids?

What is the leading cause of heart disease, our leading cause of death?

Meta-analyses of studies involving more than ten million participants confirm that greater egg consumption confers a higher risk of premature death from all causes.

Is green rooibos (analogous to green tea) healthier than red rooibos, the commercially more common oxidized form that’s akin to black tea?
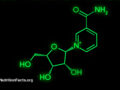
The suppression of NAD+ synthesis by NR in humans may explain the disparate rodent results.

The pros and cons of all the NAD+ supplements and what are the ways to boost NAD+ naturally with diet and lifestyle?

Resveratrol supplements may blunt some of the positive effects of exercise training.

APOE is the primary cholesterol carrier in the brain and plays a major role in packaging and transporting LDL cholesterol throughout the body.
How can we improve the capacity of our blood vessels to repair themselves?

Soy can be considered a first-line treatment for menopausal hot flash and night sweat symptoms.

The optimal intake of dietary cholesterol may be zero.

Why do the official federal Dietary Guidelines for Americans recommend limiting the intake of dietary cholesterol (found mostly in eggs) as much as possible?

What is a natural way to cut down on unhealthy food cravings?

I answer some common questions I’ve been asked about cholesterol and diabetes, such as “What is the ideal LDL?” “What’s going on when someone eats healthfully but their glucose is still out of control?”

Even nine out of ten studies funded by the egg industry show that eggs raise cholesterol.

Is the role of cholesterol in heart disease settled beyond a reasonable doubt?

Almonds are put to the test in a randomized controlled trial for facial wrinkles.

Do nut eaters live longer simply because they swap in protein from plants in place of animal protein?
What happens within hours of eating a high-fat meal?

Foods that reduce inflammation. What does an anti-inflammatory diet look like?

Weight loss, cholesterol, and PCOS treatment with diet. What can an eighth of a teaspoon a day of onion powder do for body fat, and what can raw red onion do for cholesterol?
Those with genetic mutations that leave them with an LDL cholesterol of 30 live exceptionally long lives. Can we duplicate that effect with drugs?
Why might healthy lifestyle choices wipe out 90 percent of our risk for having a heart attack, whereas drugs may only reduce risk by 20 to 30 percent?

How do barukas, also known as baru almonds, compare with other nuts?
Having a so-called normal cholesterol in a society where it’s normal to drop dead of a heart attack isn’t necessarily a good thing.

What are the pros and cons of relative risk versus absolute risk versus number-needed-to-treat versus average postponement of death taking cholesterol-lowering statin drugs?

A Mayo Clinic visualization tool can help you decide if cholesterol-lowering statin drugs are right for you.

What is the dirty little secret of drugs for lifestyle diseases? If patients knew the truth of how little these drugs actually worked, almost no one would agree to take them.