Biblical Daniel Fast Put to the Test
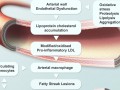
Within a matter of weeks, participants placed on the vegan diet outlined by the prophet Daniel experienced improvements in blood pressure, cholesterol and insulin levels, insulin resistance, and C-reactive protein levels, a marker of inflammation within the body.