
Probiotics
Probiotics are live bacteria and yeasts considered to have beneficial effects.
Prebiotics, Probiotics, and Postbiotics
The human colon may represent the most biodense ecosystem in the world. Though many may believe that our stool is primarily made up of undigested food, about 75 percent is pure bacteria—trillions and trillions, in fact, about half a trillion bacteria per teaspoon. As Neil deGrasse Tyson put it, “More bacteria live and work in one linear centimeter of your lower colon than all the humans who have ever lived.”
Do we get anything from these trillions of tenants taking up residence in our colon, or are they just squatting? They pay rent by boosting our immune system, making vitamins for us, improving our digestion, and balancing our hormones. We house and feed them, and they maintain and protect their house, our body. Prebiotics are what feed good bacteria. Probiotics are the good bacteria themselves, and common ones are Bifidobacteria and Lactobacillus. And postbiotics are what our bacteria make.
How Probiotics May Benefit Us
One month of probiotics has been found to significantly decrease symptoms of anxiety, depression, anger, and hostility, and a variety of mechanisms has been proposed for how our intestinal bacteria may be communicating with our brain. Taking probiotics may also result in us having significantly fewer colds, fewer sick days, and fewer symptoms.
Good Sources of Probiotics
Commercial yogurt of any kind—whether soy, rice, cow, or coconut—is an insufficient source of the level of probiotic bacteria found effective in treating diarrheal illnesses, inflammatory bowel disease, and irritable bowel syndrome. However, a plant-based diet appears to naturally modulate our gut flora.
When Should We Take Probiotics?
Does it matter if we take probiotics before, during, or after a meal? Though foods may be better carriers for probiotics than supplements, if one does choose to go with supplements, they are most effective taken within 30 minutes before, or simultaneously with a meal or beverage that contains some fat content.
Side Effects of Probiotic Supplements
Researchers gave half of their study participants, people with pancreatitis, probiotics and the other half got sugar pills. Within ten days, the mortality rates shot up in the probiotics group, compared to placebo. More than twice as many people died on the probiotics. So, taking probiotics for acute pancreatitis is probably not a good idea, but, further, taking probiotics in general can no longer be considered to be completely harmless.
Favor Eating Prebiotics Over Popping Probiotic Supplements
There are myriad concerns with probiotic supplements, and they may not even be alive by the time you buy them. They also have to survive the journey down to the large intestine. Altogether, these points suggest that the advantages of prebiotics—found in plant foods—outweigh those of probiotics.
Taking Probiotics with Antibiotics May Make Things Worse
The irony is that probiotics can actually interfere with microbiome recovery after antibiotics, rather than facilitate it. Probiotics are often intentionally selected to be antibiotic-resistant so they can be co-administered with antibiotics to reduce diarrhea rates, but they may transfer that resistance to pathogens in the gut. They can also have opposite the intended effect. Without probiotics, spontaneous post-antibiotic recovery back to baseline was found to occur within three weeks. In contrast, the microbiomes of those randomized to take probiotics remained off-kilter even six months later.
For substantiation of any statements of fact from the peer-reviewed medical literature, please see the associated videos below.
Image Credit: AnnaMariaThor / Thinkstock. This image has been modified.
Popular Videos for Probiotics


Culture Shock – Questioning the Efficacy and Safety of Probiotics
In certain medical conditions, probiotic supplements may actually make things worse.
Gut Feelings: Probiotics & Mental Health
We've known our mental state can affect our gut flora, but might our good bacteria...
Preventing & Treating Diarrhea with Probiotics
Probiotics may help prevent antibiotic-associated diarrhea, and appear to speed recovery from acute gastroenteritis.
Preventing the Common Cold with Probiotics?
Though prebiotics may be preferable, probiotics may reduce the risk of upper respiratory tract infections.
Should Probiotics Be Taken Before, During, or After Meals?
Proper timing of probiotic supplements may improve their survival.All Videos for Probiotics
-
Microbiome Manipulation with Oligomannate for Treating Dementia
A prebiotic derived from a type of brown seaweed is used for mild to moderate Alzheimer’s dementia in China. Does it work?
-

The Benefits and Side Effects of Probiotic Supplements
Probiotics can actually interfere with microbiome recovery after antibiotics, rather than facilitate it.
-
Effects of Tongue Scraping on Plaque, Gingivitis, and Cavities
Tongue scraping and tongue brushing have been practiced for centuries in many continents around the world, but do they do anything?
-

How to Keep Your Microbiome Healthy with Prebiotic Foods
We co-evolved a symbiosis with our good gut bacteria, but we are not holding up our end of the bargain.
-

Best Foods for Colon Cancer Prevention
A low-fiber diet is a key driver of microbiome depletion, the disappearance of diversity in our good gut flora.
-

Benefit of Dates for Colon Health
Seven dates a day for three weeks are put to the test in a randomized controlled trial.
-

The Role of the Gut Microbiome in Autism
What role do antibiotics play in the development and treatment of autism spectrum disorder?
-

Benefits of Blueberries for Artery Function
What is the optimum dose of wild blueberries to eat at a meal?
-

How to Convert Into an Equol Producer
Certain gut bacteria can supercharge the benefits of soy foods, resulting in even more bone protection, better control of menopausal symptoms, and lower prostate cancer risk, but how can we foster the growth of these good bacteria?
-

Culture Shock – Questioning the Efficacy and Safety of Probiotics
In certain medical conditions, probiotic supplements may actually make things worse.
-

How to Reduce Your TMAO Levels
Should we be concerned about high-choline plant foods, such as broccoli, producing the same toxic TMAO that results from eating high-choline animal foods, such as eggs?
-

How to Treat Heart Failure & Kidney Failure with Diet
One way a diet rich in animal-sourced foods like meat, eggs, and cheese may contribute to heart disease, stroke, kidney failure, and death is through the production of toxin called TMAO.
-

Treating Bacterial Vaginosis with Vaginal Vitamin C
Vitamin C is pitted head-to-head against antibiotics for bacterial vaginal infections.
-
How to Become a Fecal Transplant Super Donor
What’s more important: probiotics or prebiotics? And where can we best get them?
-

Garlic & Raisins to Prevent Premature Birth
Consumption of even small amounts of garlic or raisins are associated with significantly lower risk of pregnant women going into premature labor or having their water break too soon.
-

Gluten-Free Diets: Separating the Wheat from the Chat
How common is gluten sensitivity? Are there benefits of gluten? Why does the medical profession explicitly advise against people who suspect they might be gluten intolerant from just going on a gluten-free diet?
-

Preventing Asthma with Fruits and Vegetables
A study involving more than a million kids suggests the striking worldwide variation in childhood rates of allergies, asthma, and eczema is related to diet.
-

Gut Feelings: Probiotics & Mental Health
We’ve known our mental state can affect our gut flora, but might our good bacteria be affecting our mental state?
-
Should Probiotics Be Taken Before, During, or After Meals?
Proper timing of probiotic supplements may improve their survival.
-

Preventing the Common Cold with Probiotics?
Though prebiotics may be preferable, probiotics may reduce the risk of upper respiratory tract infections.
-
Preventing & Treating Diarrhea with Probiotics
Probiotics may help prevent antibiotic-associated diarrhea, and appear to speed recovery from acute gastroenteritis.
-
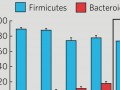
Tipping Firmicutes to Bacteroidetes
Certain phytonutrients may tip the balance of healthy gut bacteria in favor of flora associated with improved weight control.
-

Boosting Good Bacteria in the Colon Without Probiotics
Certain good bacteria in our gut can turn the fiber we eat into an anti-inflammatory, anti-cancer compound—called butyrate—that we absorb back into our system. We may be able to boost the number of butyrate-producing bacteria by eating a plant-based diet.
-

Uprooting the Leading Causes of Death
Death in America is largely a foodborne illness. Focusing on studies published just over the last year in peer-reviewed scientific medical journals, Dr. Greger offers practical advice on how best to feed ourselves and our families to prevent, treat, and even reverse many of the top 15 killers in the United States.
