Topic summary contributed by volunteer(s): Selena
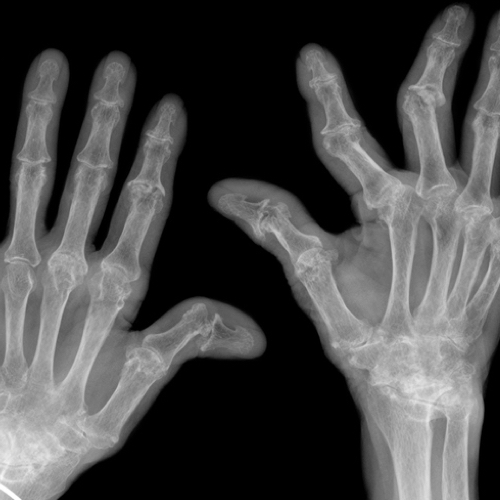
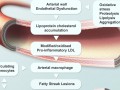
Rheumatoid arthritis appears to be more prevalent in populations with high meat consumption. This joint inflammation could be the result of an autoimmune attack response to foreign animal protein. Some researchers have proposed a “Leaky Gut Theory,” where the saturated fats in animal products contribute to the breakdown of the intestinal barrier, causing our own gut bacteria to leak into our bloodstream, thus triggering an inflammatory response. Newer research points to a state of endotoxemia caused by the bacterial toxins in animal products. The saturated fat in meat may instead facilitate the absorption of these toxins into the bloodstream.
Other components in meat also aggravate inflammation. Arachidonic acid is an inflammatory 6 fatty acid found in animal products. Neu5c, a non-human molecule which is found in human tumors most likely through meat consumption, may also cause the body to produce an inflammatory response. Plant-based diets in general are associated with a drastic reduction in symptoms.
Rosehips and potassium ease the arthritic pain caused by inflammation, while fruit and vegetables (particularly berries) help to inhibit platelet activity that is associated with inflammation. Curcumin, the yellow pigment in turmeric, worked better at easing pain than the leading pharmaceutical treatment for rheumatoid arthritis.
For substantiation of any statements of fact from the peer-reviewed medical literature, please see the associated videos below.
Image Credit: WILLSIE / Thinkstock. This image has been modified.