Turmeric
Many papers suggest turmeric can benefit a multitude of health conditions. Learn more in our easy-to-understand videos on the latest research.
In recent years, more than five thousand articles have been published in the medical literature about curcumin, the pigment in the Indian spice turmeric that gives curry powder its characteristic golden color. Curcumin was first isolated more than a century ago, yet out of the thousands of experiments, only a few in the twentieth century were clinical studies involving actual human participants. Since the turn of the century, however, more than 50 clinical trials have tested curcumin against a variety of diseases, and dozens more studies are on the way.
Since 1987, the National Cancer Institute has tested more than a thousand different compounds for chemopreventive, or cancer-preventing, activity. Only a few dozen have made it to clinical trials, and curcumin, turmeric’s bright-yellow pigment, is among the most promising. Chemopreventive agents can be classified into different subgroups based on which stage of cancer development they help to fight: Carcinogen blockers and antioxidants help prevent the initial triggering DNA mutation, and antiproliferatives work by keeping tumors from growing and spreading. Curcumin is special in that it appears to belong to all three groups, meaning it may potentially help prevent and/or arrest cancer cell growth.
The anticancer effects of curcumin extend beyond its ability to potentially prevent DNA mutations. It also appears to help regulate programmed cell death. Our cells are preprogrammed to die naturally to make way for fresh cells through a process known as apoptosis (from the Greek ptosis, falling, and apo, away from). In a sense, our body is rebuilding itself every few months with the building materials we provide it through our diet. Some cells, however, overstay their welcome—namely, cancer cells. By somehow disabling their own suicide mechanism, they don’t die when they’re supposed to. Because they continue to thrive and divide, cancer cells can eventually form tumors and potentially spread throughout the body.
So how does curcumin affect this process? It appears to have the ability to reprogram the self-destructing mechanism back into cancer cells. All cells contain so-called death receptors that trigger the self-destruction sequence, but cancer cells can disable their own death receptors. Curcumin, however, appears able to reactivate them. Curcumin can also kill cancer cells directly by activating “execution enzymes” called caspases inside cancer cells that destroy them from within by chopping up their proteins. Unlike most chemotherapy drugs, against which cancer cells can develop resistance over time, curcumin affects several mechanisms of cell death simultaneously, making it potentially harder for cancer cells to avoid destruction. For reasons not fully understood, curcumin seems to leave noncancerous cells alone.
Curcumin may play a role in preventing or treating lung disease, brain disease, and a variety of cancers, including multiple myeloma and cancers of the breast, brain, blood, colon, kidney, liver, pancreas, and skin, and may also help speed recovery after surgery and effectively treat rheumatoid arthritis better than the leading drug of choice. It also may be effective in treating osteoarthritis and other inflammatory conditions, such as lupus and inflammatory bowel disease. In a recent trial for ulcerative colitis, a multicenter, randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind study found that more than 50 percent of patients achieved remission within just one month on curcumin compared to none of the patients who received the placebo.
With few downsides at culinary doses and myriad potential health benefits, I’d suggest trying to find ways to incorporate turmeric into your daily diet.
For substantiation of any statements of fact from the peer-reviewed medical literature, please see the associated videos below.
Popular Videos for Turmeric

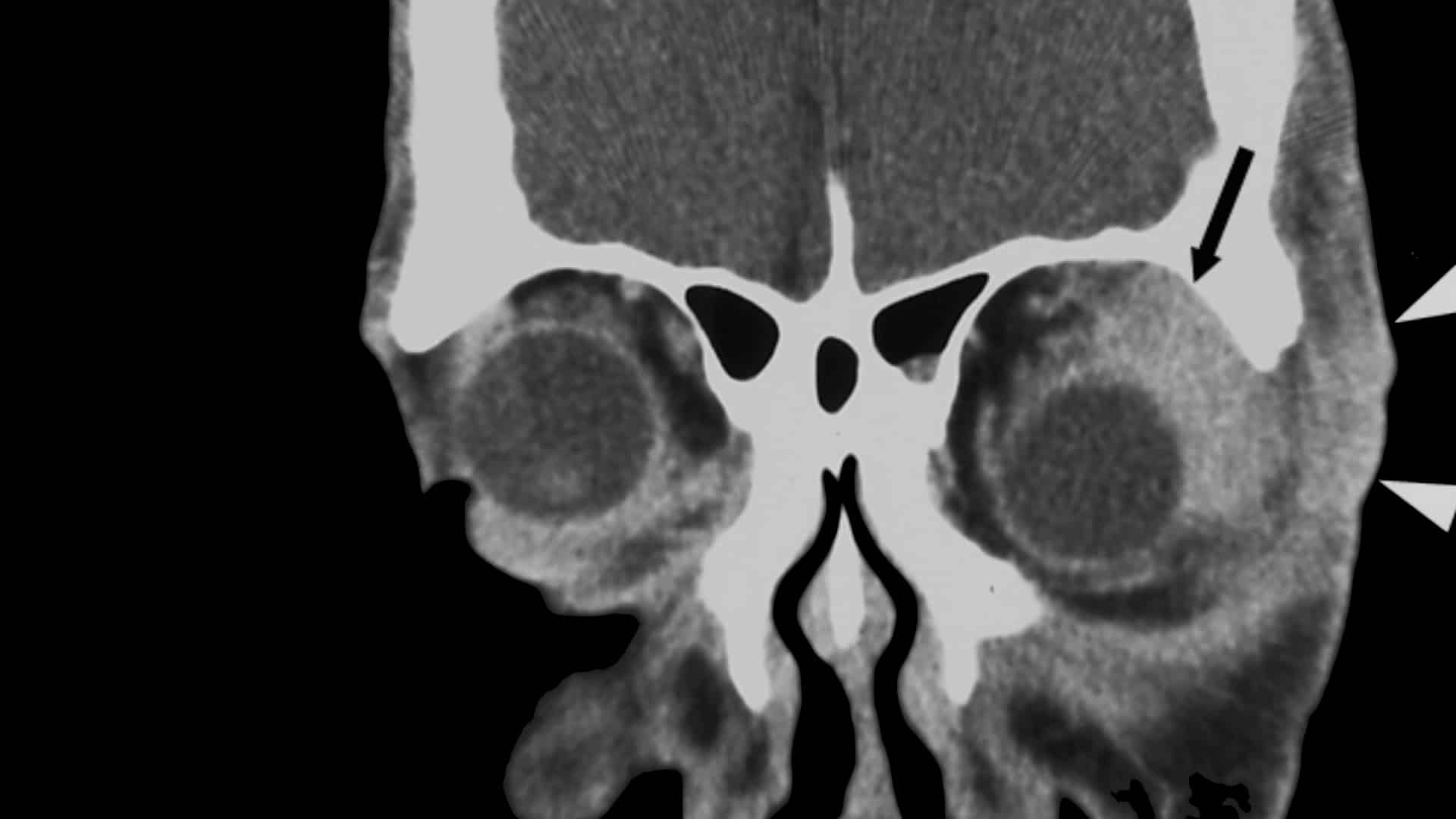
Benefits of Turmeric Curcumin for Inflammatory Orbital Pseudotumor
From conjunctivitis to uveitis to a low-grade form of non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma, there is something in...
Turmeric or Curcumin: Plants vs. Pills
Curcumin-free turmeric, from which the so-called active ingredient has been removed, may be as effective...
Which Spices Fight Inflammation?
An elegant experiment is described in which the blood of those eating different types of...
Turmeric Curcumin for Prediabetes
A randomized, double-blinded, placebo-controlled trial on the use of the turmeric pigment curcumin to prevent...
Speeding Recovery from Surgery with Turmeric
The anti-inflammatory effect of curcumin, the pigment in the spice turmeric, was put to the...
Heart of Gold: Turmeric vs. Exercise
Diet and exercise synergize to improve endothelial function, the ability of our arteries to relax...
Turmeric Curcumin & Pancreatic Cancer
Carcinogens in grilled and baked chicken may increase the risk of pancreatic cancer, while curcumin,...
Treating Alzheimer’s with Turmeric
What a teaspoon a day of the spice turmeric may be able to do for...
Back to Our Roots: Curry and Cancer
Dramatically lower cancer rates in India may in part be attributable to their more plant-based,...
Who Shouldn’t Consume Curcumin or Turmeric?
Just because something is natural and plant-based doesn’t mean it’s necessarily safe. Those who are...
Boosting the Bioavailability of Curcumin
Dietary strategies, including the use of black pepper (piperine), can boost blood levels of curcumin...
Turmeric Curcumin and Osteoarthritis
The yellow pigment curcumin in the spice turmeric may work as well as, or better...
Fighting Lupus with Turmeric: Good as Gold
A quarter teaspoon of the spice turmeric was put to the test for the treatment...
Striking with the Root: Turmeric Curcumin and Ulcerative Colitis
A double-blind, placebo-controlled trial found a dramatic effect of the anti-inflammatory spice pigment curcumin against...All Videos for Turmeric
-

Is Black Pepper Good for You?
Typical daily doses of black pepper can affect the metabolism of certain drugs, so make sure you tell your prescribing health professional about your black pepper consumption.
-

How to Get Enough Polyphenols for Life Extension
Is the link between flavonoid consumption and longevity cause-and-effect, and are all sources of flavonoids equally healthy?
-

Recipe: Lentil–Walnut Burgers with Cheesy Sauce
Our Lentil–Walnut Burgers with Cheesy Sauce are delicious, hearty, and easy to make.
-

The Benefits of Saffron for Treating Age-Related Macular Degeneration
Eight threads of saffron a day can improve visual acuity in older adults with mild or moderate age-related macular degeneration.
-

Natural Ozempic Alternatives: Boosting GLP-1 with Diet and Lifestyle
Certain spices and the quinine in tonic water can boost GLP-1, but at what cost?
-

Is Spicy Food Good for You?
Those who eat spicy foods regularly tend to live longer, but is it cause-and-effect?
-

Does Coffee Inhibit Iron Absorption? What Are the Effects of Having Too Much Iron?
Coffee and common herbal teas impair iron absorption, which may help explain some of their benefits.
-

The Best Diet for Fibromyalgia and Other Chronic Pain Relief
Anti-inflammatory diets can be effective in alleviating chronic pain syndromes.
-

Fenugreek Benefits for Sexual Function, Painful Periods, and Milk Production
The hormonal benefits of fenugreek extend beyond the muscle-bulking testosterone boost.
-

Blocking the Cancer Metastasis Enzyme MMP-9 with Beans and Chickpeas
Which legumes are best at inhibiting the matrix metalloproteinase enzymes that allow cancer to become invasive?
-

Which Foods Are Anti-Inflammatory?
Foods that reduce inflammation. What does an anti-inflammatory diet look like?
-

How to Heal a Leaky Gut with Diet
The recommended diet for leaky gut treatment. Which foods and food components can boost the integrity of our intestinal barrier?
-

The Benefits of Millet for Diabetes
What were the remarkable results of a crossover study randomizing hundreds of people with diabetes to one and a third cup of millet every day?
-

Recipe: Veggie Mac & Cheese
A cruciferous spin on macaroni and cheese, this recipe takes comfort food to a whole new level, and is a tasty way to check off a few servings on the Daily Dozen checklist. This recipe comes from Kristina, our Social Media Director.
-

Recipe: Easy Veggie Tacos
This recipe for Veggie Tacos comes from staff member Ángela.
-

Recipe: Garlic Caesar Salad Dressing
My go-to salad dressing, from the How Not to Die Cookbook.
-

Best Supplement for Canker Sores
Vitamin C, turmeric, beta-glucan fiber, and vitamin B12 are put to the test for recurring canker sores (aphthous ulcers).
-

How to Win the War on Cancer
How effective is chemotherapy for colon, lung, breast, and prostate cancers?
-

Shark Cartilage Supplements Put to the Test to Cure Cancer
Shark cartilage supplements carry risks, but so do many cancer treatments. The question is, do they work?
-

Dr. Greger’s Daily Dozen Checklist
In my book How Not to Die, I center my recommendations around a Daily Dozen checklist of everything I try to fit into my daily routine.
-

Dr. Greger in the Kitchen: My New Favorite Beverage
Dr. Greger blends up a vegetable smoothie inspired by a recipe in his How Not to Die Cookbook.
-

Tomato Sauce vs. Prostate Cancer
What happened when cancer patients were given three quarters of a cup of canned tomato sauce every day for three weeks?
-

Amla vs. Drugs for Cholesterol, Inflammation, and Blood-Thinning
Extracts of amla (Indian gooseberry) were pitted head-to-head against cholesterol-lowering statin drugs and the blood thinners aspirin and Plavix.
-

The Best Food for Fibroids
Women with uterine fibroids should consider adding green tea to their daily diet, as a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled interventional trial suggests it may help as well as surgery.
-

Benefits of Turmeric for Arsenic Exposure
What happened when turmeric curcumin was put to the test to see if it could reverse DNA damage caused by arsenic exposure?
-

Dr. Greger’s Daily Dozen Checklist
In my book How Not to Die, I center my recommendations around a Daily Dozen checklist of all the things I try to fit into my daily routine.
-

The Benefits of Açai vs. Blueberries for Artery Function
What are the effects of açai berries, cooked and raw blueberries, grapes, cocoa, green tea, and freshly squeezed orange juice on artery function?
-

Best Supplements for Prostate Cancer
What would happen if you secretly gave cancer patients four of the healthiest foods?
-
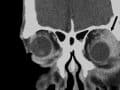
Benefits of Turmeric Curcumin for Inflammatory Orbital Pseudotumor
From conjunctivitis to uveitis to a low-grade form of non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma, there is something in the spice turmeric with dramatic anti-inflammatory effects.
-

Plants with Aspirin Aspirations
Should the active ingredient in aspirin be considered an essential vitamin?
-

Turmeric or Curcumin: Plants vs. Pills
Curcumin-free turmeric, from which the so-called active ingredient has been removed, may be as effective or even more potent.
-

Striking with the Root: Turmeric Curcumin and Ulcerative Colitis
A double-blind, placebo-controlled trial found a dramatic effect of the anti-inflammatory spice pigment curcumin against inflammatory bowel disease.
-
Fighting Lupus with Turmeric: Good as Gold
A quarter teaspoon of the spice turmeric was put to the test for the treatment of uncontrollable lupus (SLE) nephritis in a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial.
-

Turmeric Curcumin for Prediabetes
A randomized, double-blinded, placebo-controlled trial on the use of the turmeric pigment curcumin to prevent diabetes in prediabetics is published with extraordinary results.
-

Speeding Recovery from Surgery with Turmeric
The anti-inflammatory effect of curcumin, the pigment in the spice turmeric, was put to the test to see if it could reduce postoperative pain and fatigue after surgery.
-

Heart of Gold: Turmeric vs. Exercise
Diet and exercise synergize to improve endothelial function, the ability of our arteries to relax normally.
-

Turmeric Curcumin, MGUS, & Multiple Myeloma
Which plant and animal foods are associated with the development of multiple myeloma, and what effect might the spice turmeric have on the progression of monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance?
-

Preventing Alzheimer’s Disease with Plants
If foods like berries and dark green leafy vegetables have been found protective against cognitive decline, why aren’t they recognized as such in many guidelines?
-

Turmeric Curcumin vs. Exercise for Artery Function
Those who sit most of the day and are unable to use a standing or treadmill desk, or take frequent breaks from sitting, should consider the regular ingestion of the spice turmeric to protect endothelial function.
-

Turmeric Curcumin & Pancreatic Cancer
Carcinogens in grilled and baked chicken may increase the risk of pancreatic cancer, while curcumin, the yellow pigment in the spice turmeric, may sometimes help even in advanced stages of the disease.
