
Obesity: Is a GLP-1 Deficiency Its Cause, and How to Treat It Without Ozempic and Other Drugs
What is a safer and cheaper way to lose weight than GLP-1 drugs?
Topic summary contributed by volunteer(s): Daniel
While the progress of modern medicine has brought incredible advancements in surgery, lifestyle changes may be more preferable than surgery. Many surgeries still carry a great deal of risk, making diet and other healthy habits a safer alternative. Lifestyle medicine, including the adoption of a plant-based diet, may be able to reverse the progression of heart disease prevent the need for heart surgery.
For substantiation of any statements of fact from the peer-reviewed medical literature, please see the associated videos below.
Image Credit: Pixabay. This image has been modified.

What is a safer and cheaper way to lose weight than GLP-1 drugs?

Boost our natural satiety hormone GLP-1 through out diet.
Obesity can be so devastating to our health that the downsides of any effective drug would have to be significant to outweigh its weight-loss benefits.

How might we mitigate the gastrointestinal and muscle loss side effects of GLP-1 weight-loss drugs?

Why does weight loss plateau on GLP-1 drugs, and why do most stop using them within just three months even if they can afford them?

What is the hormone GLP-1, what separates GLP-1 mimics from previous weight-loss drugs, and how much weight may be lost before weight loss plateaus?

Given the clear harms and the small and uncertain benefits, most men would presumably decide to decline PSA testing if they knew all the facts, but that’s up to each man to decide.

A micromort as a unit of comparing and communicating risk to patients equivalent to a one in a million chance of dying.
Sham surgery trials have shown us that some of our most popular surgeries are themselves shams.

By losing 15 percent of their body weight, nearly 90 percent of those who’ve had type 2 diabetes for less than four years can achieve remission.

What happened when topical olive oil was pitted against an ibuprofen-type drug for osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis?

Weight regain after bariatric surgery can have devastating psychological effects.

Losing weight without rearranging your gastrointestinal anatomy carries advantages beyond just the lack of surgical risk.

The extent of risk from bariatric weight-loss surgery may depend on the skill of the surgeon.

Today, death rates after weight-loss surgery are considered to be “very low,” occurring in perhaps 1 in 300 to 1 in 500 patients on average.

Even though cannabis smoking may help with IBD symptoms in the short-term, it may make the long-term prognosis worse.
Palmitic acid, a saturated fat concentrated in meat and dairy, can boost the metastatic potential of cancer cells through the fat receptor CD36.

Cardiologists can criminally game the system by telling a patient they have a much more serious, unstable disease than they really have, fraud that results in unnecessary procedures, unnecessary cost, and unnecessary patient harm.

Over and over, studies have shown that doctors tend to make different clinical decisions for patients based on how much they will get paid personally.

Sham surgery trials prove that procedures like nonemergency stents offer no benefit for angina pain—only risk to millions of patients.

What do physicians and stent companies have to say for themselves, given that they are promoting expensive, risky procedures with no benefit?

Why are doctors killing or stroking out thousands of people a year for nothing? How do doctors even convince patients to sign up for procedures that are all risk without benefit?

Most heart attacks are caused by nonobstructive plaques that infiltrate the entire coronary artery tree. There is no such thing as “1-vessel disease,” “2-vessel disease,” or “left main disease.” Atherosclerotic plaque is continuous throughout the coronary arteries of heart attack victims.

There are demonstrably no benefits to the hundreds of thousands of angioplasty and stent procedures performed outside of an emergency setting. They don’t prevent heart attacks, enable you to live longer, or even help with symptoms any more than placebo (fake) surgery.

Rather than being some kind of disorder or failure of willpower, weight gain is largely a normal response, by normal people, to an abnormal situation.

How many fewer calories do you have to eat every day to lose one pound of body fat?

The clinical use of ketogenic diets for epilepsy and cancer: what does the science say?
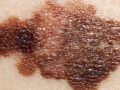
Is black salve, a paste made from bloodroot, safe and effective for the treatment of skin cancer?

We shouldn’t ever swallow aloe vera, but how does using it topically for a chronic inflammatory autoimmune disease compare to steroids?

What is the role of erectile dysfunction drugs like Cialis and Levitra in the promotion and progression of prostate cancer and melanoma?

When it comes to uterine fibroids, is soy harmful, harmless, or helpful?

I discuss the risks and benefits of aloe vera.

Fact boxes can quantify benefits and harms in a clear and accessible format.

If doctors don’t understand health statistics, how can they possibly properly counsel patients?
“Early” detection is actually really late. Without mammograms, breast cancer may not be caught for an average of 22.8 years. With mammograms, though, breast cancer may only grow and spread for…21.4 years.

After you watch this video, you’ll know more than an estimated 97 percent of doctors about a critical concept called lead-time bias.
What do nine in ten women say they were never told about mammograms, even though they thought they had the right to know?

Nine out of ten women don’t realize that some breast cancers would never have caused any problems or even become known in one’s lifetime. This is an issue ductal carcinoma in situ has brought to the forefront.

The mammogram paradox is that women who are harmed the most are the ones who claim the greatest benefit.
For every life saved by mammography, as many as two to ten women are overdiagnosed and unnecessarily turned into breast cancer patients—and let’s not overlook all of the attendant harms of chemo, radiation, or surgery without the benefits.