Almonds
Learn more about the latest evidence-based research on almonds in the videos below.
The Global Burden of Disease Study, the largest analysis of risk factors for death and disease in history, calculated that not eating enough nuts and seeds was the third-leading dietary risk factor for death and disability in the world, killing more people than processed meat consumption. Insufficient nut and seed intake is thought to lead to the deaths of millions of people every year, 15 times more than all those who die from overdoses of heroin, crack cocaine, and all other illicit drugs combined.
Major studies have shown that people who eat nuts, such as almonds, appear to suffer fewer deaths from cancer, heart disease, and respiratory disease, as well as may live longer. Indeed, our life span may be increased by an extra two years by eating nuts regularly—one handful (or about a quarter of a cup) five or more days a week.
PREDIMED, one of the largest interventional dietary trials ever performed, followed more than seven thousand men and women at high cardiovascular risk randomized into different diet groups. One group received a free half pound of nuts every week for four consecutive years. Compared with other groups, the added-nuts group appeared to cut their stroke risk in half. If this works as well in the general population, eighty-nine thousand strokes a year would be prevented in the United States alone. That would be like ten strokes an hour, around the clock, prevented simply by adding about four walnuts, almonds, and hazelnuts to the nation’s daily diet.
Regardless of which group participants were assigned to, those eating more nuts each day had a significantly lower risk of dying prematurely overall. In my Daily Dozen, I recommend a daily serving of either ¼ cup nuts or seeds, or 2 tablespoons of nut or seed butter.
For substantiation of any statements of fact from the peer-reviewed medical literature, please see the associated videos below.
Image Credit: Pixabay. This image has been modified.
Popular Videos for Almonds


Which Nut Fights Cancer Better?
Within hours the blood of those fed walnuts is able to suppress the growth of...
Nuts May Help Prevent Death
Just a few small servings of nuts a week may increase our lifespan and lower...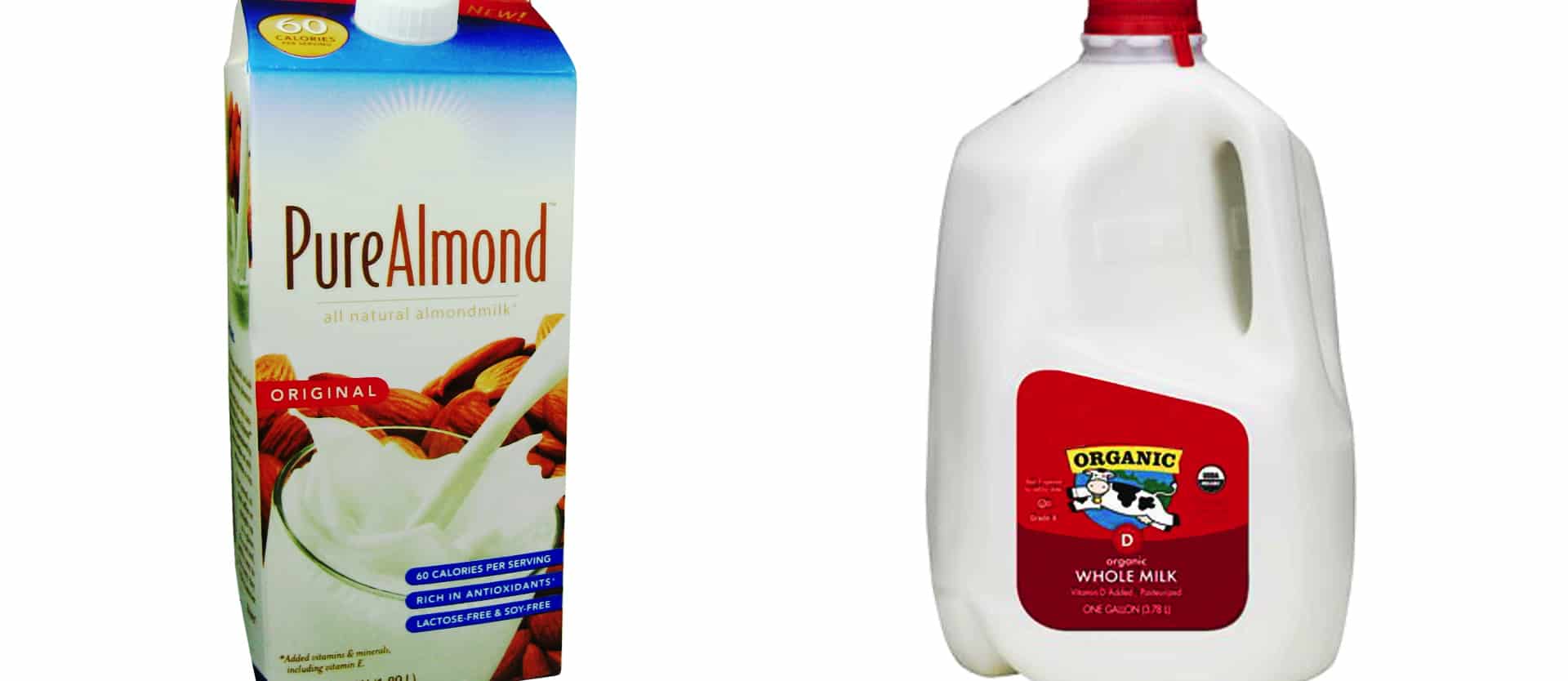
Prostate Cancer and Organic Milk vs. Almond Milk
Does the hormonal stimulation of human prostate cancer cells by cow milk in a petri...
Are Baruka Nuts the Healthiest Nut?
How do barukas, also known as baru almonds, compare with other nuts?All Videos for Almonds
-

The Highest Antioxidant: Apple, Bean, Berry, Lentil, or Nut?
The best apple, bean, berry, lentil, and nut are the ones you’ll eat the most of; but if you don’t have a strong preference, which has the highest antioxidant power?
-

3 Healthy, Easy Recipes: Appetizer, Pasta, and Dessert
Celebrate the season with recipes from my cookbooks.
-
How to Prevent Wrinkles with Diet
The evidence supports the recommendation to follow a whole food, plant-based diet for healthier looking skin.
-
Do Vegans Have Lower Bone Density and More Fractures?
What are the bone fracture rates of omnivores vs. vegetarians vs. vegans?
-

How to Naturally Reduce Wrinkles with Food
Almonds are put to the test in a randomized controlled trial for facial wrinkles.
-

Dietary Approach to Naturally Treating Menopause Symptoms
Specific foods have been shown in randomized controlled trials to improve symptoms like hot flashes.
-

Foods to Help Protect Your Arteries from Saturated Fat
If you’re going to have something unhealthy, is there anything you can eat with it to help mediate the damage it may cause?
-

Mixed Nuts Put to the Test for Erectile Dysfunction
Walnuts, almonds, and hazelnuts are put to the test for erectile and sexual function, sperm count, and semen quality.
-

Are Baruka Nuts the Healthiest Nut?
How do barukas, also known as baru almonds, compare with other nuts?
-

Should We Be Concerned About Aflatoxin?
Is “toxic mold syndrome” a real thing? And, what do we do about toxic mold contamination of food?
-

How to Lower Lp(a) with Diet
What to eat and what to avoid to lower the cardiovascular disease risk factor lipoprotein(a).
-

Kidney Stones and Spinach, Chard, and Beet Greens: Don’t Eat Too Much
Given their oxalate content, how much is too much spinach, chard, beet greens, chaga mushroom powder, almonds, cashews, star fruit, and instant tea?
-

Do Sunflower Seeds Cause Acne?
Should we be concerned about the pimples, cadmium, and “colonic crunch” associated with consumption of sunflower seeds?
-

Are Avocados Good for Your Cholesterol?
Can guacamole lower your cholesterol as well as other whole-food fat sources like nuts, or is that just spin by the avocado industry?
-

Arsenic in Rice Milk, Rice Krispies, & Brown Rice Syrup
I recommend people switch away from using rice milk.
-

How to Prevent Blood Sugar & Triglyceride Spikes After Meals
Within hours of eating an unhealthy meal, we can get a spike in inflammation, crippling our artery function, thickening our blood, and causing a fight-or-flight nerve response. Thankfully, there are foods we can eat at every meal to counter this reaction.
-
Prunes for Osteoporosis
Vegetables and fruit, such as dried plums, may help build stronger bones.
-
Almonds for Osteoporosis
What happens when you take blood from people before and then again four hours after almond consumption, and drip that blood on bone cells?
-

Liquid Calories: Do Smoothies Lead to Weight Gain?
If our body doesn’t register liquid calories as well, why are blended soups more satiating than the same ingredients eaten in solid form?
-

Which Parts of the Mediterranean Diet Extended Life?
Of all the components of a healthy Mediterranean diet, which are associated with a longer lifespan?
-

Which Nut Fights Cancer Better?
Within hours the blood of those fed walnuts is able to suppress the growth of breast cancer cells in a petri dish. Which nut might work best, though—almonds, Brazil nuts, cashews, hazelnuts, macadamias, peanuts, pecans, pine nuts, pistachios, or walnuts?
-

Nuts May Help Prevent Death
Just a few small servings of nuts a week may increase our lifespan and lower cancer risk.
-

Tart Cherries for Insomnia
The melatonin content in certain plant foods such as almonds, raspberries, and goji berries may explain the improvement in sleep quality associated with tart cherry consumption.
-

Tree Nuts or Peanuts for Breast Cancer Prevention?
Eating fiber-containing foods—especially nuts—during adolescence may significantly lower the risk of developing potentially precancerous fibrocystic breast disease (fibroadenomas).
-
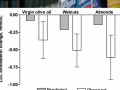
Extra Virgin Olive Oil vs. Nuts
The short-term effect of replacing refined olive oil with extra virgin olive oil, walnuts, or almonds on cardiovascular risk factors.
-

Fat Burning Via Arginine
The arginine content of nuts may explain their metabolism-boosting effects—though, in a list of the top food sources of arginine, nuts don’t even make the top ten.
-

Solving the Mystery of the Missing Calories
A few theories have been proposed as to why nuts don’t appear to contribute to weight gain, including the “pistachio principle” and the fecal excretion theory.
-
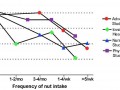
Nuts and Bolts of Cholesterol Lowering
A pooled analysis of studies on nut consumption, cholesterol levels, and risk of death from heart disease show extraordinary benefits, suggesting we should eat nuts every day.
-

Fighting Inflammation in a Nut Shell
The equivalent of eating a single walnut half per day appeared to cut the risk of dying from inflammatory disease about in half, whereas fish did not appear to play a protective role. That may be why those eating vegetarian foods have lower levels of inflammation and chronic disease risk.
-

The Best Nut
Which type of nut has the highest antioxidant content?
