Antioxidants
You can tell whether a food is rich in antioxidants by slicing it open, exposing it to air (oxygen), and then seeing what happens. If it turns brown, it’s oxidizing. Two of our most popular fruits, apples and bananas, for example, turn brown quickly, which means there aren’t a lot of antioxidants inside them. (Most of the antioxidants in apples are in the peels.) Cut open a mango and what happens? Nothing, because it’s rich with antioxidants. How do you keep fruit salad from turning brown? Add lemon juice, which contains the antioxidant vitamin C. Antioxidants can keep your food from oxidizing, and they may do the same inside your body.
In scientific circles, the phenomenon by which oxygen molecules grab stray electrons and go crazy is called oxidant (or oxidative) stress, and the resulting cellular damage may contribute to the aging process. Aging and disease have been thought of as the oxidation of the body. Those brown age spots on the back of your hands? They’re just oxidized fat under the skin. Oxidant stress is thought to be why we all get wrinkles, why we lose some of our memory, and why our organ systems break down as we get older. Eating foods containing lots of antioxidants may slow down this oxidant process.
One of the diseases antioxidant-rich foods may help prevent is stroke. Swedish researchers followed more than 30,000 older women over a period of a dozen years and found that those who ate the most antioxidant-rich foods had the lowest stroke risk. Similar findings were reported in a younger cohort of men and women in Italy.
What are the most antioxidant-rich foods? Researchers spanning the globe published a database of the antioxidant power of more than 3,000 foods, beverages, herbs, spices, and supplements. On average, plant foods contain 64 times more antioxidants than animal foods. As the researchers put it, “[A]ntioxidant rich foods originate from the plant kingdom while meat, fish and other foods from the animal kingdom are low in antioxidants….”
Antioxidant-rich diets appear to protect against stroke and may also help decrease artery stiffness, prevent blood clots from forming, and lower blood pressure and inflammation. High-antioxidant fruits and vegetables, such as berries and greens, have been found to douse systemic inflammation significantly better than the same number of servings of more common low-antioxidant fruits and veggies, such as bananas and lettuce.
For substantiation of any statements of fact from the peer-reviewed medical literature, please see the associated videos below.
Popular Videos for Antioxidants

Antioxidants and Depression
Neither antioxidant or folic acid supplements seem to help with mood, but the consumption of...
Treating Asthma with Fruits and Vegetables
Increasing fruit and vegetable consumption to seven servings a day appears to cut asthma exacerbation...
Food Antioxidants and Cancer
Antioxidant intake from foods (not supplements) is associated with lower cancer risk.
Antioxidant-Rich Foods with Every Meal
To stay out of oxidative debt, we need to take in more antioxidants than we...
Minimum “Recommended Daily Allowance” of Antioxidants
How many antioxidant-rich foods do we need to eat every day just to stay out...
Preventing Exercise-Induced Oxidative Stress with Watercress
Those eating a more plant-based diet may naturally have an enhanced antioxidant defense system to...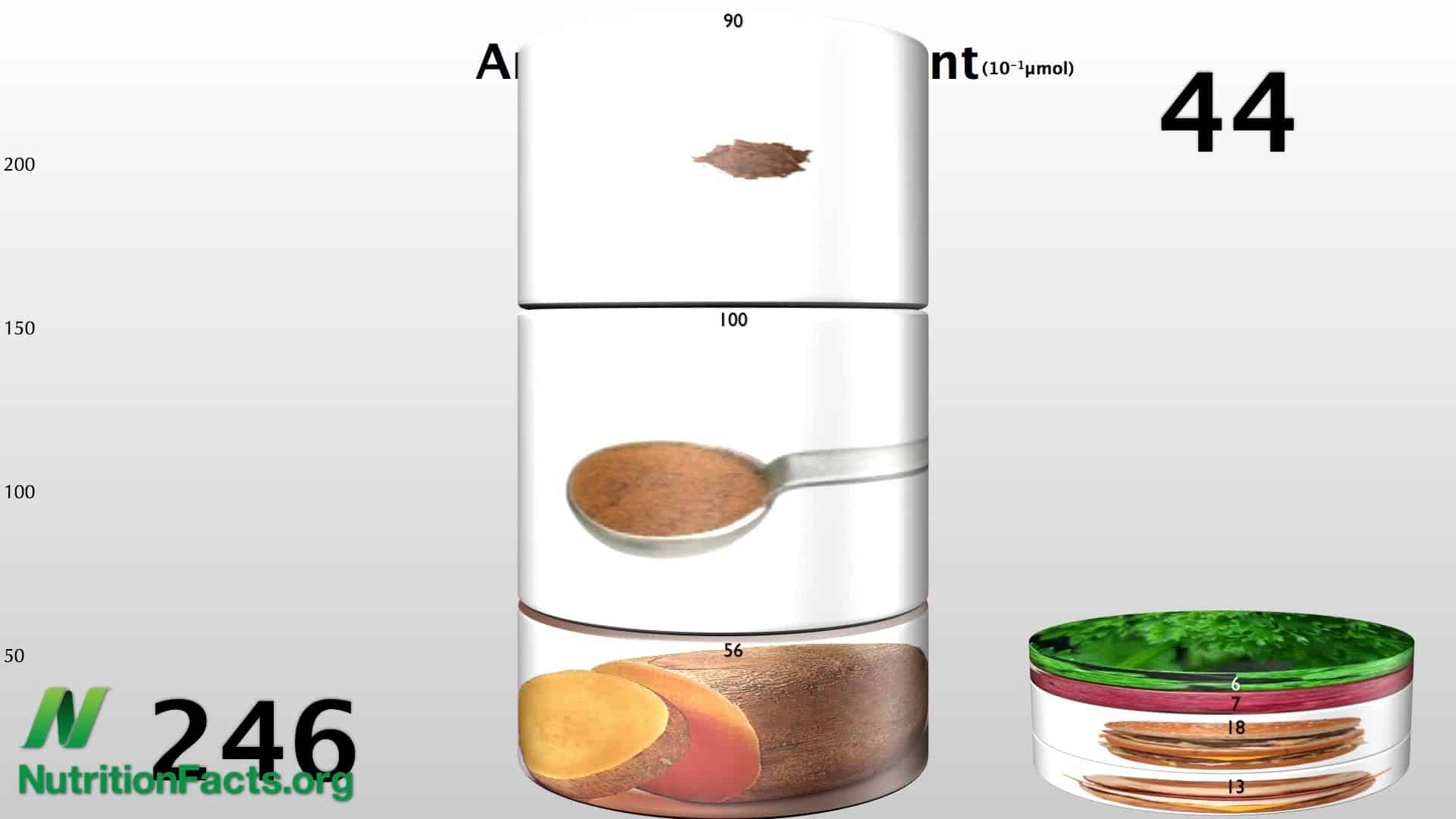
Antioxidants in a Pinch
Some herbs and spices—including cinnamon, cloves, lemon balm, marjoram, oregano, and peppermint—are so rich in...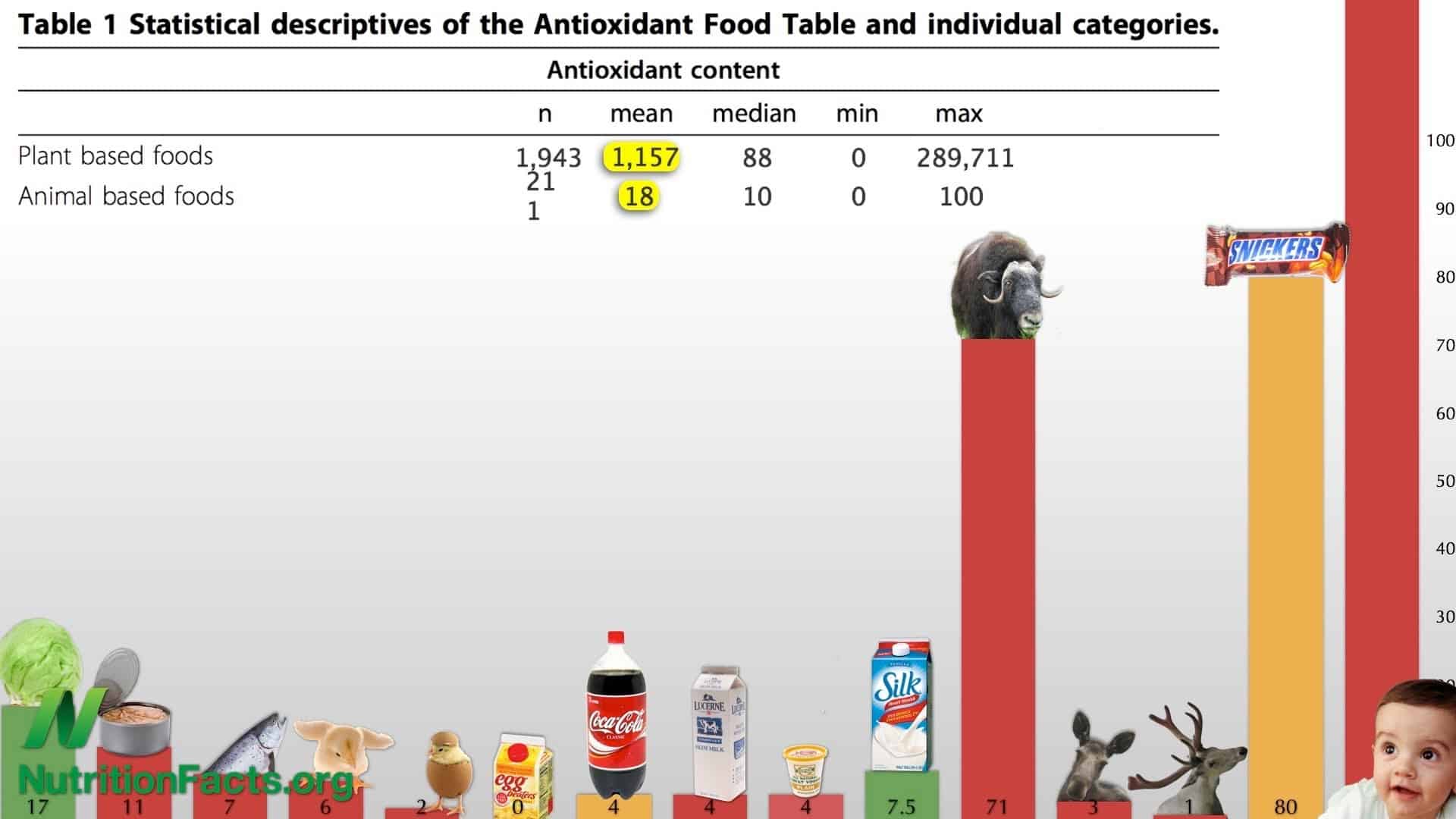
Antioxidant Power of Plant Foods vs. Animal Foods
On average, plant foods have 64 times more antioxidant power than red meat, poultry, fish,...All Videos for Antioxidants
-

Caveats and Side Effects of Taurine Supplements
What are the downsides of taurine supplementation?
-

Randomized Controlled Trials of Taurine Supplementation in Humans
Cautionary tales from carnitine and arginine complicate the taurine supplementation question.
-

Taurine Supplementation Increases Lifespan and Healthspan in Animals
The level of taurine in our bodies declines with age, dropping by nearly 80 percent. Would consuming extra improve lifespan or healthspan?
-

What Is Taurine in Energy Drinks? Does It Benefit Cognitive or Athletic Performance?
We have at least five pathways to make taurine in our body from scratch, but does taking more offer a benefit?
-

Yerba Mate and Cancer: Do Its Benefits Outweigh Its Risks?
Carcinogens like benzopyrene in cigarette smoke, grilled chicken, and yerba mate tea may explain higher rates of certain cancers in consumers.
-

The Best Way to Cook Vegetables
Which method of cooking vegetables preserves the most antioxidants?
-

How to Prevent and Treat Age-Related Hearing Loss
The diet and supplements that have been put to the test to prevent and even reverse hearing loss.
-

Preventing and Treating Sarcoidosis
The cause of sarcoidosis is unknown, but new research indicates that mycobacteria, like MAP bacteria found in dairy and meat products, are likely involved in some sarcoidosis cases.
-

Is Soil Degradation Reducing the Nutrition of Fruits and Vegetables?
Is the purported decline of nutrients in our crops due to soil degradation, or is that just supplement industry propaganda?
-

The Highest Antioxidant: Apple, Bean, Berry, Lentil, or Nut?
The best apple, bean, berry, lentil, and nut are the ones you’ll eat the most of; but if you don’t have a strong preference, which has the highest antioxidant power?
-

The Benefits and Side Effects of Red and Green Rooibos Teas
Is green rooibos (analogous to green tea) healthier than red rooibos, the commercially more common oxidized form that’s akin to black tea?
-

The Best Foods for Your Skin
Greens, apples, tomato paste, and grapes are put to the test as edible skin care candidates.
-

Does Lion’s Mane Mushroom Powder Have Benefits for Dementia?
Regular mushroom consumption is associated with a lower risk of cognitive decline and dementia, but data from interventional trials are mixed.
-

Reversible Causes of Prematurely Graying Hair
Vitamin B12 deficiency is one of the rare, reversible causes of hair graying through some unknown mechanism.
-

Why Does Hair Turn Gray?
As with vitiligo in the skin, buildup of hydrogen peroxide kills the pigment cells in hair follicles.
-
How to Prevent Wrinkles with Diet
The evidence supports the recommendation to follow a whole food, plant-based diet for healthier looking skin.
-

Centrum Multivitamin, Vitamin C, Beta Carotene, Souvenaid, Zinc, or Calcium Supplements for Preventing Alzheimer’s?
Which might actually make cognition worse: Centrum multivitamin, vitamin C, beta carotene, Souvenaid, zinc, or calcium supplements?
-

Can Vitamin E or Selenium Supplements Prevent or Treat Alzheimer’s?
The Prevention of Alzheimer’s Disease by Vitamin E and Selenium trial randomized more than 7,500 older men to take vitamin E, selenium, both, or neither (just placebos) for five years.
-

Green Tea as a Mouthwash for Halitosis (Bad Breath)
Green tea can help reduce plaque as much as the gold-standard chemical mouthwash without its side effects, but what about other aspects of oral health, such as bad breath?
-

Does Resveratrol Benefit Our Metabolic Health?
Which conditions have resveratrol supplements been shown to help?
-

Three Reasons Fruits and Vegetables May Reduce Osteoporosis Risk
Even just a single extra serving of fruits and vegetables per day is associated with lower bone fracture risk.
-

The Benefits of Topical Vitamin C for Reversing Skin Aging
What are the pros and cons of alpha hydroxy acid lotions and chemical peels, as well as the roles of topical antioxidants vitamin E and C, in reversing the signs of aging?
-

How Not To Age – Live Presentation
In this live lecture, Dr. Greger offers a sneak peek into his latest book, How Not to Age, a New York Times Best Seller.
-

The Supplement Shown to Slow Age-Related Hearing Loss
Some studies found that higher levels of folate in the blood seem to correlate with better hearing, so researchers decided to put it to the test.
-

Greens, Green Tea, and Nuts Put to the Test for Telomeres
Not all plant foods are linked to less cellular aging based on telomere attrition, and not all animal foods are linked to more.
-

What to Eat to Prevent Telomere Shortening
The anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties of plant-based diets may explain why they can effectively reverse cellular aging by elongating telomeres.
-
Fecal Transplants for Ulcerative Colitis, MS, Depression, Bipolar, and Alcoholism
I go over randomized, controlled trials and case reports of stool transplants for various clinical conditions.
-

A Case of Stage 3 Cancer Reversal with Fasting
I go over a case report of water-only fasting, followed by a whole food, plant-based diet for follicular lymphoma.
-

Update on Erythritol Sweetener Safety: Are There Side Effects?
Why are erythritol levels in the blood associated with higher levels of chronic disease?
-

How Much Erythritol Sweetener Is Too Much?
What are the maximum acute and daily doses for adults and children to avoid gastrointestinal effects?
-

The Harms Associated with Eating More Southern-Style Food
Diet appears to mediate the majority of the racial health gap.
-

Why All Athletes Should Eat Plant-Based Diets
Enhance athletic performance with diet.
-

How to Naturally Reduce Wrinkles with Food
Almonds are put to the test in a randomized controlled trial for facial wrinkles.
-

Dietary Approach to Naturally Treating Menopause Symptoms
Specific foods have been shown in randomized controlled trials to improve symptoms like hot flashes.
-
The Best Diet for Treating Atrial Fibrillation
What foods should we eat and avoid to reduce our risk of Afib?
-

The Role of Kimchi and H. Pylori in Stomach Cancer
What explains the Achilles’ heel in certain Asian diets?
-

Coffee Put to the Test for Treating Parkinson’s Disease
Coffee can improve Parkinson’s symptoms within three weeks compared to placebo, but do the benefits last?
-

Do Vitamin C Supplements Help with Anxiety?
What are the risks and benefits of using vitamin C for depression and anxiety?
-

The Healthiest Type of Potato
Are yellow-fleshed potatoes healthier than white? And, what about the glycoalkaloid toxins?
-

Which Foods Are Anti-Inflammatory?
Foods that reduce inflammation. What does an anti-inflammatory diet look like?
