Fish Oil
Thanks in part to the American Heart Association’s recommendation that individuals at high risk for heart disease should ask their physicians about omega-3 fish oil supplementation, fish oil pills have grown into a multibillion-dollar industry.
But what does the science say? Are the purported benefits of fish oil supplementation for the prevention and treatment of heart disease just a fish tale?
A systematic review and meta-analysis published in the Journal of the American Medical Association looked at all the best, randomized clinical trials evaluating the effects of omega-3 fats on life span, cardiac death, sudden death, heart attack, and stroke. These included studies not only on fish oil supplements but also studies on the effects of advising people to eat more oily fish. What did they find? Overall, the researchers reportedly found no protective benefit for overall mortality, heart disease mortality, sudden cardiac death, heart attack, or stroke. And for someone who has already had a heart attack and is trying to prevent another? Still no benefit seemed to be found.
Where did we even get this idea that the omega-3 fats in fish and fish oil supplements are good for you? There was a notion that Eskimos were protected from heart disease, but that appears to be a myth. Some early studies, however, looked promising. For example, the DART trial from the 1980s involving 2,000 men found that those advised to eat fatty fish had an impressive 29 percent reduction in mortality. However, the sequel, the DART-2 trial, found the exact opposite. Run by the same group of researchers, the DART-2 trial was an even bigger study with 3,000 men, but this time, participants advised to eat oily fish and particularly those who were supplied with fish oil capsules had a higher risk of cardiac death.
After putting all the studies together, researchers concluded there was no longer justification for the use of omega-3s in everyday clinical practice. What should doctors do when their patients follow the American Heart Association’s advice and inquire about fish oil supplements? As the director of Lipids and Metabolism at Mount Sinai’s cardiovascular institute put it: “Given this and other negative meta-analyses, our job [as doctors] should be to stop highly marketed fish oil supplementation to all our patients…”
For substantiation of any statements of fact from the peer-reviewed medical literature, please see the associated videos below.
Image Credit: Jo Christian Oterhals / Flickr. This image has been modified.
Popular Videos for Fish Oil


Is Fish Oil Just Snake Oil?
Advice to eat oily fish, or take fish oil, to lower risk of heart disease,...
Red Fish, White Fish; Dark Fish, Atrial Fibrillation
The consumption of dark fish (such as salmon, swordfish, bluefish, mackerel, and sardines) may increase...
Should Pregnant and Breastfeeding Women Take DHA?
Does maternal supplementation with the long-chain omega-3 fatty acid DHA improve psychomotor, mental, visual, or...
Should We Take EPA and DHA Omega-3 for Our Heart?
What’s the best way to fulfill the omega-3 essential fat requirements?
Omega 3s and the Eskimo Fish Tale
The concept that heart disease was rare among the Eskimos appears to be a myth.
Omega 3s, Prostate Cancer, and Atrial Fibrillation
Fish and fish oil consumption do not appear to protect against heart disease, arrhythmias, or...
PCBs in Children’s Fish Oil Supplements
A study of 13 over-the-counter children’s fish oil supplements found that all were contaminated with...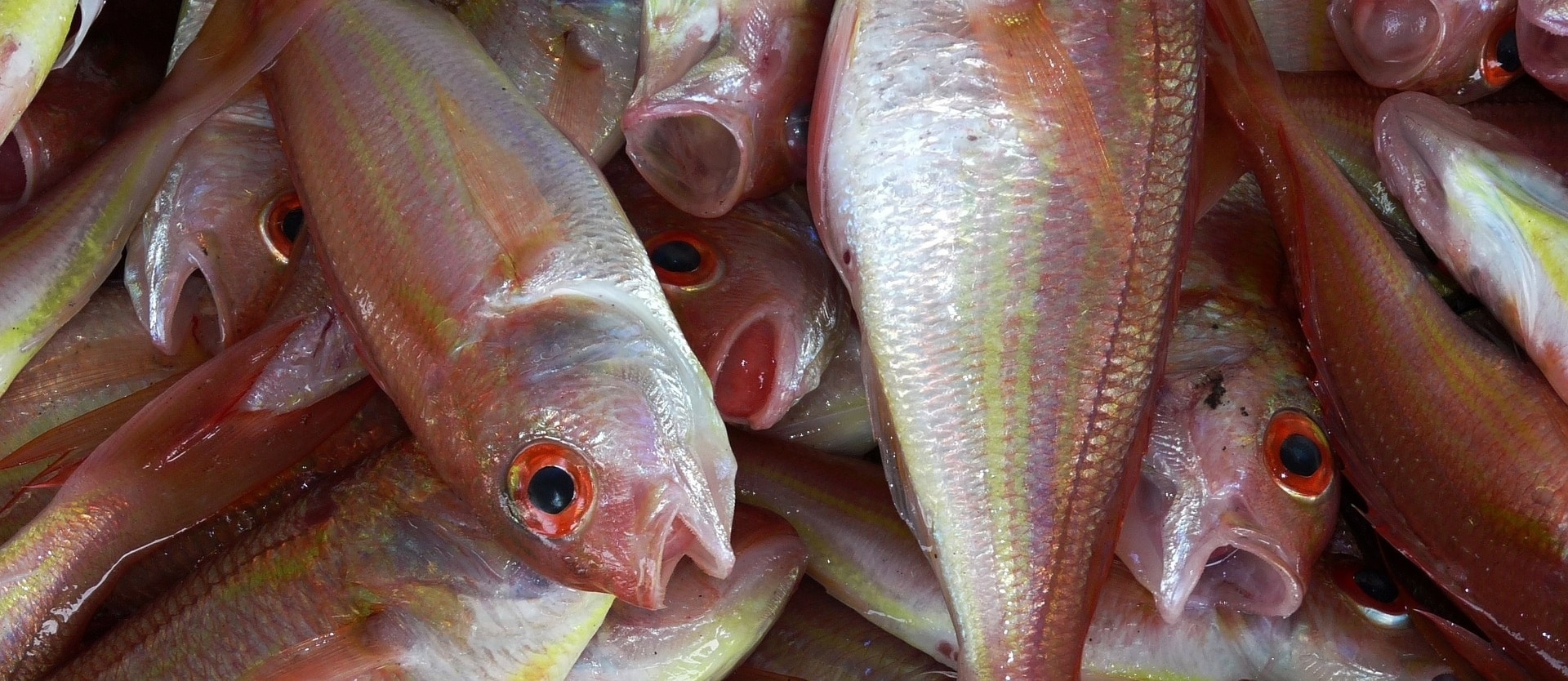
Fish and Diabetes
The relationship between fish consumption and diabetes risk may be due to toxic pollutants that...All Videos for Fish Oil
-

Supplements for Sarcopenia (Age-Related Muscle Loss)
HMB, magnesium, omega 3s, and vitamin D are put to the test for muscle strength and function.
-

Natural Ozempic Alternatives: Boosting GLP-1 with Diet and Lifestyle
Certain spices and the quinine in tonic water can boost GLP-1, but at what cost?
-

Are Fish or Fish Oil Supplements Good for the Heart?
Five massive new trials have been published recently, randomizing tens of thousands to various formulations of fish oil versus placebo.
-

The Best Dietary Detox
By eating at a lower rung on the food chain, those choosing plant-based diets suffer less exposure to the industrial pollutants that bioaccumulate up the ladder.
-

Vegetarians and Stroke Risk Factors—Omega 3s?
Does eating fish or taking fish oil supplements reduce stroke risk?
-

Benefits of Quinoa for Lowering Triglycerides
How do the nutrition and health effects of quinoa compare to whole grains?
-

Dietary Supplements for Autism
Vitamin C, vitamin D, and omega-3 fish oil supplements put to the test to improve the core symptoms of autism spectrum disorder.
-

The Best Source of Resveratrol
Is there any benefit to resveratrol? If so, should we get it from wine, grapes, peanuts, or supplements?
-

Eczema Treatment with Coconut Oil, Mineral Oil vs. Vaseline
Natural topical remedies for eczema, including licorice root gel, St. John’s Wort cream, and emollients such as coconut oil, mineral oil, and petroleum jelly, are put to the test.
-

Eczema Treatment with Evening Primrose Oil, Borage Oil vs. Hempseed Oil
Are there dietary supplements that can help with atopic dermatitis?
-

Coconut Oil and the Boost in HDL “Good” Cholesterol
The effects of coconut oil are compared to butter and tallow. Even if virgin coconut oil and other saturated fats raise LDL “bad” cholesterol, isn’t that countered by the increase in HDL “good” cholesterol?
-

Food Synergy
Combining certain foods together may be more beneficial than eating them separately.
-

How Much Vitamin D Should You Take?
The safe dose of vitamin D supplementation to get most of the population to the optimal level is 2,000 IU a day, but the elderly and overweight may need more.
-

Should Pregnant and Breastfeeding Women Take DHA?
Does maternal supplementation with the long-chain omega-3 fatty acid DHA improve psychomotor, mental, visual, or physical development of infants?
-

Should We Take EPA and DHA Omega-3 for Our Heart?
What’s the best way to fulfill the omega-3 essential fat requirements?
-

Omega 3s and the Eskimo Fish Tale
The concept that heart disease was rare among the Eskimos appears to be a myth.
-

Omega 3s, Prostate Cancer, and Atrial Fibrillation
Fish and fish oil consumption do not appear to protect against heart disease, arrhythmias, or sudden death, but why would they increase cancer risk?
-

PCBs in Children’s Fish Oil Supplements
A study of 13 over-the-counter children’s fish oil supplements found that all were contaminated with PCB pollutants.
-

Fish and Diabetes
The relationship between fish consumption and diabetes risk may be due to toxic pollutants that build up in the aquatic food chain.
-

Dietary Sources of Alkylphenol Endocrine Disruptors
Foods of animal origin (especially fish) appear to be the most important source of human exposure to industrial pollutants such as alkylphenol xenoestrogens.
-

Is Fish Oil Just Snake Oil?
Advice to eat oily fish, or take fish oil, to lower risk of heart disease, stroke, or mortality is no longer supported by the balance of available evidence.
-

Red Fish, White Fish; Dark Fish, Atrial Fibrillation
The consumption of dark fish (such as salmon, swordfish, bluefish, mackerel, and sardines) may increase our risk of atrial fibrillation—an irregular heartbeat rhythm associated with stroke, dementia, heart failure, and a shortened lifespan.
-

Fish Oil in Troubled Waters
Major fish oil manufacturers and drug stores are being sued for failing to disclose the PCB pollutants in fish oil supplements.
-

Food Sources of PCB Chemical Pollutants
The top three sources of industrial toxins in the diet are fish oil, fish, and eggs.
-
Mercury in Vaccinations vs. Tuna
Balancing the risks and benefits of fish consumption.
