
Medicine’s Response to the Changing Science on Fluoride Safety
How did the medical and dental community react to U.S. regulators’ total 180 over water fluoridation, going from presumptively safe to presumptively dangerous?
Topic summary contributed by volunteer(s): Lily
Neurotoxins are substances that deleterious to nerve tissue. Neurotoxins in meat and fish may be contributing to brain damage (including memory loss and dementia) as well as muscle tremors, and the effects of consuming contaminated fish may last for decades. Neurotoxins found in chicken may be linked to hand tremors, the most common movement disorder. The neurotoxin, BMAA, found in seafood may be linked to ALS (Lou Gehrig’s disease).
Who’s at risk? Fetuses, infants, and children (see also here) are particularly at risk, but adults should also try to avoid foods containing mercury (see also here) present in fish, other animal products, and products containing high fructose corn syrup (see comparisons to amalgam fillings and vaccines). Other potential neurotoxins include copper found in meats, arsenic found in chicken, and acrylamide found in certain fried foods such as french fries. Neurotoxins have been found in the Ayurvedic supplements, spirulina, blue-green algae (but not chlorella), fish, and fish oil, and even cheese, which may explain the connection between dairy consumption and Parkinson’s disease. Flame-retardant chemicals are also found in retail U.S meat supply. Tofu preserved with formaldehyde may also be toxic. At the same time, ginger and apple juice may be protective against Alzheimer’s disease.
For substantiation of any statements of fact from the peer-reviewed medical literature, please see the associated videos below.

How did the medical and dental community react to U.S. regulators’ total 180 over water fluoridation, going from presumptively safe to presumptively dangerous?

Based on new research, the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services’ National Toxicology Program reached a draft conclusion that fluoride should be “presumed to be a cognitive neurodevelopmental hazard to humans.”

There have been more than 50 studies showing an association between higher fluoride exposure and lower IQ, but is it cause-and-effect?

Did traffic fatalities go up or down after cannabis legalization?

Star fruit contains a neurotoxin known as caramboxin that can cause irreversible brain damage at high enough doses.
Nearly one quarter of Americans have already been infected with the brain parasite toxoplasma.

What role do antibiotics play in the development and treatment of autism spectrum disorder?

Why are millions of dollars spent on shark cartilage supplements?
If you start smoking marijuana as an adult, how much cannabis is too much?

Is the American Academy of Pediatrics’ opposition to cannabis legalization just reefer madness revisited?

Is there any benefit to resveratrol? If so, should we get it from wine, grapes, peanuts, or supplements?

Are the health benefits associated with apple consumption simply due to other healthy behaviors among apple-eaters?

Let’s review lead from occupational exposures, shooting ranges, eggs, and bone broth.

The link between Parkinson’s and dairy may not be explained just by the pesticides and lactose.

Berries counteract the neurotoxic effects of pesticides in vitro, potentially explaining why berry consumption is associated with lower risk of developing Parkinson’s disease.

Dr. Greger has scoured the world’s scholarly literature on clinical nutrition and developed this new presentation based on the latest in cutting edge research exploring the role diet may play in preventing, arresting, and even reversing some of our most feared causes of death and disability.

PBDE fire-retardant chemicals in the food supply may contribute to attention and cognitive deficits in children.

A neurotoxin called BMAA that concentrates in seafood may help explain clusters of Lou Gehrig’s disease.

The neurotoxin BMAA is found in seafood and the brains of Alzheimer’s and ALS victims. Might dietary changes help prevent amyotrophic lateral sclerosis?

The effects of the neurotoxins that can contaminate fish like red snapper and grouper can last for decades.

Neurotoxins in chicken, such as the beta-carboline alkaloid harman, may explain the link between meat consumption and hand tremor, the most common movement disorder.
Low levels of neurotoxic chemicals in cheese may explain the connection between dairy product consumption and Parkinson’s disease.

Death in America is largely a foodborne illness. Focusing on studies published just over the last year in peer-reviewed scientific medical journals, Dr. Greger offers practical advice on how best to feed ourselves and our families to prevent, treat, and even reverse many of the top 15 killers in the United States.

There’s a rare toxin, called domoic acid, that can turn up in tuna and other seafood and cause anterograde amnesia, the loss of short-term memory popularized in the movie Memento.
Ginger and apple juice appear to protect human nerve cells from the neurotoxic Alzheimer’s plaque protein amyloid beta in a petri dish.

The mercury contamination in tuna and other fish may adversely impact future earnings by impairing brain function, and leading to a loss of intelligence (IQ).

The U.S. Inspector General cites the USDA for failing to safeguard the meat supply from drug residues.

Potential neurotoxicity is another concern regarding spirulina supplements.
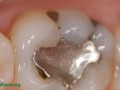
Eating a can of tuna once a week is equivalent to living with how many mercury-containing amalgam tooth fillings?
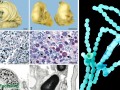
Chlorella does not have the toxins that may be present in blue-green algae supplements and spirulina.

Fifty different brands of high-fructose corn syrup-containing foods were tested for mercury.
Balancing the risks and benefits of fish consumption.

The risks associated with these supplements may outweigh the benefits.